
Baeyer's reagent is used for the detection of
A. Amines
B. Glucose
C. Unsaturated bond
D. Alcohol
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Baeyer's reagent is the hot alkaline solution of potassium permanganate (\[KMn{O_4}\]). It is utilised for the identification of the double and triple bonds in a solution which is also known as the identification of unsaturation.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Here, the provided question is asked about the role of the Baeyer's reagent in organic chemistry.
First, we have to know Baeyer's reagent to obtain a better understanding, and then we can know the working of the compound, this would help in obtaining the answer and explanation both.
Baeyer's reagent is an alkaline or basic solution of \[KMn{O_4}\]. It is pinkish-purple in colour.
- It is known as a reagent for its catalytic role.
- It is known as Baeyer's reagent as it is labelled after the German organic chemist Adolf von Baeyer.
- It is a powerful oxidising agent and is utilised in qualitative organic estimation to examine the existence of unsaturation.
- To test a given solution of alkene or alkyne, the solution is first treated with Baeyer's reagent which interacts with it altering its pinkish-purple colour to brown.
The alkene or alkyne is converted to 1,2-diol, while the permanganate is reduced to manganese dioxide (\[Mn{O_2}\]). The brown colour is due to the manganese dioxide.
The reaction happens as follows:
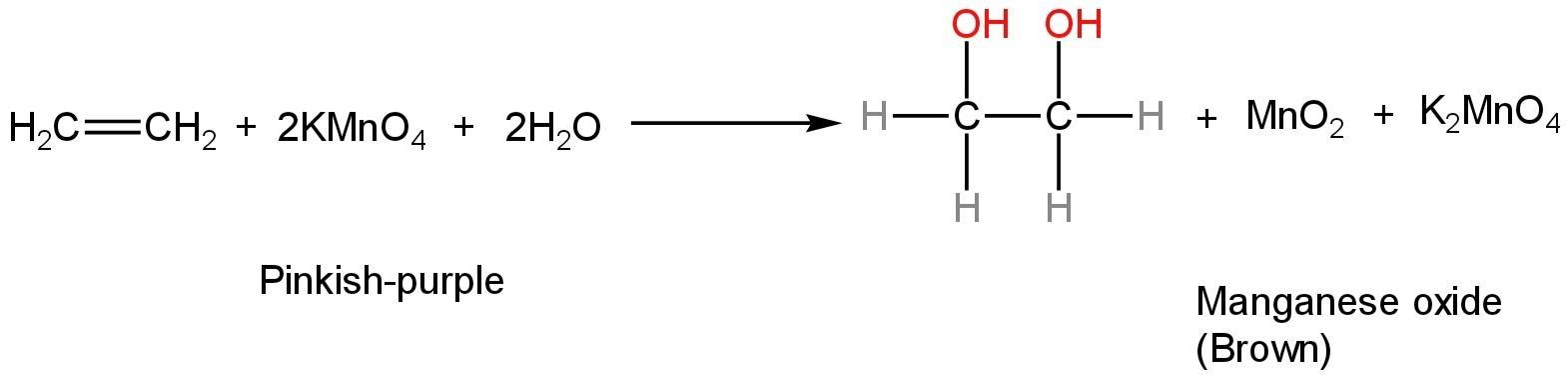
Image: Reaction of ethene with Baeyer's reagent
The reaction is crucial because it doesn't decolorize alkanes or aromatic compounds, and therefore, can be utilised to differentiate them from alkenes and alkynes.
So, Baeyer's reagent is used for the detection of unsaturated bonds.
So, option C is correct.
Note: Potassium permanganate is utilised for no.of skin conditions like fungal infections of the foot, external injuries, dermatitis, and tropical ulcers. It is utilised greatly in the water treatment industry. It is utilised to eliminate iron and hydrogen sulphide from well water. Historically it was utilised to purify drinking water.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Here, the provided question is asked about the role of the Baeyer's reagent in organic chemistry.
First, we have to know Baeyer's reagent to obtain a better understanding, and then we can know the working of the compound, this would help in obtaining the answer and explanation both.
Baeyer's reagent is an alkaline or basic solution of \[KMn{O_4}\]. It is pinkish-purple in colour.
- It is known as a reagent for its catalytic role.
- It is known as Baeyer's reagent as it is labelled after the German organic chemist Adolf von Baeyer.
- It is a powerful oxidising agent and is utilised in qualitative organic estimation to examine the existence of unsaturation.
- To test a given solution of alkene or alkyne, the solution is first treated with Baeyer's reagent which interacts with it altering its pinkish-purple colour to brown.
The alkene or alkyne is converted to 1,2-diol, while the permanganate is reduced to manganese dioxide (\[Mn{O_2}\]). The brown colour is due to the manganese dioxide.
The reaction happens as follows:

Image: Reaction of ethene with Baeyer's reagent
The reaction is crucial because it doesn't decolorize alkanes or aromatic compounds, and therefore, can be utilised to differentiate them from alkenes and alkynes.
So, Baeyer's reagent is used for the detection of unsaturated bonds.
So, option C is correct.
Note: Potassium permanganate is utilised for no.of skin conditions like fungal infections of the foot, external injuries, dermatitis, and tropical ulcers. It is utilised greatly in the water treatment industry. It is utilised to eliminate iron and hydrogen sulphide from well water. Historically it was utilised to purify drinking water.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




