
$$\mathrm{BCl}_{3}$$ does not exist as dimer but $$\mathrm{BH}_{3}$$ exists as dimer because
(A)Chlorine is more electronegative than hydrogen
(B)There is pπ– pπ back bonding in $$\mathrm{BCl}_{3}$$ but $$\mathrm{BH}_{3}$$ does not contain such multiple bonding
(C)Large sized chlorine atoms do not fit in between the small boron atoms whereas small-sized hydrogen atoms get fitted in between boron atoms
(D)None of the above
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The dimerisation is due to the unstable structure of $$\mathrm{BH}_{3}$$. There is a share of electrons in between the molecules.
Complete step by step solution:
Chlorine is a group 17 element whereas, Boron is a group 13 element Thus the size of boron is much much less than the size of the chlorine.
So if we try to make B2Cl6 it is not possible for this compound to be stable but diborane(B2H6) can form since hydrogen is a very very smaller atom than chlorine. If there is the bonding between two atoms where one atom is having one vacant orbital and another is having one lone pair of electrons, then if this electron pair is donated to that respective vacant orbital then the bonding is called pπ– pπ or pπ– dπ depending on the orbital to which the electron pair is donated and from which the electron pair is donated.
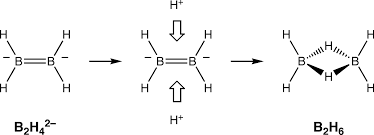
The bonding between the boron atoms and the bridging hydrogen atoms is, however, different from that in molecules such as hydrocarbons. Each boron uses two electrons in bonding to the terminal hydrogen atoms and has one valence electron remaining for additional bonding. The bridging hydrogen atoms provide one electron with each. The B2H2 ring is held together by four electrons which form two 3-centre 2-electron bonds. This type of bond is sometimes called a 'banana bond'.
The answer is option (C).
Note:/b<> There is no relation of electronegativity or back bonding for dimerisation of $$\mathrm{BH}_{3}$$. It only depends on the size of the other molecule that bonds with it.
Complete step by step solution:
Chlorine is a group 17 element whereas, Boron is a group 13 element Thus the size of boron is much much less than the size of the chlorine.
So if we try to make B2Cl6 it is not possible for this compound to be stable but diborane(B2H6) can form since hydrogen is a very very smaller atom than chlorine. If there is the bonding between two atoms where one atom is having one vacant orbital and another is having one lone pair of electrons, then if this electron pair is donated to that respective vacant orbital then the bonding is called pπ– pπ or pπ– dπ depending on the orbital to which the electron pair is donated and from which the electron pair is donated.
The bonding between the boron atoms and the bridging hydrogen atoms is, however, different from that in molecules such as hydrocarbons. Each boron uses two electrons in bonding to the terminal hydrogen atoms and has one valence electron remaining for additional bonding. The bridging hydrogen atoms provide one electron with each. The B2H2 ring is held together by four electrons which form two 3-centre 2-electron bonds. This type of bond is sometimes called a 'banana bond'.

The answer is option (C).
Note:/b<> There is no relation of electronegativity or back bonding for dimerisation of $$\mathrm{BH}_{3}$$. It only depends on the size of the other molecule that bonds with it.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




