
In the vulcanization of rubber:
A. Sulphur reacts to form a new compound
B. Sulphur cross-links are introduced
C. Sulphur forms a very thin protective layer over rubber
D. All of the above
Answer
240.6k+ views
Hint: Vulcanization of rubber consists of heating raw rubber with sulphur at 373 K to 415 K.
Vulcanization is done to improve the properties of natural rubber and also to remove its drawbacks.
The extent of toughness of the vulcanized rubber depends upon the amount of sulphur added during vulcanization.
Complete step by step answer:
Natural rubber is soft and tacky and this softness and tackiness becomes higher at high temperatures and brittle at low temperatures. So, rubber is usually used in the temperature range of 283 to 335 Kelvin where its elasticity is maintained.
Natural rubber also has huge water absorption capacity, low tensile strength and low resistance to abrasion. So, the process of vulcanization is done to improve these properties.
The raw rubber is heated with sulphur at 373 to 415 Kelvin. The vulcanized rubber obtained has excellent elasticity, low water absorption tendency and is also resistant to organic solvents.
During vulcanization, sulphur bridges or sulphur cross-links are introduced between the polymer chains either at their reactive allylic positions or at the sites of the double bonds. Since the process is slow, additives like zinc oxide are added to speed up the rate of vulcanization.
The sulphur cross-links make rubber harder and stronger and removes the stickiness as the individual chains can no longer slip over the other but are instead locked together in a giant size molecule because of the sulphur bridges.
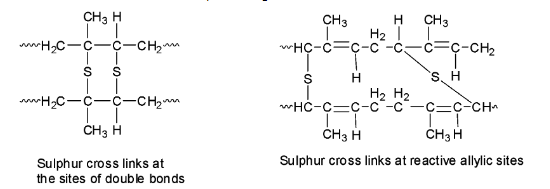
So, the correct option is B.
Note:
The best-known use of vulcanized rubber is the manufacture of vehicle tyres, which are combined with carbon black as a reinforcing agent for even greater strength.
Vulcanized rubber is also used in the manufacture of rubber hoses, shoe soles, erasers etc. and also used as insulation.
Vulcanization is done to improve the properties of natural rubber and also to remove its drawbacks.
The extent of toughness of the vulcanized rubber depends upon the amount of sulphur added during vulcanization.
Complete step by step answer:
Natural rubber is soft and tacky and this softness and tackiness becomes higher at high temperatures and brittle at low temperatures. So, rubber is usually used in the temperature range of 283 to 335 Kelvin where its elasticity is maintained.
Natural rubber also has huge water absorption capacity, low tensile strength and low resistance to abrasion. So, the process of vulcanization is done to improve these properties.
The raw rubber is heated with sulphur at 373 to 415 Kelvin. The vulcanized rubber obtained has excellent elasticity, low water absorption tendency and is also resistant to organic solvents.
During vulcanization, sulphur bridges or sulphur cross-links are introduced between the polymer chains either at their reactive allylic positions or at the sites of the double bonds. Since the process is slow, additives like zinc oxide are added to speed up the rate of vulcanization.
The sulphur cross-links make rubber harder and stronger and removes the stickiness as the individual chains can no longer slip over the other but are instead locked together in a giant size molecule because of the sulphur bridges.

So, the correct option is B.
Note:
The best-known use of vulcanized rubber is the manufacture of vehicle tyres, which are combined with carbon black as a reinforcing agent for even greater strength.
Vulcanized rubber is also used in the manufacture of rubber hoses, shoe soles, erasers etc. and also used as insulation.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More




