
If earth were to spin faster, the acceleration due to gravity at the poles will:
(A) Increase
(B) Decrease
(C) Remains the same
(D) Cannot say
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint If earth is spinning faster, this mean it has a higher angular velocity and thus a everyone on “off axis points” of earth will have a higher centrifugal force with respect to the axis of rotation of the earth
Complete step by step solution
When an object is placed on earth, it is constantly being pulled down due to gravity, this force is equal to mg. This is also the case when the earth is not rotating, if it was rotating then there would be another force which is also called the centrifugal force of the object. This force pushes the object from the surface of the earth and acts in the direction perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the earth. The net resultant of these 2 forces will give the apparent weight of the object
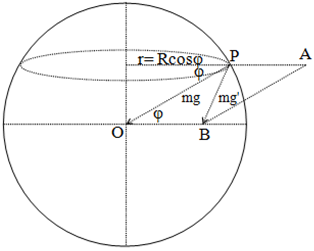
The resultant is thus given by,
\[g'\, = \,g - {\omega ^2}R\cos \phi \]
At the equator \[\phi \] is equal to 0 and at the poles, \[\phi \] is equal to 90 which makes the 2nd term as 0. Therefore the acceleration due to gravity at the poles is independent of the angular velocity of the earth.
So the correct answer is option C.
Note Note that the weight of the body is the force they exert in the surface of Earth. This is higher on poles and lower on other points.
If instead of pole, we need to take in consideration the gravity at the equator, it would be lower there. Also the angular velocity of earth under normal circumstances is \[7.29 \times {10^{ - 5}}\]
Complete step by step solution
When an object is placed on earth, it is constantly being pulled down due to gravity, this force is equal to mg. This is also the case when the earth is not rotating, if it was rotating then there would be another force which is also called the centrifugal force of the object. This force pushes the object from the surface of the earth and acts in the direction perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the earth. The net resultant of these 2 forces will give the apparent weight of the object

The resultant is thus given by,
\[g'\, = \,g - {\omega ^2}R\cos \phi \]
At the equator \[\phi \] is equal to 0 and at the poles, \[\phi \] is equal to 90 which makes the 2nd term as 0. Therefore the acceleration due to gravity at the poles is independent of the angular velocity of the earth.
So the correct answer is option C.
Note Note that the weight of the body is the force they exert in the surface of Earth. This is higher on poles and lower on other points.
If instead of pole, we need to take in consideration the gravity at the equator, it would be lower there. Also the angular velocity of earth under normal circumstances is \[7.29 \times {10^{ - 5}}\]
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




