
Among the following, the weakest base is:-
A. \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\]
B. \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{NHC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
C. \[{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{NC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\]
D. \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{NHCHO}}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Amines are significant organic species created by the substitution of one or more hydrogen atoms with alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in these compounds contains an unshared pair of electrons.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The options for the given questions are all amine compounds.
We know that Lewis's concept stated that "a chemical species is called a base if it can donate a pair of electrons to another chemical species."
We know that in amines, the nitrogen atom contains an unshared pair of electrons
Hence, amines are basic.
The basic nature of amines is attributed to their structure.
If there is the availability of a lone pair of amines it will donate it to another chemical species.
Among the given options, the amine in which the donation of a lone pair is difficult will be the weakest base.
A. \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\]
This compound is benzylamine.
In this compound, a benzyl group is attached to the amino group.
In this compound, an inductive effect comes into play.
Here the amine is attached to an electron-withdrawing group. This electron-withdrawing group holds the electron density away from the compound.
So, the availability of the lone pair on the nitrogen of the amino group is less.
This compound will not be able to donate the lone pair of electrons. So, it is a weak base.
B. \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{NHC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
In this compound, a benzyl group and a methyl are attached to the amino group.
Also in this compound, the inductive effect acts on the compound.
Here the amine is connected to an electron-withdrawing group. This electron-withdrawing group holds the electron density away from the compound.
The amino group is also attached to the methyl group which is an electron donating group.
So, the lone pair of electrons is available for donation.
Hence, this compound is more basic than benzylamine.
C. \[{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{NC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\]
In this compound, a nitro group is attached to the amino group.
In this case, also, the inductive effect acts on the compound.
We know that a nitro group is a withdrawing group. This group withdraws the electron density away from the compound.
So, the electron pair is not available for donation.
So, this is a weak base.
D. \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{NHCHO}}\]
In this compound, a carboxyl group is attached to the amino group.
The resonance effect acts on this compound.
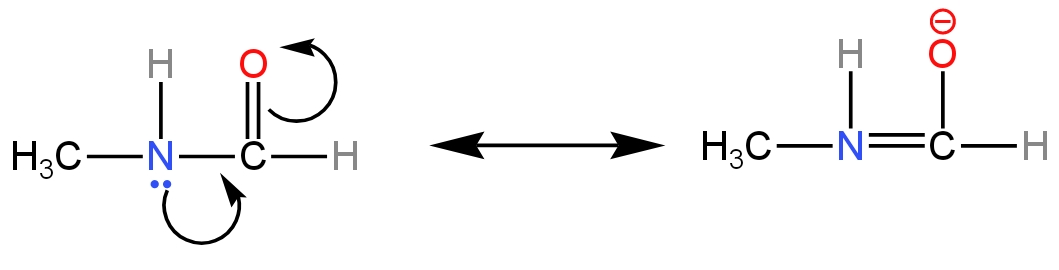
Image: Resonance effect
So, the availability of the lone pair of electrons is less.
So, this compound is also a weak base.
We know that the resonance effect is much stronger than the inductive effect.
So, this compound is the weakest base.
So, option D is correct.
Note: Dimethyl amine is more basic than methyl amine and ammonia as the cation formed by Dimethyl amine is most stable. Two methyl groups present help in positive charge delocalization. There is one methyl group present in methyl amine due to which its cation is stable but not as stable as in the case of ethyl amine. Ammonia is the least stable as it has no presence of the methyl group.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The options for the given questions are all amine compounds.
We know that Lewis's concept stated that "a chemical species is called a base if it can donate a pair of electrons to another chemical species."
We know that in amines, the nitrogen atom contains an unshared pair of electrons
Hence, amines are basic.
The basic nature of amines is attributed to their structure.
If there is the availability of a lone pair of amines it will donate it to another chemical species.
Among the given options, the amine in which the donation of a lone pair is difficult will be the weakest base.
A. \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\]
This compound is benzylamine.
In this compound, a benzyl group is attached to the amino group.
In this compound, an inductive effect comes into play.
Here the amine is attached to an electron-withdrawing group. This electron-withdrawing group holds the electron density away from the compound.
So, the availability of the lone pair on the nitrogen of the amino group is less.
This compound will not be able to donate the lone pair of electrons. So, it is a weak base.
B. \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{NHC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
In this compound, a benzyl group and a methyl are attached to the amino group.
Also in this compound, the inductive effect acts on the compound.
Here the amine is connected to an electron-withdrawing group. This electron-withdrawing group holds the electron density away from the compound.
The amino group is also attached to the methyl group which is an electron donating group.
So, the lone pair of electrons is available for donation.
Hence, this compound is more basic than benzylamine.
C. \[{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{NC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\]
In this compound, a nitro group is attached to the amino group.
In this case, also, the inductive effect acts on the compound.
We know that a nitro group is a withdrawing group. This group withdraws the electron density away from the compound.
So, the electron pair is not available for donation.
So, this is a weak base.
D. \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{NHCHO}}\]
In this compound, a carboxyl group is attached to the amino group.
The resonance effect acts on this compound.

Image: Resonance effect
So, the availability of the lone pair of electrons is less.
So, this compound is also a weak base.
We know that the resonance effect is much stronger than the inductive effect.
So, this compound is the weakest base.
So, option D is correct.
Note: Dimethyl amine is more basic than methyl amine and ammonia as the cation formed by Dimethyl amine is most stable. Two methyl groups present help in positive charge delocalization. There is one methyl group present in methyl amine due to which its cation is stable but not as stable as in the case of ethyl amine. Ammonia is the least stable as it has no presence of the methyl group.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




