
What is the action of the following reagent on toluene?
\[Cr{O_2}C{l_2}\] in \[C{s_2}\]
Answer
241.2k+ views
Hint: In the question stated above, the reaction that takes place is known as Etard’s reaction. After the formation of the chromium complex, \[{H_3}{O^ + }\] results in the formation of benzaldehyde. There is no formation of benzoic acid in the reaction that takes place.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The Etard reaction was named after a French chemist named Alexandre Leon Etard. The solvent that is used in this reaction is carbon disulfide.
Etard reaction is a chemical reaction in which there is direct oxidation of an aromatic compound or a methyl group that is bound to a heterocyclic compound into an aldehyde with the use of chromyl chloride. Etard reaction is an oxidation reaction.
This reaction takes place with an allylic-alkene hydrogen reaction in the presence of chromyl chloride resulting in the formation of a precipitate known as the Etard complex. After the formation of the Etard complex, a decomposition reaction takes place with the help of a reducing agent. This prevents the oxidation of the Etard complex and the formation of carboxylic acid.
This type of reducing environment which helps in the prevention of the formation of carboxylic acid can be achieved by using a highly saturated aqueous solution of carbon disulfide. Solvents such as carbon tetrachloride and chloroform can also be used.
Purification of Etard’s complex before its decomposition can help in obtaining an aldehyde of very high purity. This reaction can take place in the time frame of a few days to several weeks and the product that is yielded is of very high quality. The reaction occurs as follows:
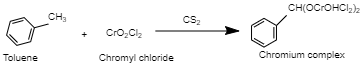
Note: Etard’s reaction is a very easy method that helps in the oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde. This method also helps to add almond flavour to the food and is used in the manufacturing of various cosmetic products. This has proven to be a very valuable chemical.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The Etard reaction was named after a French chemist named Alexandre Leon Etard. The solvent that is used in this reaction is carbon disulfide.
Etard reaction is a chemical reaction in which there is direct oxidation of an aromatic compound or a methyl group that is bound to a heterocyclic compound into an aldehyde with the use of chromyl chloride. Etard reaction is an oxidation reaction.
This reaction takes place with an allylic-alkene hydrogen reaction in the presence of chromyl chloride resulting in the formation of a precipitate known as the Etard complex. After the formation of the Etard complex, a decomposition reaction takes place with the help of a reducing agent. This prevents the oxidation of the Etard complex and the formation of carboxylic acid.
This type of reducing environment which helps in the prevention of the formation of carboxylic acid can be achieved by using a highly saturated aqueous solution of carbon disulfide. Solvents such as carbon tetrachloride and chloroform can also be used.
Purification of Etard’s complex before its decomposition can help in obtaining an aldehyde of very high purity. This reaction can take place in the time frame of a few days to several weeks and the product that is yielded is of very high quality. The reaction occurs as follows:

Note: Etard’s reaction is a very easy method that helps in the oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde. This method also helps to add almond flavour to the food and is used in the manufacturing of various cosmetic products. This has proven to be a very valuable chemical.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More




