
Assertion: Millon’s test is a test for the identification of proteins.
Reason: Millon’s reagent is a solution of mercurous nitrate and mercuric nitrate in nitric acid containing little nitrous acid.
(A) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, and the reason is the correct explanation for the assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are correct, but the reason is not the correct explanation for the assertion.
(C) Assertion is correct, but the reason is incorrect.
(D) Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Millon’s test is used to detect amino acids. Amino acids are structural units of proteins. When Millon’s reagent is added to an aqueous solution of protein white precipitate is formed which on heating turns red. Millon’s test is used to detect amino acids containing phenol. All proteins contain tyrosine residue.
Complete step by step solution:
-Presence of proteins is detected by adding Millon’s reagent.
-When a few drops of this reagent are added in the aqueous test solution to be tested, then it is heated gently. If reddish-brown colouration or precipitate appears, it indicates the presence of tyrosine.
-Tyrosine is present in nearly all proteins.
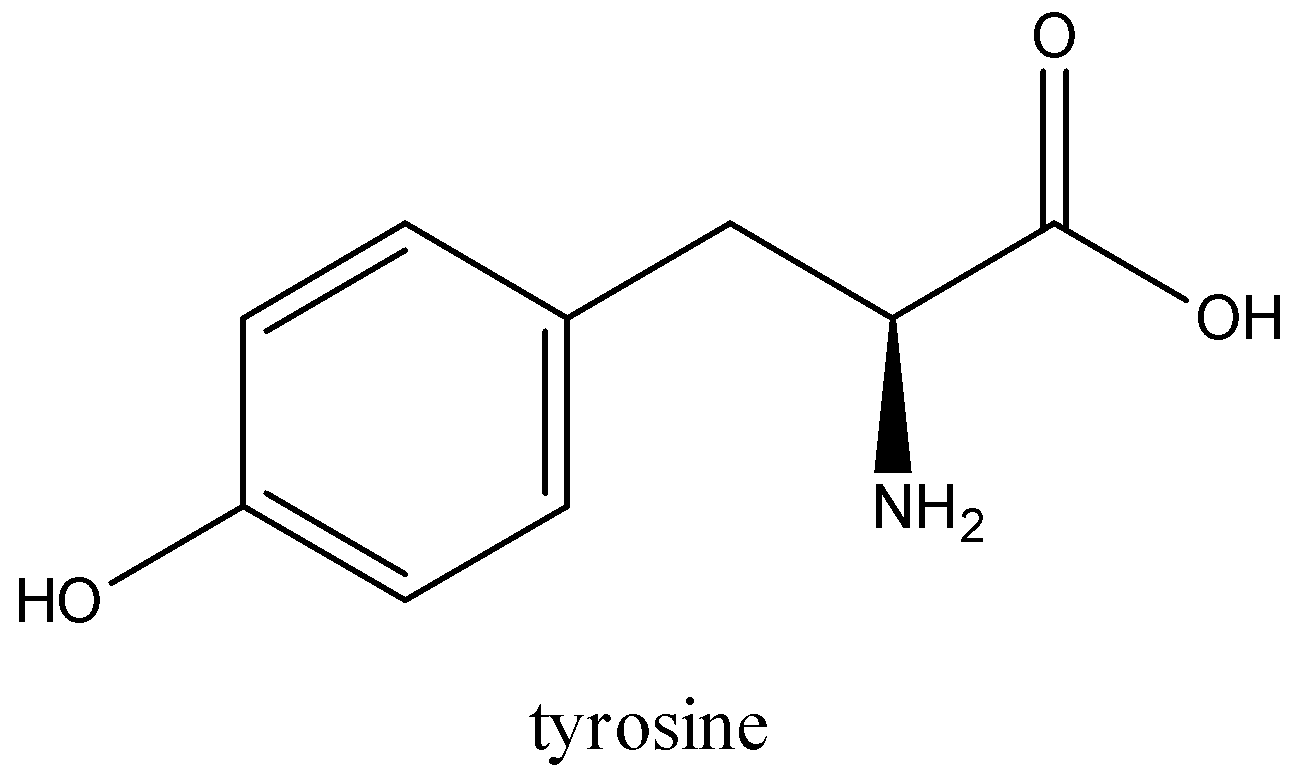
-Compounds having hydroxybenzene radical form red complexes with Millon’s reagent. Tyrosine is only amino acid which has a hydroxybenzene ring.
-Tyrosine with acidified mercuric sulphate solution produces mercury amino acid complex which is yellow precipitate. When sodium nitrate solution is added in this and heated, the mercury amino acid complex gets converted to red colour mercury phenolate.
So, (B) Both assertion and reason are correct, but the reason is not the correct explanation for the assertion.
Additional information:
The correct explanation is When Millon’s reagent is added to an aqueous solution of protein white precipitate is formed which on heating turns red. Millon’s test is used to detect amino acids containing phenol. All proteins contain tyrosine residue.
Note: When a few drops of reagent are added in the aqueous test solution to be tested, then it is heated gently. If reddish-brown colouration or precipitate appears, it indicates the presence of tyrosine. Tyrosine is present in nearly all proteins. Tyrosine with acidified mercuric sulphate solution produces mercury amino acid complex which is yellow precipitate. When sodium nitrate solution is added in this and heated, the mercury amino acid complex gets converted to red colour mercury phenolate.
Complete step by step solution:
-Presence of proteins is detected by adding Millon’s reagent.
-When a few drops of this reagent are added in the aqueous test solution to be tested, then it is heated gently. If reddish-brown colouration or precipitate appears, it indicates the presence of tyrosine.
-Tyrosine is present in nearly all proteins.

-Compounds having hydroxybenzene radical form red complexes with Millon’s reagent. Tyrosine is only amino acid which has a hydroxybenzene ring.
-Tyrosine with acidified mercuric sulphate solution produces mercury amino acid complex which is yellow precipitate. When sodium nitrate solution is added in this and heated, the mercury amino acid complex gets converted to red colour mercury phenolate.
So, (B) Both assertion and reason are correct, but the reason is not the correct explanation for the assertion.
Additional information:
The correct explanation is When Millon’s reagent is added to an aqueous solution of protein white precipitate is formed which on heating turns red. Millon’s test is used to detect amino acids containing phenol. All proteins contain tyrosine residue.
Note: When a few drops of reagent are added in the aqueous test solution to be tested, then it is heated gently. If reddish-brown colouration or precipitate appears, it indicates the presence of tyrosine. Tyrosine is present in nearly all proteins. Tyrosine with acidified mercuric sulphate solution produces mercury amino acid complex which is yellow precipitate. When sodium nitrate solution is added in this and heated, the mercury amino acid complex gets converted to red colour mercury phenolate.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




