
Can two isothermal curves cut each other?
A. Never
B. Yes
C. They will cut when temperature is ${0^ \circ }C$
D. Yes, when the pressure is critical pressure
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In an Isothermal process in a thermodynamic system, the temperature is constant and at a constant temperature, both the parameters pressure and volume vary with the different conditions of the system and surroundings hence, we will plot a $P - V$ graph for an isothermal change for two different temperatures to state the answer of this problem.
Complete step by step solution:
An isothermal process in thermodynamics is defined as the process during which the temperature $T$ of a system remains constant that’s why it is also referred to as a constant-temperature process.
In an Isothermal process, $T = \text{constant}$ and $\text{Change in Temperature} = \Delta T = 0$. Now let us draw a $P - V$ graph for an isothermal expansion of a gas at two different temperatures to have two isothermal curves as shown below: -
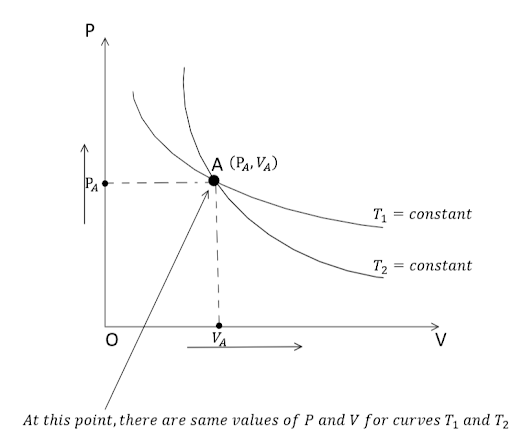
Clearly, from the above graph it can be observed that if the two isothermal curves intersect at point A, there will be the same values of pressure and volume i.e., ${P_A}$ and ${V_A}$ at that point. That’s why if the two curves intersect, the volume and pressure of the gas will be the same at two distinct isothermal temperatures, which is not possible. As a result, two isothermal curves can ‘Never’ intersect.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: In this problem, to determine whether the two isothermal curves intersect with each other or not, we need to find the conditions of other parameters of gas in a particular thermodynamic system such as pressure and volume hence, we will plot a $P - V$ graph and if the conditions of pressure and volume are justified for the given situation then the curves can intersect otherwise not.
Complete step by step solution:
An isothermal process in thermodynamics is defined as the process during which the temperature $T$ of a system remains constant that’s why it is also referred to as a constant-temperature process.
In an Isothermal process, $T = \text{constant}$ and $\text{Change in Temperature} = \Delta T = 0$. Now let us draw a $P - V$ graph for an isothermal expansion of a gas at two different temperatures to have two isothermal curves as shown below: -

Clearly, from the above graph it can be observed that if the two isothermal curves intersect at point A, there will be the same values of pressure and volume i.e., ${P_A}$ and ${V_A}$ at that point. That’s why if the two curves intersect, the volume and pressure of the gas will be the same at two distinct isothermal temperatures, which is not possible. As a result, two isothermal curves can ‘Never’ intersect.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: In this problem, to determine whether the two isothermal curves intersect with each other or not, we need to find the conditions of other parameters of gas in a particular thermodynamic system such as pressure and volume hence, we will plot a $P - V$ graph and if the conditions of pressure and volume are justified for the given situation then the curves can intersect otherwise not.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




