
When ethene reacts with bromine, it forms
A) Chloroethane
B) Ethylene dibromide
C) 1-bromopropane
D) 1,2-dichloroethene
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: We know that ethene is the simplest of alkenes having one double bond. It is present in the gaseous state having a sweet flavour. And we know that bromine is a halogen of red-brown colour present in the liquid state.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Let’s discuss the reaction of bromine with ethene. Ethene, when a reaction with liquid bromine, or with a bromine solution in tetrachloromethane which is an organic solvent, breaks the double bond of ethene and attaching of one bromine atom at each carbon takes place. Therefore, the product formed in this reaction is dibromo-ethane or ethylene dibromide. The chemical reaction is,
\[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}} = {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}} + {\rm{B}}{{\rm{r}}_{\rm{2}}} \to \mathop {{\rm{Br}} - {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}} - {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}} - {\rm{Br}}}\limits_{{\rm{Ethylene}}\,{\rm{bromide}}} \]
Let’s understand the mechanism of the reaction. In the first step, the attachment of one bromine atom to both carbon atoms. And the bromine atom is positively charged.
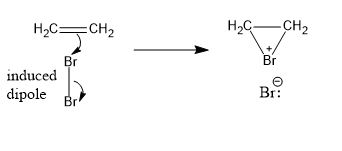
Image: Formation of bromonium ion
In the second step, the attack of the bromide ion at the bromonium ion from the back side happens. The resultant product is ethylene dibromide. The reaction is:
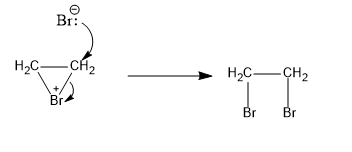
Image: Formation of ethylene dibromide
Therefore, the reaction of ethene and bromine gives ethylene dibromide.
Hence, option B is right.
Note: The reaction of ethene and bromine is an electrophilic addition. The electrophilic addition defines an addition reaction of a nucleophile and an electrophile that causes the addition of a double or a triple bond. An electrophile defines a species that has a tendency to react with other molecules having a donatable electron pair.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Let’s discuss the reaction of bromine with ethene. Ethene, when a reaction with liquid bromine, or with a bromine solution in tetrachloromethane which is an organic solvent, breaks the double bond of ethene and attaching of one bromine atom at each carbon takes place. Therefore, the product formed in this reaction is dibromo-ethane or ethylene dibromide. The chemical reaction is,
\[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}} = {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}} + {\rm{B}}{{\rm{r}}_{\rm{2}}} \to \mathop {{\rm{Br}} - {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}} - {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}} - {\rm{Br}}}\limits_{{\rm{Ethylene}}\,{\rm{bromide}}} \]
Let’s understand the mechanism of the reaction. In the first step, the attachment of one bromine atom to both carbon atoms. And the bromine atom is positively charged.

Image: Formation of bromonium ion
In the second step, the attack of the bromide ion at the bromonium ion from the back side happens. The resultant product is ethylene dibromide. The reaction is:

Image: Formation of ethylene dibromide
Therefore, the reaction of ethene and bromine gives ethylene dibromide.
Hence, option B is right.
Note: The reaction of ethene and bromine is an electrophilic addition. The electrophilic addition defines an addition reaction of a nucleophile and an electrophile that causes the addition of a double or a triple bond. An electrophile defines a species that has a tendency to react with other molecules having a donatable electron pair.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




