
Rank the following alkenes in order of decreasing heats of hydrogenation: (largest first)
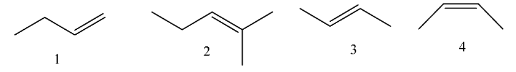
(A) 2 > 3 > 4 > 1
(B) 2 > 4 > 3 > 1
(C) 1 > 3 > 4 > 2
(D) 1 > 4 > 3 > 2
Answer
232.5k+ views
Hint:Heat of hydrogenation of an alkene is the standard enthalpy of catalytic hydrogenation of an alkene. Catalytic hydrogenation of an alkene is always exothermic. Therefore, the heat of hydrogenation of alkenes is always negative
Complete step by step solution:
We know that Heat of hydrogenation is related to stability of the alkenes.
If an alkene is very stable its heat of hydrogenation is very less.
If an alkene is less stable its heat of hydrogenation is more.
Stability of alkene means alkene won’t convert into alkane easily.
The stability of alkenes can be calculated using hyper conjugation.
Hyper conjugation is directly proportional to the number of alpha hydrogens.
The carbon which is adjacent to the double bond is called alpha carbons, and the hydrogens which are attached to alpha carbon are called alpha hydrogens.
As the number of alpha hydrogens are increasing the stability of the alkene increases that much, meaning less heat of hydrogenation.
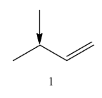
Coming to given options, molecule-1, the molecule has two alpha hydrogens.
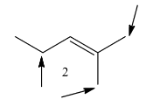
Coming to molecule-2, the molecule has eight alpha hydrogens.
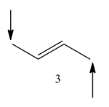
Coming to molecule-3, the molecule has six alpha hydrogens, sterically stable.
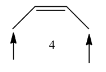
Coming to molecule-4, the molecule has six alpha hydrogens, sterically less stable.
Stability of the given molecules is as follows.
2 > 3 > 4 >1
But according to the heat of hydrogenation the order is as follows.
1 > 4 > 3 > 2
So, the correct option is D.
Note: Stability of the molecule is going to depend on the number of alpha hydrogens and steric hindrance of the molecule. If steric hindrance is high, the molecule is less stable.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that Heat of hydrogenation is related to stability of the alkenes.
If an alkene is very stable its heat of hydrogenation is very less.
If an alkene is less stable its heat of hydrogenation is more.
Stability of alkene means alkene won’t convert into alkane easily.
The stability of alkenes can be calculated using hyper conjugation.
Hyper conjugation is directly proportional to the number of alpha hydrogens.
The carbon which is adjacent to the double bond is called alpha carbons, and the hydrogens which are attached to alpha carbon are called alpha hydrogens.
As the number of alpha hydrogens are increasing the stability of the alkene increases that much, meaning less heat of hydrogenation.
Coming to given options, molecule-1, the molecule has two alpha hydrogens.

Coming to molecule-2, the molecule has eight alpha hydrogens.

Coming to molecule-3, the molecule has six alpha hydrogens, sterically stable.

Coming to molecule-4, the molecule has six alpha hydrogens, sterically less stable.

Stability of the given molecules is as follows.
2 > 3 > 4 >1
But according to the heat of hydrogenation the order is as follows.
1 > 4 > 3 > 2
So, the correct option is D.
Note: Stability of the molecule is going to depend on the number of alpha hydrogens and steric hindrance of the molecule. If steric hindrance is high, the molecule is less stable.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




