
When acetamide is treated with $HN{{O}_{2}}$, gas evolved is
A. ${{H}_{2}}$
B. ${{O}_{2}}$
C. ${{N}_{2}}$
D. $C{{H}_{4}}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Amides undergo hydrolysis under acidic or basic medium. An indirect process of hydrolysis is the reaction with nitrous acid $HN{{O}_{2}}$. Primary amides react with $HN{{O}_{2}}$ and are converted to carboxylic acid but secondary amides give N-nitroso compounds.
Complete step by step solution:
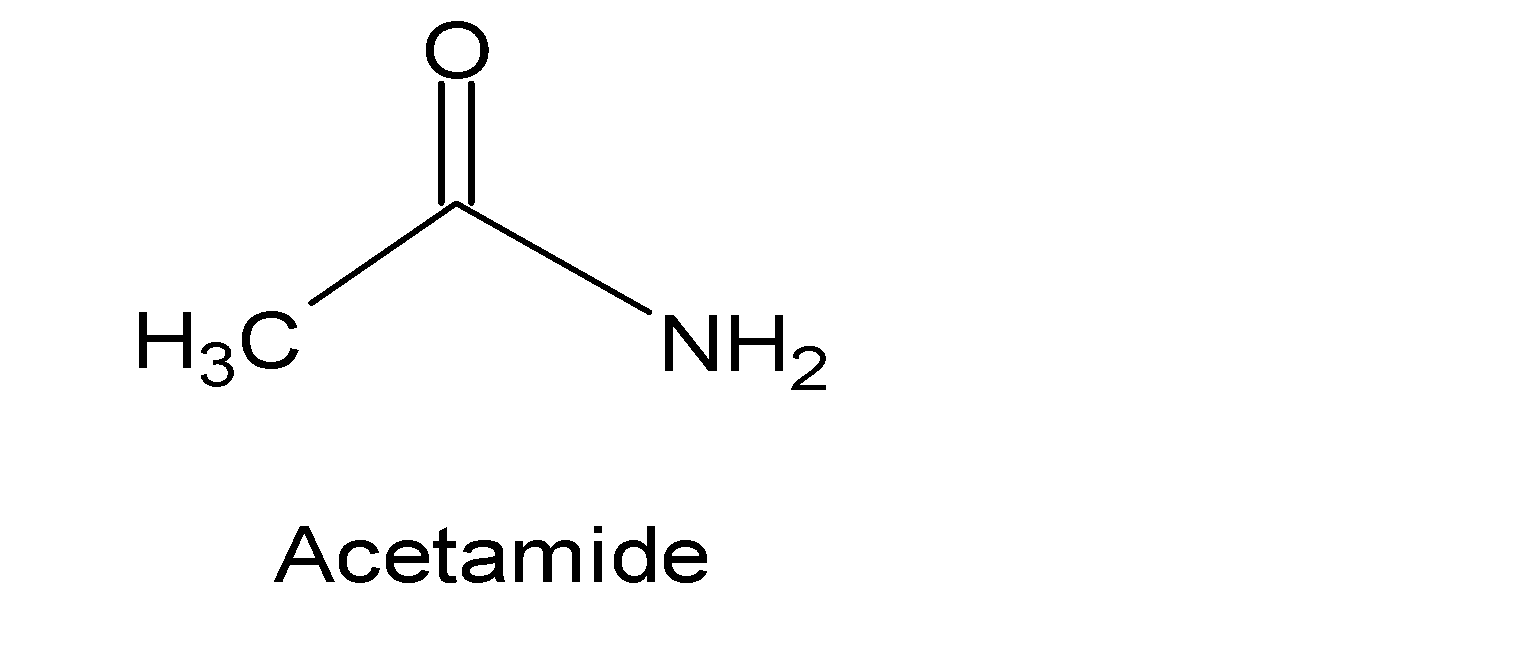
The products of amide hydrolysis depend upon whether the whole process occurs under an acidic or basic medium. Because under an acidic medium it forms carboxylic acid and in the basic condition carboxylic acid salts are formed. Acetamide is a kind of primary amide that reacts with nitrous acid under acidic conditions to give acetic acid, water, and nitrogen gas releases. The structure of acetamide is:
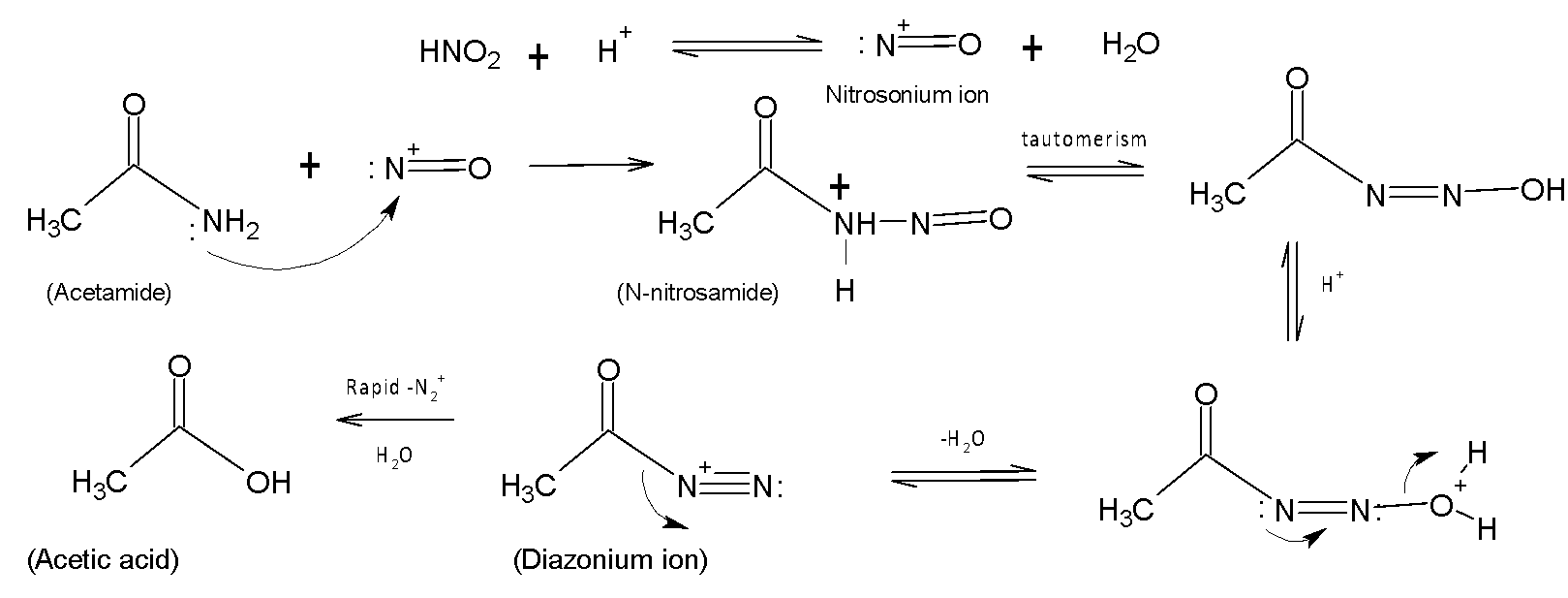
The main reactive group of this particular chemical reaction is the nitrosonium ion. The lone pair of nitrogen atoms attack the nitrosonium ion and form an intermediate N-nitrosamine. This intermediate undergoes proton shift by a sequence of keto-enol tautomerism to form diazoic acid followed by decompositions to diazonium ions in an acidic medium. Finally, diazonium salts decompose to trivalent gaseous nitrogen. An acyl cation$C{{H}_{3}}C{{O}^{+}}$is formed from the substrate acetamide. This carbocation further reacts with water to form acetic acid. The following mechanism gives us a brief idea of how the reaction proceeds.
Therefore, acetamide reacts $HN{{O}_{2}}$to form acetic acid, and water and releases nitrogen, ${{N}_{2}}$and gas.
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Note: Amide hydrolysis has many applications in chemistry. Under biological conditions, peptide hydrolysis of protein occurs which is nothing but hydrolysis of an amide. They can also serve as a solvent and as a drug intermediate in the manufacture of (ampicillin, cephalexin, cephradine, etc) in many organic and inorganic synthesis.
Complete step by step solution:
The products of amide hydrolysis depend upon whether the whole process occurs under an acidic or basic medium. Because under an acidic medium it forms carboxylic acid and in the basic condition carboxylic acid salts are formed. Acetamide is a kind of primary amide that reacts with nitrous acid under acidic conditions to give acetic acid, water, and nitrogen gas releases. The structure of acetamide is:

The main reactive group of this particular chemical reaction is the nitrosonium ion. The lone pair of nitrogen atoms attack the nitrosonium ion and form an intermediate N-nitrosamine. This intermediate undergoes proton shift by a sequence of keto-enol tautomerism to form diazoic acid followed by decompositions to diazonium ions in an acidic medium. Finally, diazonium salts decompose to trivalent gaseous nitrogen. An acyl cation$C{{H}_{3}}C{{O}^{+}}$is formed from the substrate acetamide. This carbocation further reacts with water to form acetic acid. The following mechanism gives us a brief idea of how the reaction proceeds.

Therefore, acetamide reacts $HN{{O}_{2}}$to form acetic acid, and water and releases nitrogen, ${{N}_{2}}$and gas.
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Note: Amide hydrolysis has many applications in chemistry. Under biological conditions, peptide hydrolysis of protein occurs which is nothing but hydrolysis of an amide. They can also serve as a solvent and as a drug intermediate in the manufacture of (ampicillin, cephalexin, cephradine, etc) in many organic and inorganic synthesis.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




