Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 1 Summary Notes PDF Download
FAQs on Introduction to Accounting Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What is the core concept of accounting that I should remember for a quick revision?
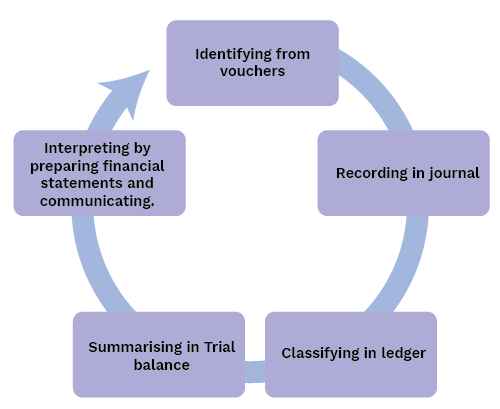
For a quick recap, remember that accounting is a systematic process of identifying, recording, classifying, summarising, interpreting, and communicating financial information. Its main purpose is to provide clear and useful data about a business's financial performance and position to various stakeholders.
2. What are the primary objectives of accounting in Chapter 1?
The primary objectives of accounting, as covered in the introductory chapter, are to:
- Maintain a systematic record of all business transactions.
- Calculate the net profit or loss for a specific period.
- Determine the financial position of the business through the Balance Sheet.
- Provide essential financial information to various users like owners, managers, and creditors for decision-making.
3. How is book-keeping different from accounting, and why is this distinction important for understanding the subject?
The key difference is that book-keeping is just the recording phase of accounting—it's about correctly entering financial transactions in the books. Accounting is a much broader concept that includes not only recording but also summarising, analysing, and interpreting that data to generate insights. This distinction is crucial because book-keeping provides the raw data, while accounting turns that data into meaningful information for strategic decisions.
4. What are the key qualitative characteristics that make accounting information useful?
To be useful, accounting information must possess four key characteristics:
- Reliability: The information must be factual, verifiable, and free from error or bias.
- Relevance: The information must be capable of influencing the decisions of its users.
- Understandability: It must be presented in a clear and concise manner so that users can easily comprehend it.
- Comparability: The information should allow users to compare a firm's performance over time and against other firms.
5. Why is accounting often called the 'language of business'?
Accounting is called the 'language of business' because it communicates the financial results and health of an organisation to various stakeholders. Just as a language uses words to convey ideas, accounting uses financial statements like the Profit & Loss Account and Balance Sheet to report on a company's activities and performance, enabling informed business decisions.
6. What is the fundamental difference between an 'asset' and a 'liability'?
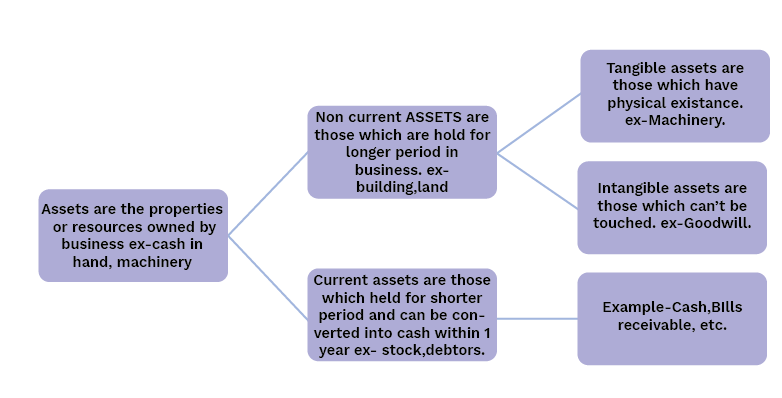
An asset is an economic resource owned by a business that is expected to provide future benefits (e.g., cash, machinery, stock). In contrast, a liability is a financial obligation or debt that the business owes to another party (e.g., loans from a bank, amounts owed to suppliers). Simply put, assets are what a business owns, and liabilities are what it owes.
7. Can you explain the difference between 'Capital' and 'Drawings'?
Capital is the amount invested in the business by its owner(s), which can be in the form of cash or assets. It represents the owner's claim on the business's assets. Drawings, on the other hand, refer to any cash or goods withdrawn from the business by the owner for personal use. Capital increases the owner's equity, while drawings decrease it.
8. How does the distinction between Capital Expenditure and Revenue Expenditure affect the summary of a company's finances?
This distinction is crucial for accurate financial reporting. Capital Expenditure is an amount spent to acquire a long-term asset (like machinery) and is shown on the Balance Sheet. Its benefit lasts for more than one year. Revenue Expenditure is an expense incurred for day-to-day operations (like salaries) and is shown in the Trading and Profit & Loss Account. Incorrectly classifying these can distort the reported profit and the company's financial position.
9. Who are the main users of accounting information according to the CBSE syllabus?
The users of accounting information are broadly classified into two groups:
- Internal Users: These are individuals within the organisation, such as owners and management, who use the information for planning, controlling, and decision-making.
- External Users: These are individuals or entities outside the organisation, including investors, creditors, banks, and government authorities, who use the information to assess the business's profitability and financial soundness.
10. Why does accounting only record transactions that can be measured in money? What is the main drawback of this principle?
Accounting uses money as a common denominator to record and compare diverse business activities, a concept known as the Money Measurement Principle. This allows for uniform and objective financial reporting. The major drawback is that it ignores crucial non-monetary factors that significantly impact a business, such as the skill of the management team, employee morale, or brand reputation, as these cannot be assigned a precise monetary value.