
Aniline in a set of reactions yielded a product D?
The product D is:
A.\[{C_6}{H_5}NHOH\]
B.\[{C_6}{H_5}NHC{H_2}C{H_3}\]
C.\[{C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}N{H_2}\]
D.\[{C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}OH\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Aniline is an aromatic amine having a primary aromatic amine functional group. The reaction here is an example of a coupling reaction where carbon couples with carbon to form a C-C single bond.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In the first step, \[\left( {NaN{O_2} + HCl} \right)\]reacts with each other to form nitrous acid\[\left( {HONO} \right)\], which reacts with aniline to give a diazotization reaction and form benzene diazonium chloride salt product (A). This product (A) further reacts with copper cyanide \[\left( {CuCN} \right)\]to give a Sandmayer’s reaction and forms cyano benzene or benzonitrile product (B). Then product (B) reacts with hydrogen gas in presence of nickel catalyst to give benzylamine (C) by reduction, which further reacts with nitrous acid \[\left( {HONO} \right)\]which is an oxidising agent and forms benzyl alcohol, the final product (D). The reaction mechanism is shown below:
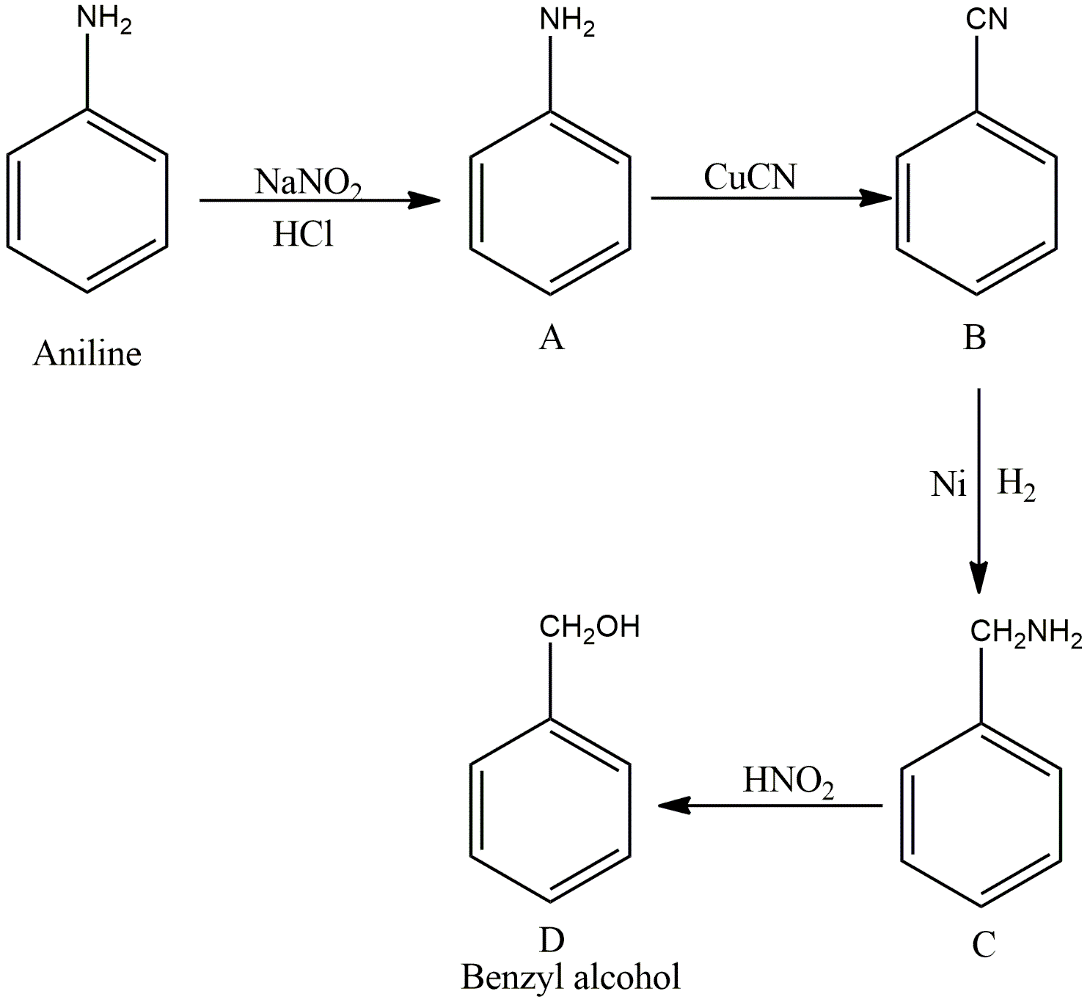
Image:Reaction with aniline to give benzyl alcohol
So, option D is correct.
Additional Information:Aromatic diazonium chloride salts formed by the reaction of aniline and nitrous acid are electrophiles and undergo electrophilic substitution reaction i.e., electron-loving compounds attack them. In this way, it works in coupling reactions.
In the reaction of copper cyanide with aromatic diazonium chloride salt, partial positive charges on Cu forms a bond with negative charges on chloride ion of salts and form \[CuCl\]and \[{N_2}\]releases as nitrogen gas and partial negative charges on cyanide attack the aromatic ring to form cyanobenzene.
Note: Anilines are also known as phenyl benzene or aminobenzene. Nitrous acid is a weak acid used in the preparation of diazonium salts. The reaction asked in this question is an azo coupling reaction used to form C-C bonds.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In the first step, \[\left( {NaN{O_2} + HCl} \right)\]reacts with each other to form nitrous acid\[\left( {HONO} \right)\], which reacts with aniline to give a diazotization reaction and form benzene diazonium chloride salt product (A). This product (A) further reacts with copper cyanide \[\left( {CuCN} \right)\]to give a Sandmayer’s reaction and forms cyano benzene or benzonitrile product (B). Then product (B) reacts with hydrogen gas in presence of nickel catalyst to give benzylamine (C) by reduction, which further reacts with nitrous acid \[\left( {HONO} \right)\]which is an oxidising agent and forms benzyl alcohol, the final product (D). The reaction mechanism is shown below:

Image:Reaction with aniline to give benzyl alcohol
So, option D is correct.
Additional Information:Aromatic diazonium chloride salts formed by the reaction of aniline and nitrous acid are electrophiles and undergo electrophilic substitution reaction i.e., electron-loving compounds attack them. In this way, it works in coupling reactions.
In the reaction of copper cyanide with aromatic diazonium chloride salt, partial positive charges on Cu forms a bond with negative charges on chloride ion of salts and form \[CuCl\]and \[{N_2}\]releases as nitrogen gas and partial negative charges on cyanide attack the aromatic ring to form cyanobenzene.
Note: Anilines are also known as phenyl benzene or aminobenzene. Nitrous acid is a weak acid used in the preparation of diazonium salts. The reaction asked in this question is an azo coupling reaction used to form C-C bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




