
A rolling body is kept on a plank B. There is sufficient friction between A and B and no friction between B and the inclined plane. Then body
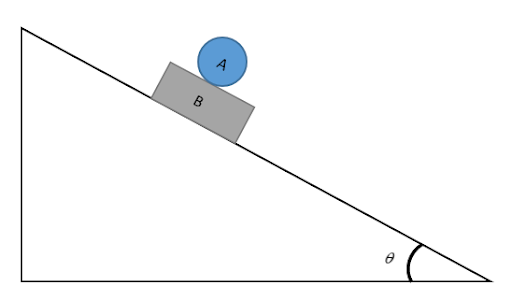
A. A Rolls
B. A doesn’t experience any friction
C. A and B have equal acceleration and unequal velocities.
D. A rolls depending upon the angle of inclination
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:when a body is moving under the influence on only gravitational force then the motion is said to be free fall. The body is at equilibrium along the direction perpendicular to the surface in contact.
Formula used:
\[{F_{net}} = ma\]
here \[{F_{net}}\] is the net force acting on the body of mass m and a is the acceleration produced.
Complete step by step solution:
As there is no friction between body B and the inclined surface, there will be no resistive force acting on it to oppose the motion. Using vector resolution for the weight of the plank B, we get the force on the plank B as,
\[{F_{B\parallel }} = {m_B}g\sin \theta \]
If acceleration of B on the inclined surface is \[{a_B}\] then using Newton’s 2nd law of motion,
\[{F_{B\parallel }} = m{a_B}\]
\[\Rightarrow {a_B} = \dfrac{{{m_B}g\sin \theta }}{{{m_B}}} = g\sin \theta \]
Similarly, for rolling sphere A, using vector resolution for the weight of the sphere A, we get the force on the sphere as,
\[{F_{A\parallel }} = m{a_A}\]
\[\Rightarrow {a_A} = \dfrac{{{m_A}g\sin \theta }}{{{m_A}}} = g\sin \theta \]
The magnitude of plank B and the sphere A along the inclined surface is same and also the direction is down the inclined surface. Hence, the relative acceleration of the sphere with respect to the plank is zero.
Using Newton’s 2nd law of motion,
\[{F_{net}} = ma\]
The force between the surfaces of the sphere and the plank is zero as the relative acceleration is zero. As we know that the frictional force is the resistive force which opposes the relative motion between the surfaces in contact, so there will be no friction between the surfaces of the sphere and the plank.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: If the relative acceleration between the sphere and the plank was non-zero then frictional force will act on the sphere which will try to rotate the sphere and hence it may roll or slip based on the relative acceleration between A and B.
Formula used:
\[{F_{net}} = ma\]
here \[{F_{net}}\] is the net force acting on the body of mass m and a is the acceleration produced.
Complete step by step solution:
As there is no friction between body B and the inclined surface, there will be no resistive force acting on it to oppose the motion. Using vector resolution for the weight of the plank B, we get the force on the plank B as,
\[{F_{B\parallel }} = {m_B}g\sin \theta \]
If acceleration of B on the inclined surface is \[{a_B}\] then using Newton’s 2nd law of motion,
\[{F_{B\parallel }} = m{a_B}\]
\[\Rightarrow {a_B} = \dfrac{{{m_B}g\sin \theta }}{{{m_B}}} = g\sin \theta \]
Similarly, for rolling sphere A, using vector resolution for the weight of the sphere A, we get the force on the sphere as,
\[{F_{A\parallel }} = m{a_A}\]
\[\Rightarrow {a_A} = \dfrac{{{m_A}g\sin \theta }}{{{m_A}}} = g\sin \theta \]
The magnitude of plank B and the sphere A along the inclined surface is same and also the direction is down the inclined surface. Hence, the relative acceleration of the sphere with respect to the plank is zero.
Using Newton’s 2nd law of motion,
\[{F_{net}} = ma\]
The force between the surfaces of the sphere and the plank is zero as the relative acceleration is zero. As we know that the frictional force is the resistive force which opposes the relative motion between the surfaces in contact, so there will be no friction between the surfaces of the sphere and the plank.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: If the relative acceleration between the sphere and the plank was non-zero then frictional force will act on the sphere which will try to rotate the sphere and hence it may roll or slip based on the relative acceleration between A and B.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




