
In a triangle ABC, if vector BC=8, CA=7, AB=10, then find the projection of the vector AB on AC.
A.\[\dfrac{{25}}{4}\]
B. \[\dfrac{{85}}{{14}}\]
C. \[\dfrac{{127}}{{20}}\]
D. \[\dfrac{{115}}{{16}}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: First draw the triangle with the given information, then apply the cosine law to find \[\cos A\].Then apply the projection formula to obtain the required solution.
Formula used
Cosine formula:
For a triangle ABC with sides a, b, c and A the angle between AB and AC then \[{a^2} = {b^2} + {c^2} - 2bc\cos A\].
The projection of the vector PQ on QR is \[PQ\cos Q\], where Q is the angle between PQ and QR.
Complete step by step solution
The diagram of the given problem is,
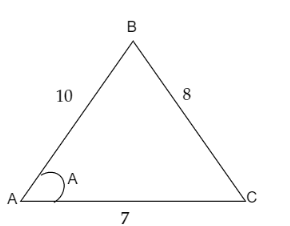
Image: Triangle ABC
Now, apply the cosine law,
\[{8^2} = {10^2} + {7^2} - 2 \times 10 \times 7\cos A\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2 \times 10 \times 7\cos A = {10^2} + {7^2} - {8^2}\]
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow \cos A = \dfrac{{{{10}^2} + {7^2} - {8^2}}}{{2 \times 10 \times 7}}\\{\rm{ = }}\dfrac{{85}}{{140}}\end{array}\]
Now, the projection of AB on AC is \[AB\cos A\] .
That is,
\[\begin{array}{c}10\cos \left( {\dfrac{{85}}{{140}}} \right) = 10 \times \dfrac{{85}}{{140}}\\ = \dfrac{{85}}{{14}}\end{array}\]
Therefore the correct option is B.
Note: Students sometime confused with the fact that in triangle ABC what is the value of a, b, c. So, the side opposite to angle A is a, or we can say that the side that does not correspond to angle A is a, like this we can compute the values of b and c.
Formula used
Cosine formula:
For a triangle ABC with sides a, b, c and A the angle between AB and AC then \[{a^2} = {b^2} + {c^2} - 2bc\cos A\].
The projection of the vector PQ on QR is \[PQ\cos Q\], where Q is the angle between PQ and QR.
Complete step by step solution
The diagram of the given problem is,

Image: Triangle ABC
Now, apply the cosine law,
\[{8^2} = {10^2} + {7^2} - 2 \times 10 \times 7\cos A\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2 \times 10 \times 7\cos A = {10^2} + {7^2} - {8^2}\]
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow \cos A = \dfrac{{{{10}^2} + {7^2} - {8^2}}}{{2 \times 10 \times 7}}\\{\rm{ = }}\dfrac{{85}}{{140}}\end{array}\]
Now, the projection of AB on AC is \[AB\cos A\] .
That is,
\[\begin{array}{c}10\cos \left( {\dfrac{{85}}{{140}}} \right) = 10 \times \dfrac{{85}}{{140}}\\ = \dfrac{{85}}{{14}}\end{array}\]
Therefore the correct option is B.
Note: Students sometime confused with the fact that in triangle ABC what is the value of a, b, c. So, the side opposite to angle A is a, or we can say that the side that does not correspond to angle A is a, like this we can compute the values of b and c.
Recently Updated Pages
Area vs Volume: Key Differences Explained for Students

Mutually Exclusive vs Independent Events: Key Differences Explained

Square vs Rhombus: Key Differences Explained for Students

Power vs Exponent: Key Differences Explained for Students

Arithmetic Mean Formula Explained Simply

Algebraic Formula: Key Concepts & Easy Examples

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Jan 21 Shift 1 Question Papers with Solutions & Answer Keys – Detailed Day 1 Analysis

JEE Main Marks vs Percentile 2026: Calculate Percentile and Rank Using Marks

JEE Main 2026 Jan 22 Shift 1 Today Paper Live Analysis With Detailed Solutions

JEE Mains 2026 January 21 Shift 2 Question Paper with Solutions PDF - Complete Exam Analysis

JEE Main 2026 Jan 22 Shift 2 Today Paper Live Analysis With Detailed Solutions

Other Pages
Pregnancy Week and Due Date Calculator: Find How Far Along You Are

NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 11 Areas Related to Circles (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Surface Areas and Volumes (2025-26)

All Mensuration Formulas with Examples and Quick Revision

Complete List of Class 10 Maths Formulas (Chapterwise)

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Statistics




