
Number of shared electrons in between carbon-carbon atoms in ethylene molecule is
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 3
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The ionic compound is formed by the complete transfer of one or more than one electron from a more electropositive atom to an electronegative atom as a result of the formation of positive-negative ion pair formed. But in contrast, most chemical compounds are formed by the covalent bonds i.e., by sharing their valence electrons between the atoms having the same electronegativity.
Complete step by step solution:Ethylene is the common name for ethene.
Ethene is an organic compound that is represented by \[C{H_2} = C{H_2}\]molecular formula.
Ethylene belongs to the category of unsaturated hydrocarbons.
The unsaturated hydrocarbons represent those hydrocarbons that possess double and triple bonds between carbon atoms.
Ethylene is also known as the simplest alkene because it has a minimum of two carbon atoms which has a carbon-carbon double bond.
The carbon atom can form a variety of covalent compounds. And the covalent compounds of carbon may contain sigma (single bond or single) and pi-bond (double and triple bond).
By the presence of single, double, and triple carbon-carbon bonds we can determine the structure of hydrocarbons. When hydrocarbons possess a single bond, then the structure will be tetrahedral. Whereas, when carbon possesses carbon-carbon double and triple bond then the structure will be planar and linear respectively.
In hydrocarbons, each carbon atom has four valence electrons.
In the structure of the ethylene molecule, the carbon-carbon double bond has four shared pairs of electrons, and the rest two electrons \[C - C\]bond with hydrogen atoms.
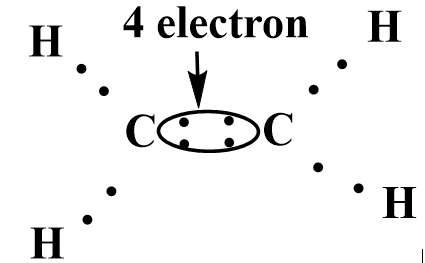
Image: Structure of ethylene.
Therefore from the above explanation we can say option (b) will be the correct option:
Note: Ethylene is used as plant growth and regulator hormone.
Ethylene is also useful for the synthesis of various types of plastics.
Ethylene gas is lighter than air.
Complete step by step solution:Ethylene is the common name for ethene.
Ethene is an organic compound that is represented by \[C{H_2} = C{H_2}\]molecular formula.
Ethylene belongs to the category of unsaturated hydrocarbons.
The unsaturated hydrocarbons represent those hydrocarbons that possess double and triple bonds between carbon atoms.
Ethylene is also known as the simplest alkene because it has a minimum of two carbon atoms which has a carbon-carbon double bond.
The carbon atom can form a variety of covalent compounds. And the covalent compounds of carbon may contain sigma (single bond or single) and pi-bond (double and triple bond).
By the presence of single, double, and triple carbon-carbon bonds we can determine the structure of hydrocarbons. When hydrocarbons possess a single bond, then the structure will be tetrahedral. Whereas, when carbon possesses carbon-carbon double and triple bond then the structure will be planar and linear respectively.
In hydrocarbons, each carbon atom has four valence electrons.
In the structure of the ethylene molecule, the carbon-carbon double bond has four shared pairs of electrons, and the rest two electrons \[C - C\]bond with hydrogen atoms.

Image: Structure of ethylene.
Therefore from the above explanation we can say option (b) will be the correct option:
Note: Ethylene is used as plant growth and regulator hormone.
Ethylene is also useful for the synthesis of various types of plastics.
Ethylene gas is lighter than air.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




