Science Class 7 Chapter 1 Question Answer Explained for Easy Exam Prep
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition In Plants - 2025-26
1. Explain the process of how nutrients are replenished in the soil from class 7 science chapter 1 question answer.
The plants absorb mineral nutrients from the soil. The fertilizers and manures containing various nutrients like nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus need to be added from time to time to enrich the soil. Nitrogen gas is available in large amounts but plants cannot use it directly from the air. The bacterium Rhizobium lives in the roots of the leguminous plants. Rhizobium bacteria convert the non-usable form of nitrogen. In this way, the nutrients are replenished in the soil by using fertilizers and manures, and by sowing leguminous plants.
2. Explain the mechanism of eating insects by a pitcher plant as a nutritious source related to NCERT class 7 science chapter 1
The leaves of the pitcher plants are tailored into a pitcher-like structure. The tip of the leaves forms a lid that can open and close the mouth of the pitcher-like structure of the leaves. There is hair inside the pitcher, which is directed downwards. When an insect lands in the pitcher, it gets entangled in the hair. The pitcher secretes some digestive juices that help the plant digest the insect. Such insects eating plants are insectivorous plants. These plants do not get all the necessary nutrients from the soil. So, they are called partial heterotrophs.
3. Summarize Science ch 1 class 7.
In Class 7 Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants, students are introduced to topics related to plants and how they get nutrition for themselves. The concepts covered in these topics include the photosynthesis process, chlorophyll and stomata. The chapter also teaches other modes of nutrition in insectivorous plants.
Students also learn how nutrients are replenished in the soil and how atmospheric nitrogen is fixed in the soil through a bacterium called Rhizobium.
4. Why should we grow crops inside greenhouses as described in class 7 science ch 1 question answer?
Factors like diseases, rodents, wind, and adverse climatic conditions cannot affect the crops grown in greenhouses. Therefore, growing crops in greenhouses is beneficial for the farmers in the long run.
5. How can I download the Solutions of Class 7th Science Chapter 1 NCERT?
The solutions are easily available on the Vedantu site.
Click on NCERT Solutions of Class 7 Science and choose Chapter 1.
The webpage with Vedantu’s solutions for Chapter 1 of Class 7th Science NCERT Textbook will open.
To download this, click on the Download PDF button and you can view the solutions offline.
For other solutions and concept-related modules on other topics or subjects, visit the Vedantu and go through the related modules. The solutions are free of cost and also available on the Vedantu Mobile app.
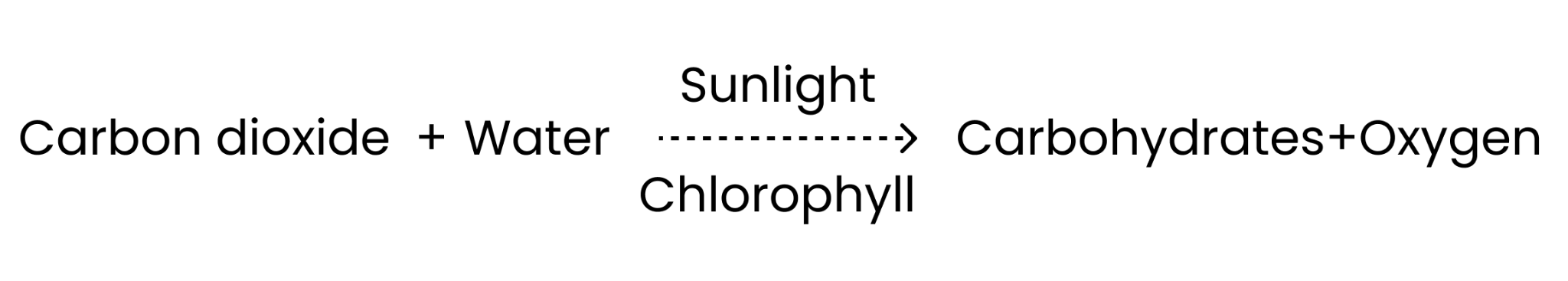
6. What do you understand about photosynthesis according to class 7 science chapter 1 question answer?
During photosynthesis, the light energy is converted into chemical energy by green plants and other organisms. Chloroplasts are tiny particles found inside plant cells that perform photosynthesis. Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air and water from the earth via their roots. The Sun gives out light energy. The leaves release the oxygen that has been generated into the air. Since it is an important topic, do understand it properly along with all its components such as chloroplasts and so on.
7. What are the different modes of Nutrition in Plants from Science Class 7 Chapter 1 question answer?
Class 7 Science Chapter 1 categorises plants into two main types:
Autotrophic Nutrition, in which plants can synthesise their own food using sunlight.
Heterotrophic Nutrition, in which plants cannot produce their own food and rely on other organisms for their nutritional needs.
8. How can I improve my understanding of the concepts covered in science class 7 chapter 1 question answer?
Here are some tips to solidify your understanding:
Relate to real-world examples
Perform experiments
Use diagrams and illustrations
Ask questions
Students can download and refer to class 7 science chapter 1 PDF to get all the solved answers related to this chapter.
9. What is the importance of nutrition for plants?
NCERT class 7 science chapter 1 explains the concepts related to nutrition and its importance. A few of the points to remember are:
Growth and development
Energy Production
Repair and maintenance
10. What is the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll is a green pigment present in plant leaves and plays a crucial role in photosynthesis by absorbing sunlight energy. To learn more about chapter 1, students can refer to class 7th science chapter 1 solutions provided by Vedantu.