Must-Know Math Topics for Class 3 Students
The third-grade Maths lessons are structured so that students can practise their Maths skills while engaging in third-grade Maths games. Every effort has been made to explain new concepts in simple language so that the kid may readily understand them, keeping in mind a child's mental ability in the third grade. The difficulty level of the exercises has been lowered, and mathematical ideas have been simplified to the greatest extent possible.
Each topic offers a substantial number of examples to understand how concepts are used. The key arithmetic topics we'll cover in third grade include four-digit numbers, number comparisons, addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and geometric shapes and figures. The measurement of length, mass, capacity, time, money, fractional numbers, and pictographs.
Formation of Four-digit Numbers
Four-digit numbers are those numbers that consist of only 4 digits in which the first digit should be 1 or greater than 1, and the rest of the digits can be any number between 0 and 9. For example, 5693, 1023, and 9825 are four-digit numbers.
4-digit numbers are written or read according to the place values of the digits. In 4-digit numbers, the four digits correspond to the four-place values - ones, tens, hundreds, and thousands. When a number is written in standard form, each group of digits is separated by a comma which forms a period.
For example, 3510 is a 4-digit number, and after placing the comma, it is written as 3,510.
International and Roman Numerals
Roman numerals are created by converting numbers to their respective Roman digits. The numerals used in English or international numeration in the Hindu-Arabic system are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 0. Roman numeral values for the international system are as follows:
One as I, Five as V, Ten as X, Fifty as L, Hundred as C, and Five hundred as D
Now, numbers to roman numerals as follows:
4 as IV, 9 as IX, 24 as XXIV, 20 as XX, 39 as XXXIX, 11 as XI

International and Roman Numerals
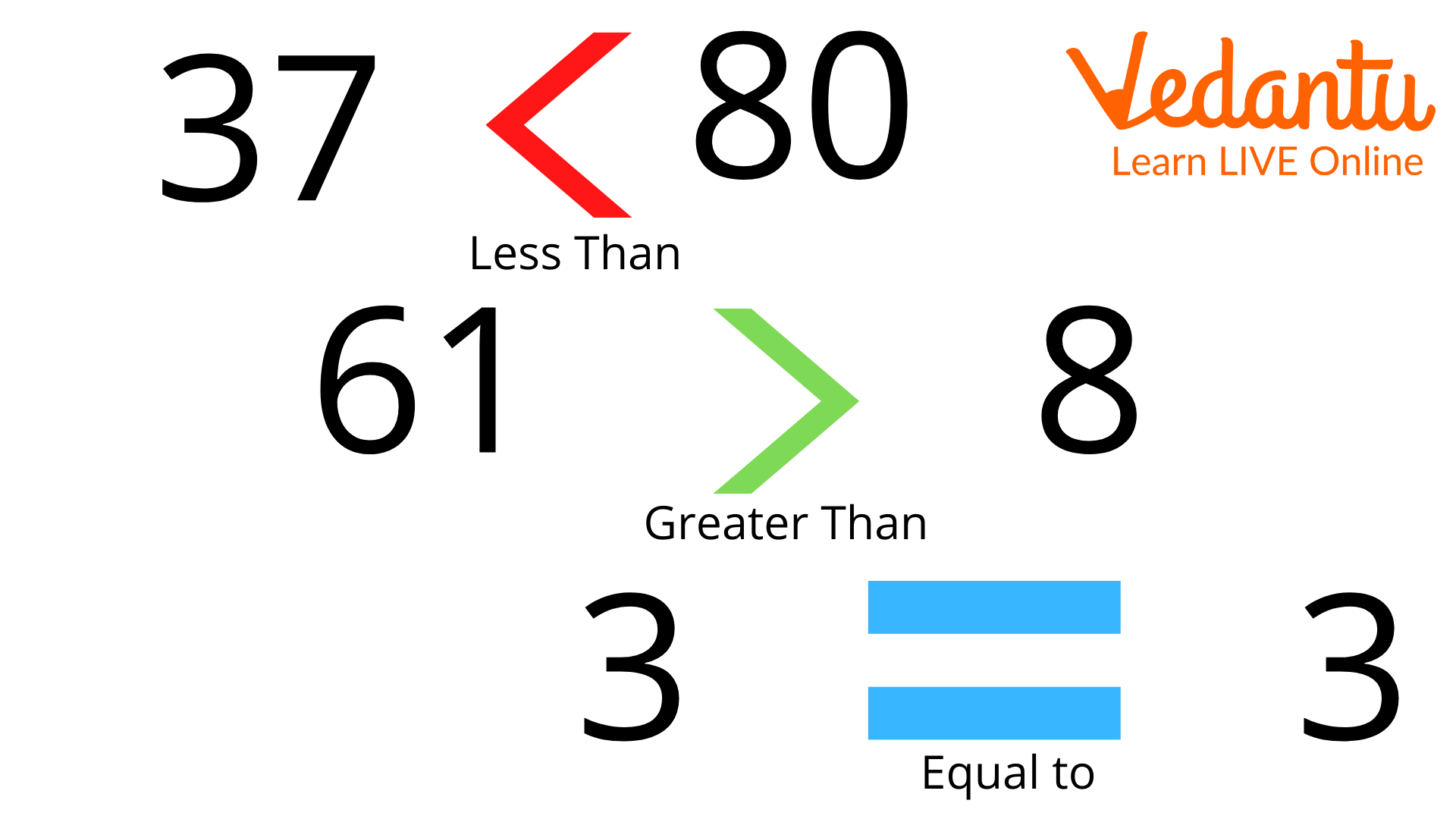
Comparing Numbers
We are going to show class 3 maths questions by using the topic of comparing numbers. In the end, we provide an image that shows numbers by comparing them.
Step 1: To compare the digit count. The number increases as the number of digits increases.
Step 2: Compare the higher place values if the number of digits is the same. For example, 789 and 889.
Here we can see that the ones and tens place values are the same, so in this case, we will compare the higher values, i.e. of hundred places. As 7 < 8. Therefore, 789 < 889.
Step 3: Compare the digits in the next place value to the right if they are the same at the highest place value.
For Example, 789 and 779.
Here, out of 789 and 779, the hundred-place and ones place values are the same. So we will see the tens place value. As 8>7, therefore, 789>779.
Step 4: Continue comparing digits with the same place value until you discover digits with a different place value. The greater number is the one with the higher face value.
Comparing Numbers
Geometrical Shapes and Figures
In mental Maths for Class 3, we can show the concept of geometrical shapes and figures. Here, we also show examples of geometrical shapes in two- dimensional and in three- dimensional.
Geometric shapes are defined as figures closed by a boundary that combines a definite amount of curves, points, and line segments. Each shape has a unique name, such as a circle, square, triangle, rectangle, etc.
Class 3 Maths Chapter 1 Numbers
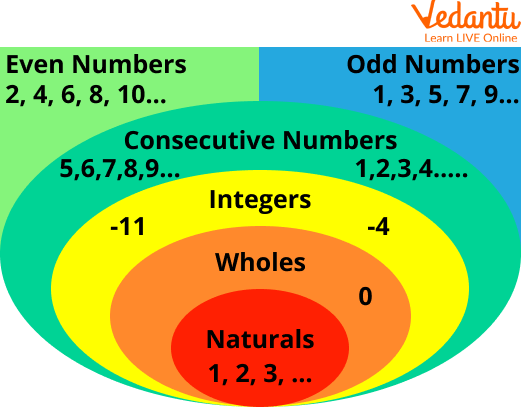
A number is a basic component of Mathematics. Numbers are used for counting, measuring, keeping things in order, indexing, etc. We have different types of numbers based on their properties such as natural numbers, whole numbers, rational and irrational numbers, integers, real numbers, complex numbers, even and odd numbers, etc in class 3 maths chapter 1 numbers.
Numbers
Class 3 Maths Chapter 2 Worksheet
Here, we are going to solve questions related to the Class 3 Maths Chapter 2 worksheet.
Q1. oh! 206! How many more are needed to reach a triple century?
Ans: As we know that triple century means 300
This implies we have to make 300 runs.
Thus, 300 – 206 = 94
Implies 94 runs are needed.
Q2. Who am I? Match with the number.
Ans:
The following are the correct match:
Maths Games for Grade 3
There are Maths games for grade 3 that you can play without computers i.e.
Prodigy maths
Maths baseball
Bouncing sums
Maths is fun
Solved Examples
Q1. Which of the following is not an even number: 2, 3, 4, 6, 8?
Ans: An even number is a number that is a multiple of 2. It can be said that any number that is completely divisible by 2 is an even number.
Therefore, 3 is the number that can’t be divisible by 2. Hence, 3 is not an even number.
Q2. What is LVI in Roman numerals?
Ans: We know that L = 50, V = 5, and I = 1.
So we will expand and add the values of all the letters.
This will be L + V + I = 50 + 5 + 1 = 56.
Q3. Complete the series i.e. 1, 3, 6, 10, ____
Ans. We have given that 1, 3, 6, 10,?
1 + 2 = 3
3 + 3 = 6
6 + 4 = 10
10 + 5 = 15
Thus, the answer is 15.
Q4. Which of the following numbers is greater, 89 or 98?
Ans: As we have learned while comparing numbers, we always take the highest place value first. Here, at tens place; we can see that 8 < 9. Hence, 89 < 98.
Practice Questions
Q1. What does XXVI mean in numbers?
Ans: 26
Q2. Write all the even numbers between 155 and 165.
Ans: 156, 158, 160, 162, 164
Q3. Are cylinders and oval both 3D shapes?
Ans: No, only the cylinder comes under a 3D shape.
Q4. 3 friends want a bike and a car. Rahul had Rs.48.50, Rishi had Rs.55.50, and sona had Rs.38.00. find how much money they all have.
Ans: Rs.142
Summary
4-digit numbers are numbers having 4 digits, and we can form 4-digit numbers by using any digits from 0-9, but the number should begin with a digit 1 or a number greater than 1. Roman numerals are the symbolic representation of numbers that do not follow a place value system. They comprise Latin alphabets I, V, X, L, C, D, and M. These are used to represent the numbers 1, 5, 10, 50, 100, 500, and 1000.
Comparing numbers is a method of comparing two or more numbers and identifying if one number is equal, lesser, or greater than the other numbers. When comparing natural numbers, the number with more digits is greater than the number with a lesser number of digits. Geometric shapes are also known as geometric figures made up of a combination of lines or curves. Then in the end, we added some solved and practice questions, to get a better command of the topic.
FAQs on Essential Math For Class 3: Concepts & Examples
1. What are the basic math topics taught in class 3?
In class 3 math, students learn addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, shapes, measurements, time, and basic fractions. These topics help children build a strong foundation in mathematics, supporting further studies in later classes and everyday problem solving.
2. How do you explain place value to a class 3 student?
Place value tells us the value of each digit in a number. For example, in 342, 3 is in the hundreds place, 4 in the tens, and 2 in the ones. So, 342 means 3 × 100 + 4 × 10 + 2 × 1.
3. Why is learning multiplication important in class 3?
Multiplication helps class 3 students deal with repeated addition easily. It speeds up calculations, assists in solving word problems, and supports learning more advanced math concepts like division, fractions, and measurements in later grades.
4. How can third graders practice subtraction?
Third graders can practice subtraction by using mental math, working with number lines, and solving daily life problems. Practicing through worksheets and hands-on activities, like taking away objects or using coins, also helps strengthen subtraction skills.
5. What is a fraction and how is it taught in class 3?
Fractions show equal parts of a whole. In class 3, students learn to recognize, write, and compare simple fractions like 1/2, 1/4, and 3/4 using shapes and real-life examples to make understanding easier.
6. What are the common geometric shapes studied in class 3?
Class 3 math introduces these major geometric shapes:
- Square
- Rectangle
- Circle
- Triangle
7. How do class 3 students measure length and weight?
Class 3 students learn to measure length using rulers or tape (centimeters, meters) and weight with scales (grams, kilograms). They practice comparing different objects and use real-life situations, such as measuring their height or weighing fruits.
8. What is the focus of word problems in class 3 math?
Class 3 word problems help students use math to solve everyday situations. These questions focus on addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, encouraging children to read carefully, understand the problem, and choose the right operations to find solutions.
9. How is time taught in class 3 mathematics?
Class 3 math teaches students to read clocks, understand hours and minutes, and calculate how much time has passed. They learn using analog and digital clocks, and practice telling time in daily routines, improving time management skills.
10. What strategies help class 3 students understand division?
Division in class 3 is explained as sharing equally or making equal groups. Strategies include using repeated subtraction, drawing pictures, or distributing objects, so students see that for $12 \div 4$, they split 12 into 4 equal groups, each with 3.
11. Why are tables important in class 3 math?
Tables in class 3 math, like multiplication tables, make calculations faster and easier. Memorizing tables up to 10 helps students do multiplication and division quickly, which is useful in complex calculations and when solving later math problems.
12. How do class 3 students compare numbers?
In class 3 math, students compare numbers by checking digits from left to right, using symbols like 'greater than' (>), 'less than' (<), and 'equal to' (=). Comparing numbers helps children decide which is bigger or smaller in real-life situations.