
Arrange the following compounds in decreasing order of coupling with benzene diazonium chloride.
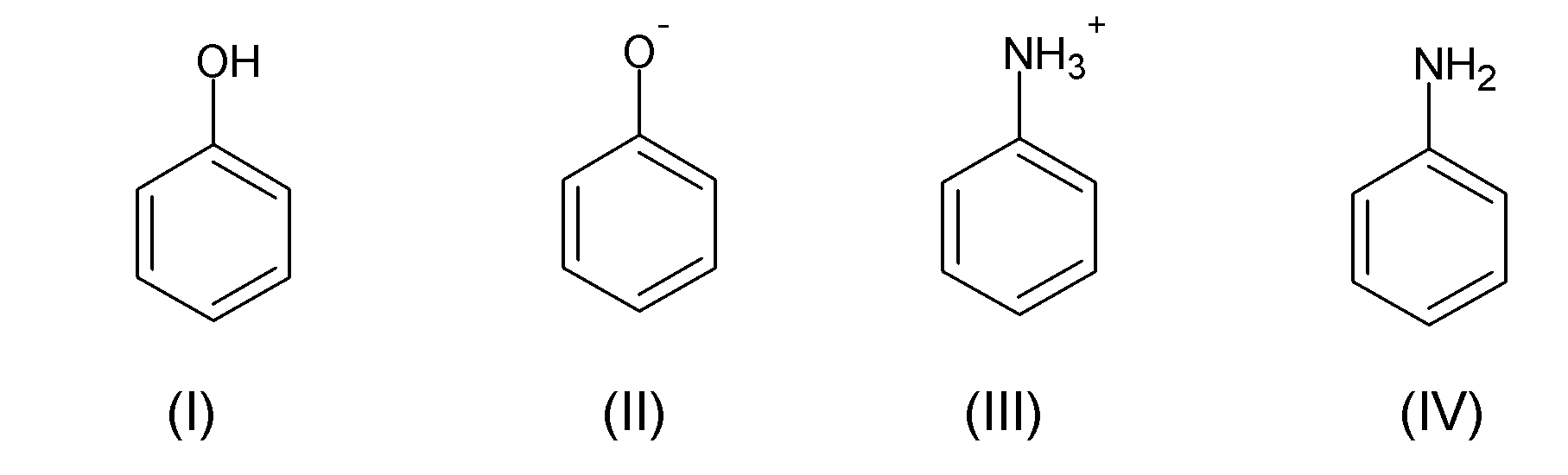
A. IV > I > II > III
B. II > I > IV > III
C. II > IV > I > III
D. II > III > IV > I
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Benzene diazonium chloride couples with highly reactive aromatic compounds containing electron-releasing groups such as $-OH,-N{{H}_{2}}$ etc. Bright-colored azo compounds are found as a product. The rate of coupling depends upon the strength of electron donating groups present in the systems.
Complete step by step solution:
The benzene diazonium chloride or diazonium salts have one diazo group ($-{{N}^{+}}\equiv N:$) and have a formula $ArN_{2}^{+}C{{l}^{-}}$. The structure of benzene diazonium chloride is:
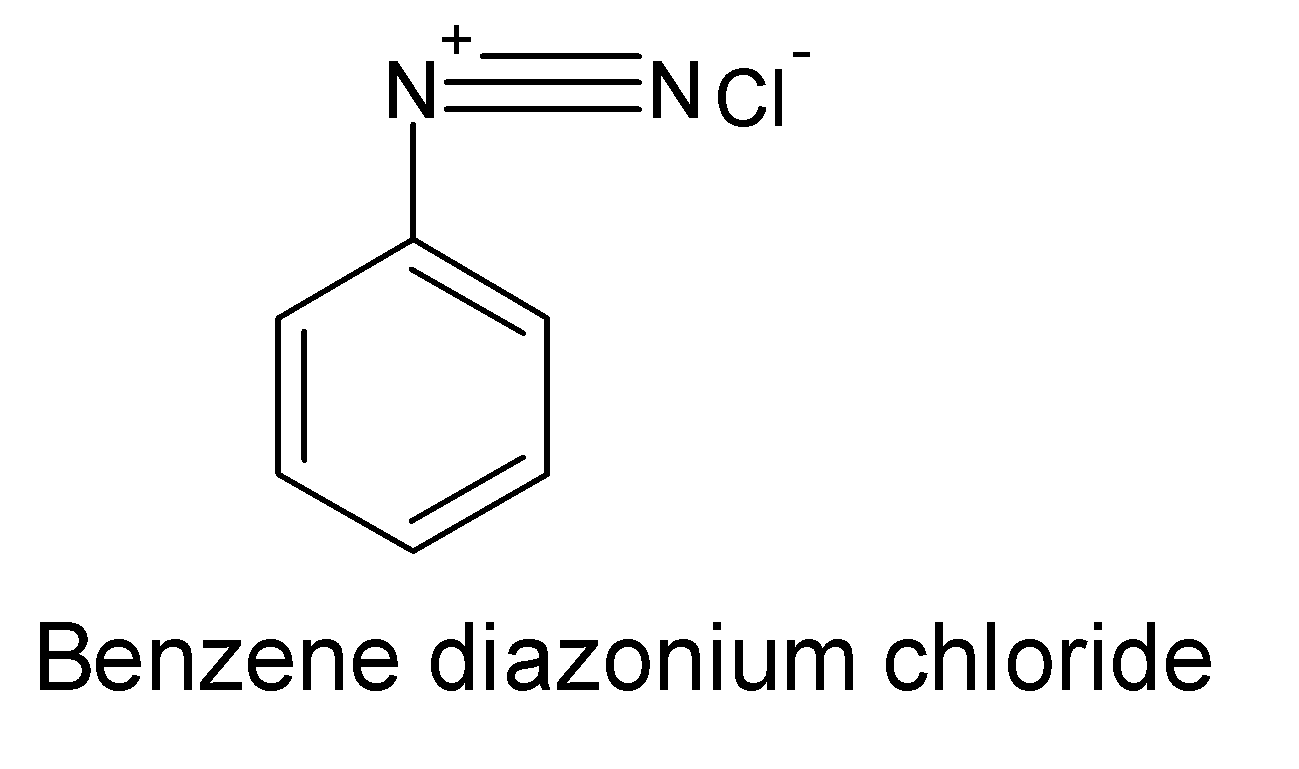
This type of coupling reaction is known as azo coupling. Here diazonium cation with a positive charge on the nitrogen atom acts as an electrophile and electron-rich arene compounds act as a nucleophile. The overall reaction process is an example of an electrophilic substitution reaction.
Consider a general azo-coupling reaction:
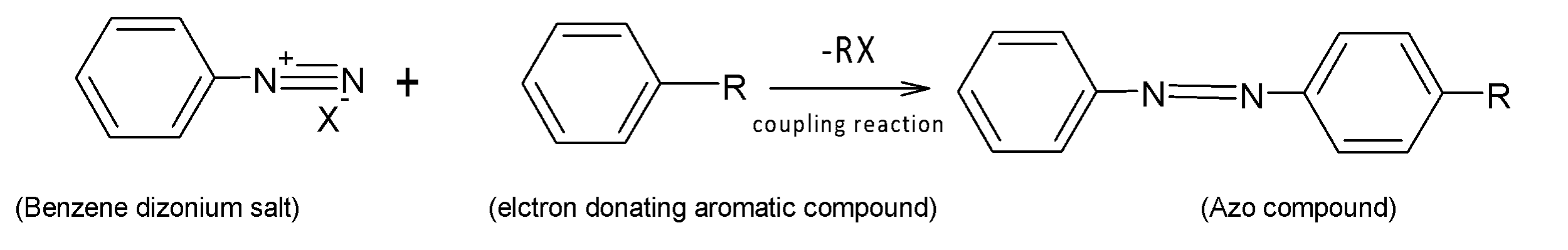
Here R = electron donating group (-OH,$-N{{H}_{3}}$)
X= halogen ion
In the given questions, there are four aromatic compounds with different groups attached to them. To answer the given question, first, we have to see the order of electron-donating ability of the given compounds. Except $-NH_{3}^{+}$, all three ($-OH,-{{O}^{-}}and-N{{H}_{2}}$) are electron-releasing groups and we know that diazonium salts react with electron-rich compounds more effectively. A positive charge on the nitrogen atom increases its electron-withdrawing power and undergoes a coupling reaction with the diazonium ion very slowly.
In compound (II), phenoxide is more reactive than (I)[phenol] and (IV) [aniline] because the electron density is concentrated onto a single atom of oxygen and it is very easy to donate.
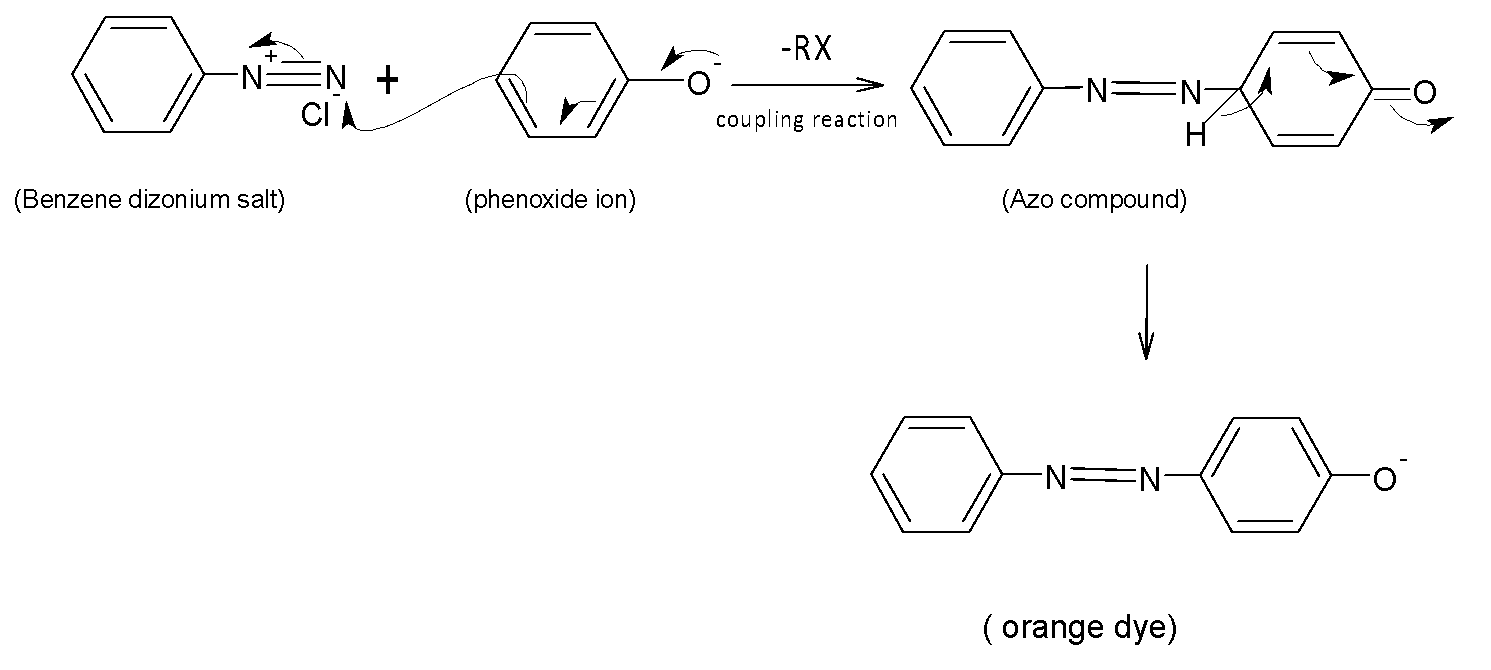
Between phenol and aniline, aniline couples with diazonium salts at a faster rate, since the electronegativity of nitrogen is less than oxygen, and can act as a very good nucleophile in the coupling reaction. Therefore the decreasing order of coupling with diazonium chloride follows the order:
(II)>(IV)>(I)>(III)
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Note: Generally, coupling occurs at para position to electron releasing group. If the para position is blocked then coupling occurs at the ortho position. The presence of the electron-withdrawing group on the diazonium group also facilitates the coupling reaction as it increases the electrophilicity of the diazonium ion.
Complete step by step solution:
The benzene diazonium chloride or diazonium salts have one diazo group ($-{{N}^{+}}\equiv N:$) and have a formula $ArN_{2}^{+}C{{l}^{-}}$. The structure of benzene diazonium chloride is:

This type of coupling reaction is known as azo coupling. Here diazonium cation with a positive charge on the nitrogen atom acts as an electrophile and electron-rich arene compounds act as a nucleophile. The overall reaction process is an example of an electrophilic substitution reaction.
Consider a general azo-coupling reaction:

Here R = electron donating group (-OH,$-N{{H}_{3}}$)
X= halogen ion
In the given questions, there are four aromatic compounds with different groups attached to them. To answer the given question, first, we have to see the order of electron-donating ability of the given compounds. Except $-NH_{3}^{+}$, all three ($-OH,-{{O}^{-}}and-N{{H}_{2}}$) are electron-releasing groups and we know that diazonium salts react with electron-rich compounds more effectively. A positive charge on the nitrogen atom increases its electron-withdrawing power and undergoes a coupling reaction with the diazonium ion very slowly.
In compound (II), phenoxide is more reactive than (I)[phenol] and (IV) [aniline] because the electron density is concentrated onto a single atom of oxygen and it is very easy to donate.

Between phenol and aniline, aniline couples with diazonium salts at a faster rate, since the electronegativity of nitrogen is less than oxygen, and can act as a very good nucleophile in the coupling reaction. Therefore the decreasing order of coupling with diazonium chloride follows the order:
(II)>(IV)>(I)>(III)
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Note: Generally, coupling occurs at para position to electron releasing group. If the para position is blocked then coupling occurs at the ortho position. The presence of the electron-withdrawing group on the diazonium group also facilitates the coupling reaction as it increases the electrophilicity of the diazonium ion.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




