
Aniline is not a major product in one of the following reactions. Identify that reaction.
A. ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{OH + N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\xrightarrow[{300^\circ {\text{C}}}]{{{\text{ZnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}}}$
B. ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{ + ZnPowder}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{alcoholicKOH}}}}$
C. ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Cl + N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{C}}{{\text{u}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}}]{{200^\circ {\text{C}}}}$
D. ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{ + Fe + }}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{HCl}}}}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The reduction of nitro compounds with active metals in alkaline medium gives hydrazobenzene.
The catalytic reduction of nitro compounds in acidic medium is a very convenient method of preparing aromatic primary amines as they cannot be prepared from the corresponding aryl halides on treatment with ammonia.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us study the given reactions one by one.
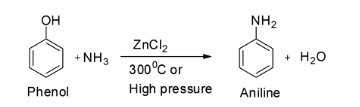
The first reaction is given to be ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{OH + N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\xrightarrow[{300^\circ {\text{C}}}]{{{\text{ZnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}}}$ .
This is a reaction between phenol and ammonia in presence of zinc chloride.
When a mixture of the vapours of phenol and ammonia are passed over zinc chloride, aniline is formed. Since phenols are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions, so, severe conditions like high pressure are usually employed. Thus, aniline can be prepared by the action of ammonia on phenol. So the major product of the given reaction is aniline and hence option A is not correct.
The next reaction is given to be ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{ + ZnPowder}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{alcoholicKOH}}}}$ .
This is a reaction between nitrobenzene and zinc powder in presence of alcoholic potassium hydroxide.
It is known that the reduction of nitrobenzene with zinc in presence of alcoholic potassium hydroxide gives hydrazobenzene.
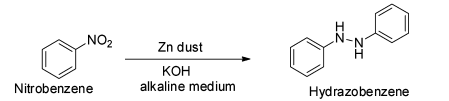
Thus, the reduction of nitrobenzene with zinc in alkaline medium produces hydrazobenzene. So, the major product of this reaction is not aniline and so the option B is correct.
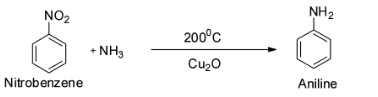
The next reaction is ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Cl + N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{C}}{{\text{u}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}}]{{200^\circ {\text{C}}}}$ .
This is a reaction between chlorobenzene with ammonia in presence of cuprous oxide. This reaction gives aniline as the major product and so C is wrong.
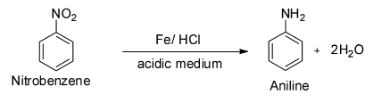
The last reaction is given to be ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{ + Fe + }}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{HCl}}}}$ .
This is a reaction between nitrobenzene and iron in presence of hydrochloric acid.
It is known that the catalytic reduction of nitro compounds with an active metal like iron, tin, zinc etc. in acidic medium like concentrated hydrochloric acid gives aromatic primary amines.
Thus, the given reaction will give aniline as the major product and so option D is incorrect.
Note:
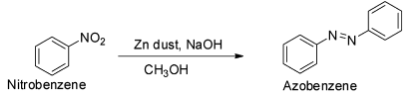
The reduction of nitrobenzene with zinc and methanolic sodium hydroxide gives azobenzene.
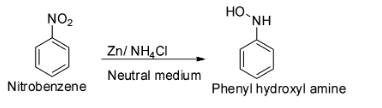
The reduction of nitrobenzene with zinc dust and aqueous ammonium chloride (neutral medium) gives phenyl hydroxylamine.
The catalytic reduction of nitro compounds in acidic medium is a very convenient method of preparing aromatic primary amines as they cannot be prepared from the corresponding aryl halides on treatment with ammonia.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us study the given reactions one by one.
The first reaction is given to be ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{OH + N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\xrightarrow[{300^\circ {\text{C}}}]{{{\text{ZnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}}}$ .
This is a reaction between phenol and ammonia in presence of zinc chloride.
When a mixture of the vapours of phenol and ammonia are passed over zinc chloride, aniline is formed. Since phenols are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions, so, severe conditions like high pressure are usually employed. Thus, aniline can be prepared by the action of ammonia on phenol. So the major product of the given reaction is aniline and hence option A is not correct.

The next reaction is given to be ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{ + ZnPowder}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{alcoholicKOH}}}}$ .
This is a reaction between nitrobenzene and zinc powder in presence of alcoholic potassium hydroxide.
It is known that the reduction of nitrobenzene with zinc in presence of alcoholic potassium hydroxide gives hydrazobenzene.

Thus, the reduction of nitrobenzene with zinc in alkaline medium produces hydrazobenzene. So, the major product of this reaction is not aniline and so the option B is correct.
The next reaction is ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Cl + N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{C}}{{\text{u}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}}]{{200^\circ {\text{C}}}}$ .
This is a reaction between chlorobenzene with ammonia in presence of cuprous oxide. This reaction gives aniline as the major product and so C is wrong.

The last reaction is given to be ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{ + Fe + }}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{HCl}}}}$ .
This is a reaction between nitrobenzene and iron in presence of hydrochloric acid.
It is known that the catalytic reduction of nitro compounds with an active metal like iron, tin, zinc etc. in acidic medium like concentrated hydrochloric acid gives aromatic primary amines.
Thus, the given reaction will give aniline as the major product and so option D is incorrect.

Note:
The reduction of nitrobenzene with zinc and methanolic sodium hydroxide gives azobenzene.

The reduction of nitrobenzene with zinc dust and aqueous ammonium chloride (neutral medium) gives phenyl hydroxylamine.

Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Understanding Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions

AssertionIn electrolytic refining of metal impure metal class 12 chemistry JEE_Main

JEE Main Syllabus 2026: Download Detailed Subject-wise PDF

Other Pages
Alcohol Phenol and Ether Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Solutions Hindi Medium (2025-26)

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Set 1 56/2/1 2025: Question Paper, Answers & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Set 3 2025 with Answers

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students




