
On the velocity in a reversible reaction, the correct explanation of the effect of the catalyst is-
A. It provides a new reaction path of low activation energy
B. It increases the kinetic energy of reacting molecules
C. It displaces the equilibrium state on the right side
D. It decreases the velocity of the backward reaction
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In a chemical reaction when reactants react to form the products at a certain concentration of the products, the products start to convert into the reactant simultaneously. Both reactions proceed simultaneously. Such types of reactions are called reversible reactions. A catalyst is used to change the rate of reaction.
Complete answer:A catalyst is a substance, compound, or element which is used in a reaction to change its rate of reaction or to form any specific product in the reaction. Catalyst themselves does not react in the reaction they only provide an alternative way to the reaction. The amount of catalyst used in the reaction remains constant. Catalysts are used to increase or decrease the rate of reaction, generally, it is used to increase the rate of reaction. A small amount of catalyst is required for increasing the rate of reaction for a large amount of reactants. When the reaction takes a longer duration to complete a reaction it shows that the reactant is having higher energy of activation to lower that energy of activation catalyst is used. The catalyst provides another pathway with a lower energy of activation of the reactant to the reaction.
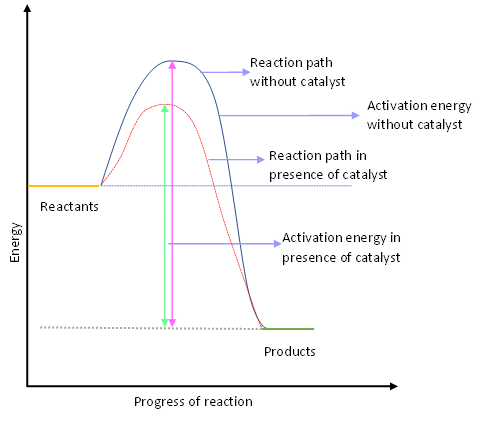
The above graph describes the activity of the catalyst in the reaction.
Thus, Option (A) is correct
Note: Not all reaction gets effect by the catalyst. Some reactions do not change their rate of reaction in presence of a catalyst. One catalyst cannot act as a catalyst in all reactions. Reactions have their suitable and specific catalysts.
Complete answer:A catalyst is a substance, compound, or element which is used in a reaction to change its rate of reaction or to form any specific product in the reaction. Catalyst themselves does not react in the reaction they only provide an alternative way to the reaction. The amount of catalyst used in the reaction remains constant. Catalysts are used to increase or decrease the rate of reaction, generally, it is used to increase the rate of reaction. A small amount of catalyst is required for increasing the rate of reaction for a large amount of reactants. When the reaction takes a longer duration to complete a reaction it shows that the reactant is having higher energy of activation to lower that energy of activation catalyst is used. The catalyst provides another pathway with a lower energy of activation of the reactant to the reaction.

The above graph describes the activity of the catalyst in the reaction.
Thus, Option (A) is correct
Note: Not all reaction gets effect by the catalyst. Some reactions do not change their rate of reaction in presence of a catalyst. One catalyst cannot act as a catalyst in all reactions. Reactions have their suitable and specific catalysts.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




