
What is not true about ice?
A. It has open cage like structure
B. It has less density than water
C. Each \[O\]atom is surrounded by \[4\,H\]atoms
D. Each \[O\]atom has four \[H\]-bonds around it
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Ice is a material that solidifies when liquid water or water vapour is frozen. When it is below zero degrees Celsius, water vapour condenses into snowflakes in the clouds and frost on the ground. When a system is in a static equilibrium, a reaction is totally stopped and there is no movement between the reactants and products that correspond to the chemical reaction.
Complete Step-by-Step Explanation:
In order to know when ice or solid water is described as a normally liquid fluid that freezes to a solid-state at a temperature of \[0^\circ C\]or below and expands to the gaseous form at a temperature of \[100^\circ C\] or higher. Water is an amazing substance that exhibits nearly no normal physical or chemical characteristics. typically. It is the most complex single-chemical compound known. A water molecule's three-dimensional structure can be represented as a tetrahedron, with an oxygen nucleus at the centre and four legs that may each have a high electron density.
At the normal air temperatures and pressures which is close to \[0^\circ C\]and the ice crystal that is often to take the form of the planes or some sheets of the oxygen atoms that are joined in an open hexagonal ring series. Additionally, the optical axis of the crystal structure is the \[c - \]axis which is also known as the parallel to the hexagonal rings axis.
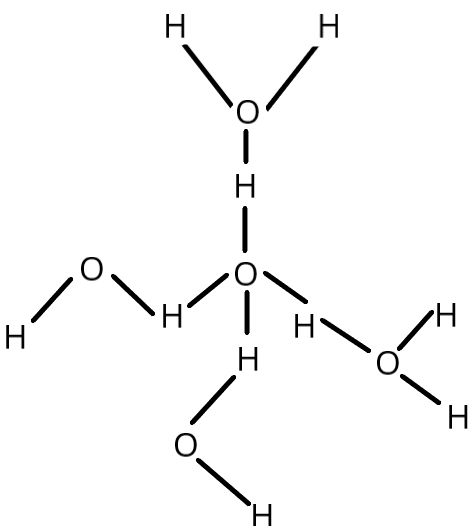
As seen in the image, there are two \[H - \]bonds around each \[O\] atom. Covalent bonds are used to join two \[H\].
Thus, the correct option is:(D) Each \[O\]atom has four \[H\]-bonds around it
Note: It should be noted that the steam which is water in its gaseous condition begins to change into the liquid form when the energy is removed because the temperature of the water molecules is dropping. And condensation is the term for this occurrence. Our daily lives allow us to observe this phenomenon. All of these phenomena are significant components of our natural water cycle.
Complete Step-by-Step Explanation:
In order to know when ice or solid water is described as a normally liquid fluid that freezes to a solid-state at a temperature of \[0^\circ C\]or below and expands to the gaseous form at a temperature of \[100^\circ C\] or higher. Water is an amazing substance that exhibits nearly no normal physical or chemical characteristics. typically. It is the most complex single-chemical compound known. A water molecule's three-dimensional structure can be represented as a tetrahedron, with an oxygen nucleus at the centre and four legs that may each have a high electron density.
At the normal air temperatures and pressures which is close to \[0^\circ C\]and the ice crystal that is often to take the form of the planes or some sheets of the oxygen atoms that are joined in an open hexagonal ring series. Additionally, the optical axis of the crystal structure is the \[c - \]axis which is also known as the parallel to the hexagonal rings axis.

As seen in the image, there are two \[H - \]bonds around each \[O\] atom. Covalent bonds are used to join two \[H\].
Thus, the correct option is:(D) Each \[O\]atom has four \[H\]-bonds around it
Note: It should be noted that the steam which is water in its gaseous condition begins to change into the liquid form when the energy is removed because the temperature of the water molecules is dropping. And condensation is the term for this occurrence. Our daily lives allow us to observe this phenomenon. All of these phenomena are significant components of our natural water cycle.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




