
In the following reaction X is \[C{H_3}N{H_2} + X + KOH \to C{H_3}NC\] (Highly offensive odour)
A. \[C{H_2}C{l_2}\]
B. \[CHC{l_3}\]
C. \[C{H_3}Cl\]
D. \[CC{l_4}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The reaction given above is called the Carbylamine reaction. In this reaction, primary amines are converted into isocyanides. Isocyanides have a very offensive odour. Knowledge of the reagents involved in the reaction will help us answer this question.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The carbylamine reaction involves the synthesis of isocyanides from primary amines. This reaction is also known as Hoffmann’s isocyanide synthesis.
The carbylamine reaction occurs only with primary amines. If we looked at the mechanism of the reaction, we could see that the carbylamine reaction proceeds through a dichlorocarbene (\[:CC{l_2}\]) intermediate. Therefore, to make this reaction occur, this intermediate must form in-situ from the reagents involved. It turns out that dichlorocarbene can form from the reaction of a strong base such as alcoholic potash (\[KOH\]) and chloroform (\[CHC{l_3}\]). The process of dichlorocarbene formation is shown below:
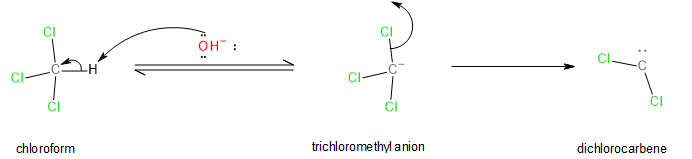
Image: Formation of dichlorocarbene from chloroform and alcoholic potash.
Thus, in the reaction given in the question, X stands for chloroform (\[CHC{l_3}\]).
Thus, option B is correct.
Additional Information:
Isocyanides are very well-known for their disagreeable odour, to the point that they have been investigated as potential non-lethal weapons. Their signature unpleasant smell is so recognizable that even trace amounts of isocyanides formed as by-products in certain reactions can be recognized simply by the smell.
Note: Carbene formation is a necessary step for this reaction to occur. The formation of carbene dictates what reagents are chosen for this reaction. It will be beneficial for the student to know some of the various ways in which carbenes are synthesised.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The carbylamine reaction involves the synthesis of isocyanides from primary amines. This reaction is also known as Hoffmann’s isocyanide synthesis.
The carbylamine reaction occurs only with primary amines. If we looked at the mechanism of the reaction, we could see that the carbylamine reaction proceeds through a dichlorocarbene (\[:CC{l_2}\]) intermediate. Therefore, to make this reaction occur, this intermediate must form in-situ from the reagents involved. It turns out that dichlorocarbene can form from the reaction of a strong base such as alcoholic potash (\[KOH\]) and chloroform (\[CHC{l_3}\]). The process of dichlorocarbene formation is shown below:

Image: Formation of dichlorocarbene from chloroform and alcoholic potash.
Thus, in the reaction given in the question, X stands for chloroform (\[CHC{l_3}\]).
Thus, option B is correct.
Additional Information:
Isocyanides are very well-known for their disagreeable odour, to the point that they have been investigated as potential non-lethal weapons. Their signature unpleasant smell is so recognizable that even trace amounts of isocyanides formed as by-products in certain reactions can be recognized simply by the smell.
Note: Carbene formation is a necessary step for this reaction to occur. The formation of carbene dictates what reagents are chosen for this reaction. It will be beneficial for the student to know some of the various ways in which carbenes are synthesised.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




