




Top Seafood Types and Their Unique Nutritional Benefits
"Seafood" is any aquatic animal that can be consumed by humans. It is one of the important source of nutrients.
Since ancient times, people have eaten seafood all across the world. They are abundant in minerals, healthy fats, and lean protein.
All bony fish species, as well as the more primitive sharks, skates, rays, sawfish, sturgeons, and lampreys, are considered to be seafood, along with crustaceans like lobster, crab, shrimp, and crayfish, mollusks like clams, oysters, shellfish cockles, mussels, periwinkles, whelks, snails, abalones, scallops, and limpets, as well as edible jellyfish
The salmon, herring, cod, flatfish (halibut, sole, and turbot), redfish (ocean perch), jack mackerel, tuna, mackerel, and sardine species are the most important ocean fish for commerce.
Carp, eel, trout, whitefish, pike, pike perch, and catfish are the main species of freshwater fish.
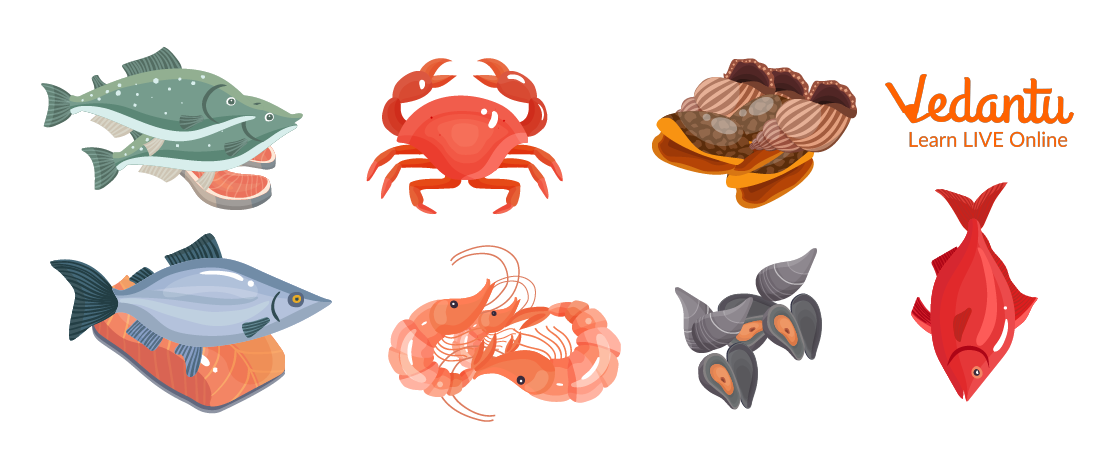

Different Types of Seafood
Fish
Fish is highly perishable and degrades quickly. Therefore, the bulk of the catch has been dried, smoked, salted, pickled, or fermented when not consumed immediately.
Fish can be prepared whole, in steak, fillet, or chunk form.
The majority of mollusks and crustaceans are typically cooked whole and alive.
To soften the tough flesh, larger, tougher mollusks are ground, diced, or pounded. A lot of seafood is consumed raw, either entirely or only slightly prepared.
Fish is the Most Consumed Aquatic Food
Other Seafood
A variety of aquatic items, such as octopus, fish, shrimp, lobsters, mussels, scallops, oysters, and more, are chilling on ice.
Foods like shrimp, salmon, and lobster are frequently referred to as "seafood."
Salmonids (salmon, trout), carps, cichlids (tilapia), cod (cod, haddock, pollock), tiny pelagic fish (herring, sardines, anchovies), medium pelagic fish (bonito, mahi-mahi), large pelagic fish (tuna, swordfish), and demersal fish are all examples of finfish (flounder)
Crustaceans, such as lobster, crab, shrimp, krill, and prawns
Cephalopods—squid and octopus
Clams, cockles, sea snails, mussels, and scallops are mollusks.
Aquatic vegetation: water spinach.
Algae—seaweed
Other aquatic creatures, including mammals, insects, and sea cucumbers
Aquatic foods are derived from interior waters like lakes, rivers, and wetlands; coastal regions like estuaries, mangroves, or near-shore; and marine or ocean waters. They can be farmed or wild-caught.
Aquatic Seafood
Many different aquatic species that live in both saltwater and freshwater are usually referred to as "shellfish."
Additionally, shellfish have a hard shell that is frequently formed of chitin. Mollusks, or creatures like clams and limpets, are found in shellfish, and they filter their food from the environment.
Animals like lobsters and crabs are not considered to be shellfish.

Shellfish
Since "shellfish" is protected by a tough outer shell, no one taxonomic group may claim ownership of the name. The process by which utterly unrelated organisms might gain similar traits because having them is extraordinarily valuable in the environment they live in is known as "convergent evolution."
Shellfish List
Shellfish occur in a wide range of sizes and forms, from the very familiar to the very foreign.
Some have claws that can punch so hard that the water around them boils, while others have eyes that can perceive wavelengths of light well outside the human visible spectrum.
Some have pincers that can crush bones. Some are terribly dangerous, while others are frequently consumed as a delicacy.
But all of them are fascinating; here are a few names:
Brown Crab, American Lobster, Mantis Shrimp, Butter Clam, Sea Urchin, Oyster, Mussel, Abalone, Crawfish, Cockle, Prawn, Shrimp, crab are, and whelk are just a few of the seafood options.
Seafood Production
The production of food from the sea, which currently makes up 17% of the world's total production of edible meat, comes from both wild fisheries and animals raised in the water.
Seafood is well positioned to contribute to global food and nutrition security because it provides bioavailable micronutrients and critical fatty acids that are difficult to get in land-based diets, in addition to protein.
increasing the environmentally and economically viable production of seafood to meet world food needs.
Summary
In the coming decades, there will be a significant increase in the demand for nutrient-dense foods due to human population expansion, rising incomes, and preference changes.
Many nations still struggle with malnutrition and hunger, and estimates of population growth and income levels through 2050 imply that more than 500 megatonnes (Mt) of meat will be required annually for human consumption.
Food crops grown on land are difficult to scale up because of diminishing yield rates and competition for limited water and land resources.
Oysters are a very nutritious food source that is rich in vitamins C, D, and B. Additionally, they are a good source of phosphorus, iron, and calcium.
The majority of shellfish are a good source of calcium and protein.
FAQs on Sea Food Names: Essential Guide for Students
1. Can oysters and liquor be taken together?
Oysters that are raw- frequently enjoyed with drinks. It is a fatal combination. While alcohol intake might potentially harm the liver, it increases the drinker's susceptibility to a harmful bacterium found in shellfish.
Oysters and liquor are not advised to be taken together. Beverages having a high alcohol percentage are avoided; powerful liquor doesn’t help oysters digest. It is advised that consume beer and wine with oysters. Some of the traditional beverages to serve with oysters include champagne and stout.
2. How long does seafood remain fresh?
Raw fish and shellfish should be kept in the refrigerator. The shelf life of shellfish is influenced by two factors: product handling and storage temperature. Only 1 or 2 days before cooking or freezing it should be consumed.
Seafood should be refrigerated for three to four days after cooking. Any frozen fish or shellfish will remain safe eternally, but with prolonged storage, the flavor and texture will deteriorate. With a higher storage temperature, fish will quickly lose quality.















