
Compound (X) with molecular formula ${C}_{3}{H}_{8}O$ is treated with acidified potassium dichromate to form a product (Y) with molecular formula ${C}_{3}{H}_{6}O$. (Y) does not form a shining silver mirror on warming with ammoniacal $Ag{NO}_{3}$. (Y) when treated with an aqueous solution of $N{H}_{2}CONHN{H}_{2}$, HCl and sodium acetate, gives a product (Z). The structure of (Z) is:
A. $C{H}_{3}C{H}_{2}CH=NNHCON{H}_{2}$
B. ${(C{H}_{3})}_{2}=NNHCON{H}_{2}$
C. ${(C{H}_{3})}_{2}=NCONHN{H}_{2}$
D. $C{H}_{3}C{H}_{2}CH=NCONHN{H}_{2}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The Tollen's reagent test is used to distinguish between aldehyde and a ketone. If after the reaction a silver mirror is formed then it indicates the presence of a ketone group, else an aldehyde group is present.
Complete step by step answer: It is given in the question that a compound X that has a molecular formula ${C}_{3}{H}_{8}O$ is treated with acidified potassium dichromate to form a product (Y) with molecular formula ${C}_{3}{H}_{6}O$. The reaction can be written as follows.
$ \underset { ({ C }_{ 3 }{ H }_{ 8 }O) }{ X } \quad \xrightarrow [ { K }_{ 2 }{ Cr }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 7 } ]{ H^{ + } } \quad \underset { ({ C }_{ 3 }{ H }_{ 6 }O) }{ Y }$
And then the compound Y, when heated with ammoniacal $Ag{NO}_{3}$ does not give a shining silver mirror. After this the compound Y is made to react with an aqueous solution of $N{H}_{2}CONHN{H}_{2}$, HCl and sodium acetate, gives a product (Z). The reaction can be written as follows.
\[\underset{({{C}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}O)}{\mathop{Y}}\,\quad \xrightarrow[{}]{Aq.(N{{H}_{2}}CONHN{{H}_{2}}+HCl+C{{H}_{3}}CO{{O}^{-}}N{{a}^{+}})}\quad Z\]
Let us now find out the compounds X, Y, and Z.
We know that aldehydes gives a shining silver mirror but in this case no shining silver mirror is formed. Therefore, from this we can come to the conclusion that the compound Y is a ketone. Thus, the molecular structure of compound Y is given as:
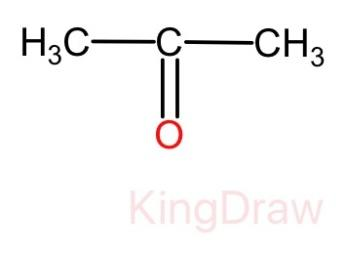
And we know that the compound X is getting oxidized with the help of potassium dichromate. Therefore, the compound X must be alcohol. Thus, the molecular structure of compound X is given as:
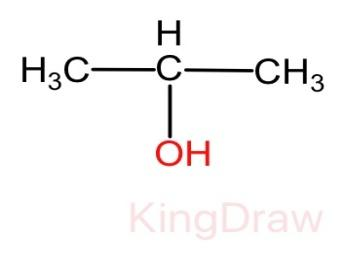
Now the reaction of compound X to form compound Y when treated with acidic potassium dichromate can be given as follows.
$ \underset { Propan-2-ol }{ C{ H }_{ 3 }-CH(OH)-C{ H }_{ 3 } } \quad \xrightarrow [ { K }_{ 2 }{ Cr }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 7 } ]{ H^{ + } } \quad \underset { Propanone }{ C{ H }_{ 3 }-CO-C{ H }_{ 3 } }$
And further, when the ketone i.e., propanone is reacted with an aqueous solution of $N{H}_{2}CONHN{H}_{2}$, HCl and sodium acetate, the oxygen in the compound Y gets replaced by $N{H}_{2}NHCON{H}_{2}$. The reaction involved is given as:
$\underset{Propanone}{\mathop{C{{H}_{3}}-CO-C{{H}_{3}}}}\,\quad \xrightarrow[{}]{Aq.(N{{H}_{2}}CONHN{{H}_{2}}+HCl+C{{H}_{3}}CO{{O}^{-}}N{{a}^{+}})}\quad {{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}=NNHCON{{H}_{2}}$
Therefore, the compound Z is ${(C{H}_{3})}_{2}=NNHCON{H}_{2}$. Hence, option (B) is the correct option.
Note: The $-N{H}_{2}$ group is an electron withdrawing group and shows -I effect. And the more the no. of EWG, the more the electron density at the atom and thus more reactive. Therefore, $N{H}_{2}NHCON{H}_{2}$ gets attached from the side which has more no. of $-N{H}_{2}$ groups.
Complete step by step answer: It is given in the question that a compound X that has a molecular formula ${C}_{3}{H}_{8}O$ is treated with acidified potassium dichromate to form a product (Y) with molecular formula ${C}_{3}{H}_{6}O$. The reaction can be written as follows.
$ \underset { ({ C }_{ 3 }{ H }_{ 8 }O) }{ X } \quad \xrightarrow [ { K }_{ 2 }{ Cr }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 7 } ]{ H^{ + } } \quad \underset { ({ C }_{ 3 }{ H }_{ 6 }O) }{ Y }$
And then the compound Y, when heated with ammoniacal $Ag{NO}_{3}$ does not give a shining silver mirror. After this the compound Y is made to react with an aqueous solution of $N{H}_{2}CONHN{H}_{2}$, HCl and sodium acetate, gives a product (Z). The reaction can be written as follows.
\[\underset{({{C}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}O)}{\mathop{Y}}\,\quad \xrightarrow[{}]{Aq.(N{{H}_{2}}CONHN{{H}_{2}}+HCl+C{{H}_{3}}CO{{O}^{-}}N{{a}^{+}})}\quad Z\]
Let us now find out the compounds X, Y, and Z.
We know that aldehydes gives a shining silver mirror but in this case no shining silver mirror is formed. Therefore, from this we can come to the conclusion that the compound Y is a ketone. Thus, the molecular structure of compound Y is given as:

And we know that the compound X is getting oxidized with the help of potassium dichromate. Therefore, the compound X must be alcohol. Thus, the molecular structure of compound X is given as:

Now the reaction of compound X to form compound Y when treated with acidic potassium dichromate can be given as follows.
$ \underset { Propan-2-ol }{ C{ H }_{ 3 }-CH(OH)-C{ H }_{ 3 } } \quad \xrightarrow [ { K }_{ 2 }{ Cr }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 7 } ]{ H^{ + } } \quad \underset { Propanone }{ C{ H }_{ 3 }-CO-C{ H }_{ 3 } }$
And further, when the ketone i.e., propanone is reacted with an aqueous solution of $N{H}_{2}CONHN{H}_{2}$, HCl and sodium acetate, the oxygen in the compound Y gets replaced by $N{H}_{2}NHCON{H}_{2}$. The reaction involved is given as:
$\underset{Propanone}{\mathop{C{{H}_{3}}-CO-C{{H}_{3}}}}\,\quad \xrightarrow[{}]{Aq.(N{{H}_{2}}CONHN{{H}_{2}}+HCl+C{{H}_{3}}CO{{O}^{-}}N{{a}^{+}})}\quad {{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}=NNHCON{{H}_{2}}$
Therefore, the compound Z is ${(C{H}_{3})}_{2}=NNHCON{H}_{2}$. Hence, option (B) is the correct option.
Note: The $-N{H}_{2}$ group is an electron withdrawing group and shows -I effect. And the more the no. of EWG, the more the electron density at the atom and thus more reactive. Therefore, $N{H}_{2}NHCON{H}_{2}$ gets attached from the side which has more no. of $-N{H}_{2}$ groups.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




