




How to Calculate Perimeter: Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
In mathematics, area and perimeter are the two important properties of any shape. It is used in our day-to-day lifestyle. The region enclosed by an object's shape is called the area. The shape's area can also be described as the area in a plane covered by a figure or any geometric shape. The dimensions and qualities of any shape determine its surface area.
Different shapes have different regions, each of which can be defined differently. The whole distance surrounding a figure is referred to as its perimeter. In a two-dimensional plane, a shape's perimeter is its entire circumference. Depending on their measurements, different shapes' perimeters may be equal in length.
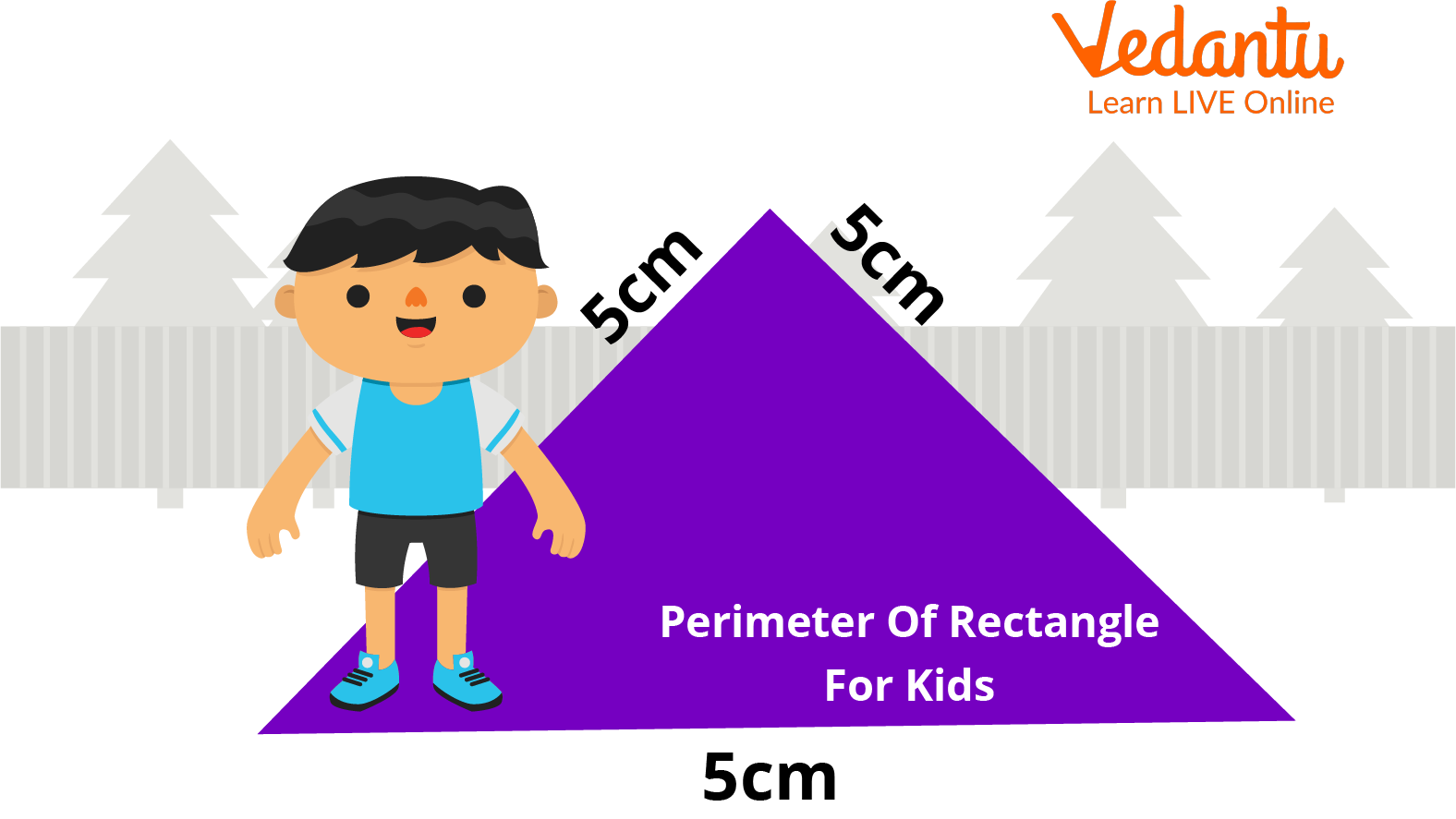
Perimeter
Square Line Page:
It is a coordinate paper and grid paper. It is a type of writing paper printed with tiny lines forming a consistent grid. The lines are often used as a guide when producing graphs of functions or experimental data and sketching curves. It is frequently used in laboratory notebooks, as well as in mathematics and engineering education. Graph paper can be purchased either loose or bound in notebooks. Most graph paper pages have dimensions of 8.5 inches wide by 11 inches long.
Square line page
Different types of square line paper:
The different types of graph paper are:
Grid Paper:- The widely used graph paper, on which students frequently plot or draw experimental data, curves, etc., is quite similar to grid paper. As the name implies, grid graph paper is mainly composed of regular grids, also known as standard lines in layman's terms.
Quad Graph Paper:- This graph paper is referred to as the first kind of graph paper used, also known as quadrille graph paper. It is derived from French. The paper is grey and light blue in tone. Using a light grey hue, the grids are created. Usually made up of two to five blocks, quad graph paper displays smaller amounts of data.
Engineering Graph Paper:- This graph paper is mainly for engineering-related tasks. The sheet of paper has ten grids and is bright green. Each page has a margin. This paper is mainly used to demonstrate a well-done job.
Millimetre Graph Paper:- This graph paper is used for drawing tasks. Ten squares, each measuring one centimetre, make up the graph paper.
Hexagonal Graph Paper:- The field of the geometric diagram uses this graph paper. The various structures are depicted on the graph.
Dot Graph Paper:- Dot graph paper is simply another type of graph paper with a unique application among academics and professionals. Dot paper, frequently used for bullet journaling, drawing, etc., can be broadly defined as paper with dots spaced regularly across it.
Conclusion:
A perimeter is a closed path that surrounds, encircles, or outlines a two-dimensional shape or a one-dimensional length. The perimeter is measured in unit. The perimeter chart of different figures is given below:
FAQs on Perimeter Chart: Essential Formulas & Applications
1. What is perimeter and why is it an important concept in Maths?
Perimeter is the total length of the boundary or path that encloses a two-dimensional (2D) shape. It is a fundamental concept in geometry because it helps us understand and quantify one of the most basic properties of a shape. Mastering perimeter is crucial before moving on to more complex concepts like area (the space inside the shape) and volume (for 3D objects).
2. What are some common real-world applications of calculating perimeter?
The concept of perimeter is used frequently in everyday life for various measurement tasks. Some key examples include:
Fencing: Calculating the total length of fence needed to enclose a garden, yard, or farm.
Construction: Determining the amount of material needed for the foundation outline of a building or a room's skirting boards.
Crafts & Decor: Measuring the length of ribbon for a gift, lace for a tablecloth border, or wood for a picture frame.
Sports: Finding the total distance of one lap around a running track or a sports field.
3. What are the basic formulas for the perimeter of a square, rectangle, and circle?
The formulas for the perimeter of common shapes are essential tools. A perimeter chart often summarises these:
Square: The perimeter is 4 × side length, as all four sides are equal.
Rectangle: The perimeter is 2 × (length + width), as it has two pairs of equal sides.
Circle: The perimeter of a circle is called the circumference, and its formula is 2 × π × radius (2πr).
4. What is the key difference between perimeter and area?
The key difference lies in what is being measured. Perimeter measures the length of the outer boundary of a shape (a one-dimensional measure, like metres or cm). In contrast, area measures the total space enclosed within that boundary (a two-dimensional measure, like square metres or cm²). For example, a fence around a field is its perimeter, while the grass covering the field is its area.
5. How is the perimeter of an irregular or composite shape calculated?
For any irregular polygon (a shape with straight sides of different lengths), the method is straightforward: you must add the lengths of all its individual outer sides. For composite shapes (made by joining simple shapes like rectangles), the same principle applies. You must carefully identify only the exterior boundary and sum the lengths of those segments, ensuring not to include any internal lines where the shapes were joined.
6. If two shapes have the same area, must they also have the same perimeter?
No, this is a common misconception. Two shapes can have the exact same area but vastly different perimeters. For example, a rectangle that is 8 cm long and 2 cm wide has an area of 16 cm² and a perimeter of 20 cm (2 × (8+2)). A square that is 4 cm by 4 cm also has an area of 16 cm², but its perimeter is only 16 cm (4 × 4). This shows that the shape's dimensions, not just its area, determine its perimeter.
7. What is a 'perimeter chart' and how is it a useful tool for learning?
A perimeter chart is a visual aid, usually in the form of a table or diagram, that lists various geometric shapes alongside their corresponding perimeter formulas. It is a highly useful tool because it helps students to:
Quickly reference the correct formula for a specific shape.
Compare and contrast the formulas for different shapes.
Memorise the fundamental formulas needed for solving geometry problems effectively.























