
Find the maximum magnifying power of a compound microscope having a $25\;$ diopter lens as the objective, a $5$ diopter lens as the eyepiece, and the separation $30\;cm$ between the two lenses. The least distance for clear vision is $25\;cm$.
(A) $8.4\;$
(B) $7.4\;$
(C) $9.4\;$
(D) $10.4\;$
Answer
239.4k+ views
Hint: A compound microscope consists of two lenses, the focal length of both lenses can be calculated by reciprocating their powers. It is known that the maximum magnification is achieved when the image is formed at the least distance of clear vision, thus all of these values can be then used to calculate the maximum magnifying power of the microscope.
Complete step by step solution:
The first step is to find the focal length of both the eyepiece and the objective lens.
We know that,
The focal length, $f$ of a lens, is given by-
$f = \dfrac{1}{P}$
where $P$ is the power of the lens.
Therefore, the focal length of the objective lens ${f_o}$is given by-
${f_0} = \dfrac{1}{{25}}m$
or in centimeters,
${f_o} = \dfrac{{100}}{{25}} = 4cm$
Similarly for the eyepiece,
The focal length ${f_e}$ is given by-
${f_e} = \dfrac{{100}}{5} = 20cm$
The light first enters the objective lens, then the image formed by the objective acts as an object for the eyepiece lens, and then the final image is formed by the eyepiece, which should be formed at $25cm\;$ for clear vision.
Therefore, the position of the image formed by the eyepiece ${v_e}$is-
${v_e} = - 25cm$
The lens formula is given by-
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{v}$
where $f$ is the focal length, $u$ is the position of the object, and $v$ is the position of the image formed.
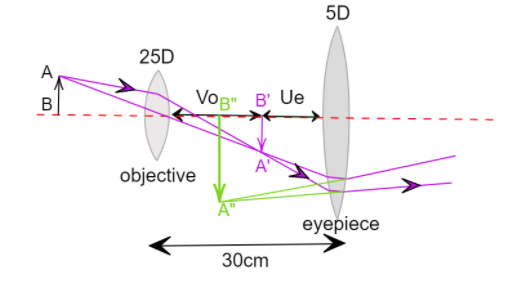
For the eyepiece lens, by applying the lens formula we see that-
$\dfrac{1}{{20}} = \dfrac{1}{{{u_e}}} + \dfrac{1}{{\left( { - 25} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{20}} + \dfrac{1}{{25}} = \dfrac{1}{{{u_e}}}$
Upon rearranging,
$\dfrac{1}{{{u_e}}} = \dfrac{{4 + 5}}{{100}} = \dfrac{9}{{100}}$
$ \Rightarrow {u_e} = \dfrac{{100}}{9} = 11.11cm$
We know that the distance between the lenses is $30cm\;$, and the position where the first image is formed lies between both lenses. The first image is made by the objective lens and acts as an object for the eyepiece lens, therefore the distance of this image $A'B'\;$ can be given by-${v_o} + {u_e} = 30$
${v_0} = 30 - 11.11$
$ \Rightarrow {v_0} = 18.89cm$
The image is formed on the right of the objective lens and hence carries a positive sign with it.
Now applying the lens formula for the objective lens, we have-
$\dfrac{1}{{{f_o}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{u_o}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{v_o}}}$
Putting the values and rearranging,
$\dfrac{1}{{{u_o}}} = \dfrac{1}{4} - \dfrac{1}{{18.89}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{u_o}}} = 0.053 - 0.25 = - 0.197$
On reciprocating,
${u_o} = \dfrac{1}{{0.197}} = - 5.07cm$
$ \Rightarrow {u_o} = - 5.07cm$
The maximum magnification power by a compound microscope is given by the formula-
$M = \dfrac{{{v_o}}}{{{u_o}}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{D}{{{f_e}}}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow M = \dfrac{{18.89}}{{( - 5.07)}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{{25}}{{20}}} \right)$
On simplifying,
$M = - 3.72 \times 2.25$
$ \Rightarrow M = - 8.37$
The maximum magnification produced by the microscope is $8.37\;$and the image is inverted.
Since, $8.37 \approx 8.4$ the correct answer is option (A).
Note: It should be kept in mind that using the correct sign convention in each step is very important. A ray diagram is necessary in order to determine the sign convention of the position of an image or an object relative to a lens. Assuming that light travels from left to right, if the position of the object/image is on the left of the lens then it is negative and vice versa.
Complete step by step solution:

The first step is to find the focal length of both the eyepiece and the objective lens.
We know that,
The focal length, $f$ of a lens, is given by-
$f = \dfrac{1}{P}$
where $P$ is the power of the lens.
Therefore, the focal length of the objective lens ${f_o}$is given by-
${f_0} = \dfrac{1}{{25}}m$
or in centimeters,
${f_o} = \dfrac{{100}}{{25}} = 4cm$
Similarly for the eyepiece,
The focal length ${f_e}$ is given by-
${f_e} = \dfrac{{100}}{5} = 20cm$
The light first enters the objective lens, then the image formed by the objective acts as an object for the eyepiece lens, and then the final image is formed by the eyepiece, which should be formed at $25cm\;$ for clear vision.
Therefore, the position of the image formed by the eyepiece ${v_e}$is-
${v_e} = - 25cm$
The lens formula is given by-
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{v}$
where $f$ is the focal length, $u$ is the position of the object, and $v$ is the position of the image formed.

For the eyepiece lens, by applying the lens formula we see that-
$\dfrac{1}{{20}} = \dfrac{1}{{{u_e}}} + \dfrac{1}{{\left( { - 25} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{20}} + \dfrac{1}{{25}} = \dfrac{1}{{{u_e}}}$
Upon rearranging,
$\dfrac{1}{{{u_e}}} = \dfrac{{4 + 5}}{{100}} = \dfrac{9}{{100}}$
$ \Rightarrow {u_e} = \dfrac{{100}}{9} = 11.11cm$
We know that the distance between the lenses is $30cm\;$, and the position where the first image is formed lies between both lenses. The first image is made by the objective lens and acts as an object for the eyepiece lens, therefore the distance of this image $A'B'\;$ can be given by-${v_o} + {u_e} = 30$
${v_0} = 30 - 11.11$
$ \Rightarrow {v_0} = 18.89cm$
The image is formed on the right of the objective lens and hence carries a positive sign with it.
Now applying the lens formula for the objective lens, we have-
$\dfrac{1}{{{f_o}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{u_o}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{v_o}}}$
Putting the values and rearranging,
$\dfrac{1}{{{u_o}}} = \dfrac{1}{4} - \dfrac{1}{{18.89}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{u_o}}} = 0.053 - 0.25 = - 0.197$
On reciprocating,
${u_o} = \dfrac{1}{{0.197}} = - 5.07cm$
$ \Rightarrow {u_o} = - 5.07cm$
The maximum magnification power by a compound microscope is given by the formula-
$M = \dfrac{{{v_o}}}{{{u_o}}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{D}{{{f_e}}}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow M = \dfrac{{18.89}}{{( - 5.07)}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{{25}}{{20}}} \right)$
On simplifying,
$M = - 3.72 \times 2.25$
$ \Rightarrow M = - 8.37$
The maximum magnification produced by the microscope is $8.37\;$and the image is inverted.
Since, $8.37 \approx 8.4$ the correct answer is option (A).
Note: It should be kept in mind that using the correct sign convention in each step is very important. A ray diagram is necessary in order to determine the sign convention of the position of an image or an object relative to a lens. Assuming that light travels from left to right, if the position of the object/image is on the left of the lens then it is negative and vice versa.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Step-by-Step Guide to Young’s Double Slit Experiment Derivation

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Common Ion Effect: Concept, Applications, and Problem-Solving

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Essential Derivations for CBSE Class 12 Physics: Stepwise & PDF Solutions

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/2/3) 2025: PDF, Answer Key & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis




