
A plot of log(a-x) against time ’t’ is a straight line. This indicates that the reaction is of:
(A) Zero order
(B) First order
(C) Second order
(D) Third order
Answer
525.2k+ views
Hint: Reaction in which the reaction rate is linearly dependent on the concentration of only one reactant is called a first order reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that for a first order reaction,
\[{\text{ - }}\dfrac{{{\text{dC}}}}{{{\text{dt}}}}{\text{ = k}}{\text{.C}}\]
On integrating we get, \[\int\limits_{{{\text{C}}_{\text{0}}}}^{\text{C}} {\dfrac{{{\text{dC}}}}{{\text{C}}}} {\text{ = - k }}\int\limits_{\text{0}}^{\text{t}} {{\text{dt}}} \]
Where, \[{{\text{C}}_0}\] is the concentration of the reactant at time t = 0 and C is the concentration of the reactant at time t = t.
So, we get, \[{\text{log C - log}}{{\text{C}}_0}{\text{ = - k}}{\text{. t}}\]
\[{\text{log C = - k}}{\text{.t + log }}{{\text{C}}_0}\]
But, \[{\text{log }}{{\text{C}}_0}\] is the initial concentration of the reactant which will be constant. So, if \[{{\text{C}}_0}\] i.e. initial concentration of the reactant is considered to be ‘a’ then C which is concentration at time t will be (a-x).
So, we write it as \[{\text{log (a - x) = - k}}{\text{.t + log a}}\]. This equation is of the form \[{\text{y = mx + c}}\].
Thus, graph of log(a-x) against time ’t’ will look like –
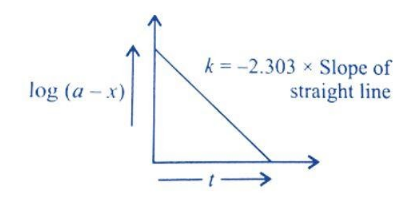
Hence, option B is correct.
Additional information:
The power dependence of rate on the concentration of all reactants is called as order of the reaction. When the rate of reaction depends on concentration of only one reactant, it is called as a first order reaction.
The rate of reaction is independent of the concentration of the reactants, the reaction is said to be zero order reaction.
When the rate of a reaction depends either on the concentration of one reactant squared or from the concentration of two separate reactants, the reaction is called a second order reaction.
Note: A plot of log(a-x) against time ’t’ is a straight line is a very peculiar feature of first order reactions only. Hence, the answer is first order reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that for a first order reaction,
\[{\text{ - }}\dfrac{{{\text{dC}}}}{{{\text{dt}}}}{\text{ = k}}{\text{.C}}\]
On integrating we get, \[\int\limits_{{{\text{C}}_{\text{0}}}}^{\text{C}} {\dfrac{{{\text{dC}}}}{{\text{C}}}} {\text{ = - k }}\int\limits_{\text{0}}^{\text{t}} {{\text{dt}}} \]
Where, \[{{\text{C}}_0}\] is the concentration of the reactant at time t = 0 and C is the concentration of the reactant at time t = t.
So, we get, \[{\text{log C - log}}{{\text{C}}_0}{\text{ = - k}}{\text{. t}}\]
\[{\text{log C = - k}}{\text{.t + log }}{{\text{C}}_0}\]
But, \[{\text{log }}{{\text{C}}_0}\] is the initial concentration of the reactant which will be constant. So, if \[{{\text{C}}_0}\] i.e. initial concentration of the reactant is considered to be ‘a’ then C which is concentration at time t will be (a-x).
So, we write it as \[{\text{log (a - x) = - k}}{\text{.t + log a}}\]. This equation is of the form \[{\text{y = mx + c}}\].
Thus, graph of log(a-x) against time ’t’ will look like –

Hence, option B is correct.
Additional information:
The power dependence of rate on the concentration of all reactants is called as order of the reaction. When the rate of reaction depends on concentration of only one reactant, it is called as a first order reaction.
The rate of reaction is independent of the concentration of the reactants, the reaction is said to be zero order reaction.
When the rate of a reaction depends either on the concentration of one reactant squared or from the concentration of two separate reactants, the reaction is called a second order reaction.
Note: A plot of log(a-x) against time ’t’ is a straight line is a very peculiar feature of first order reactions only. Hence, the answer is first order reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




