
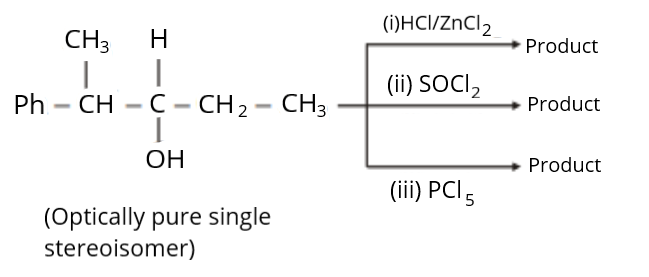
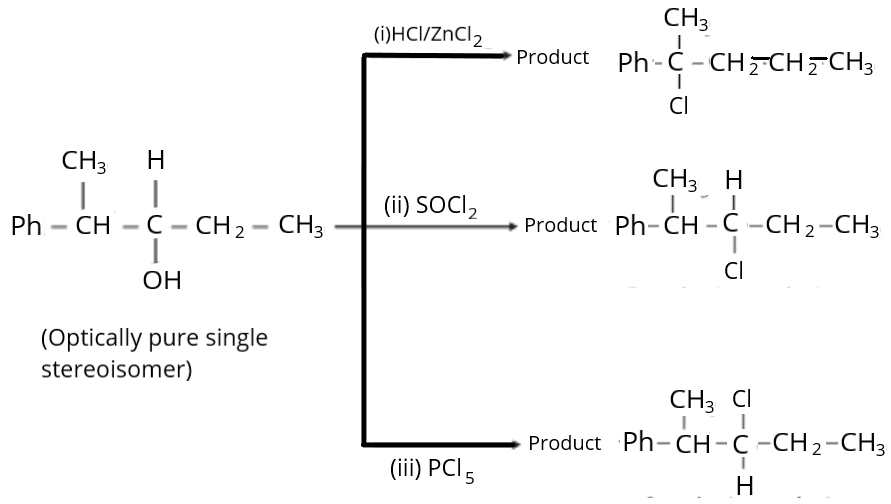
Find the sum of total number of isomeric chlorides obtained in these reactions (consider only the major products).
\[4\]
\[1\]
\[2\]
\[3\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Acyclic compounds with a linear structure as opposed to a cyclic structure are known as open-chain compounds. A kind of isomerism known as "cis-trans" isomerism is geometric isomerism. We shall not include this isomer when counting the molecule\[{C_6}{H_9}ClO\].
Complete Step by Step Solution:
We shall start by comprehending the isomers. Isomers are molecules of substances that share a similar molecular formula, meaning that the isomer's number of atoms is the same as that of the original compound or molecule. Isomer has a unique chemical composition. We shall now talk about geometrical isomerism, one of the isomerism types.
Thus, directional organisation is taken into account in geometrical isomerism. Geometrical isomerism is the process of creating a new molecule with a similar molecular formula but a different chemical structure by rotating the attached atoms or groups of atoms around the double-bonded atoms.
(Self made)
We can see from the aforementioned isomers that while they all share the same molecular formula, \[{C_6}{H_9}ClO\], their chemical structures differ. To create an isomer with a comparable molecular formula, the double bond and chloride group's location are altered.
As a result, there are a total of \[4\] open chain isomeric chloride compounds with the chemical formula \[{C_6}{H_9}ClO\] that are unable to exhibit geometric isomerism.
Thus, the correct option is: (A) \[4\].
Note: It should be noted that to separate one isomeric acid chloride from the other is impractical because the isomeric acid chlorides produced by treating the half-methyl esters of \[3 - \] methoxyphthalic acid with thionyl chloride interconvert so easily. Acid chloride, which is generated from the \[1 - \]methyl ester, is the primary isomer at equilibrium.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
We shall start by comprehending the isomers. Isomers are molecules of substances that share a similar molecular formula, meaning that the isomer's number of atoms is the same as that of the original compound or molecule. Isomer has a unique chemical composition. We shall now talk about geometrical isomerism, one of the isomerism types.
Thus, directional organisation is taken into account in geometrical isomerism. Geometrical isomerism is the process of creating a new molecule with a similar molecular formula but a different chemical structure by rotating the attached atoms or groups of atoms around the double-bonded atoms.

(Self made)
We can see from the aforementioned isomers that while they all share the same molecular formula, \[{C_6}{H_9}ClO\], their chemical structures differ. To create an isomer with a comparable molecular formula, the double bond and chloride group's location are altered.
As a result, there are a total of \[4\] open chain isomeric chloride compounds with the chemical formula \[{C_6}{H_9}ClO\] that are unable to exhibit geometric isomerism.
Thus, the correct option is: (A) \[4\].
Note: It should be noted that to separate one isomeric acid chloride from the other is impractical because the isomeric acid chlorides produced by treating the half-methyl esters of \[3 - \] methoxyphthalic acid with thionyl chloride interconvert so easily. Acid chloride, which is generated from the \[1 - \]methyl ester, is the primary isomer at equilibrium.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




