
The distance between two towns is 300 km. Car A and car B start simultaneously from these towns and move towards each other. The speed of car A is more than that of car B by 7 km/hr. If the distance between the cars after two hours is 34 km. Find the speed of both cars.
(a) Speed of car B is 63 km/hr and speed of car A is 70 km/hr
(b) Speed of car B is 70 km/hr and speed of car A is 75 km/hr
(c) Speed of car B is 50 km/hr and speed of car A is 65 km/hr
(d) Speed of car B is 72 km/hr and speed of car A is 80 km/hr
Answer
242.1k+ views
Hint: First of all, consider the speed of car B and car A as x km/hr and (x + 7) km/hr respectively. Now, find the distance travelled by both the cars in 2 hours by using Distance = Speed x Time. Now, use (distance travelled by car A) + (distance travelled by car B) + 34 km = 300 km and from this find the value of x which is the speed of car B and (x + 7) for speed of car A. Draw the diagram to visualize the situation.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we are given that the distance between two towns is 300 km. Car A and car B start simultaneously from these towns and move towards each other. The speed of car A is more than that of car B by 7 km/hr. If the distance between the cars after two hours is 34 km, we have to find the speed of both cars.

\[{{T}_{A}}\text{ and }{{T}_{B}}\] are two towns at a distance of 300 km and car A and car B starts from \[{{T}_{A}}\text{ and }{{T}_{B}}\] simultaneously. Let us consider the speed of car B as x km/hr. As we are given that the speed of car A is more than the speed of car B by 7 km/hr. So, we get the speed of car A as (x + 7) km/hr.
Now, we are given that both cars travel for 2 hours. So, let us consider that car A reaches points C and car B reaches point D after 2 hours as shown below.
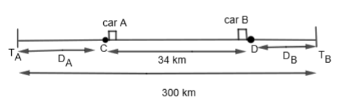
We know that Distance = Speed x Time. By using this, we get,
Distance travelled by car A in 2 hours,
\[{{D}_{A}}=\text{Speed of car A }\times 2\text{ hours}\]
\[{{D}_{A}}=\left( 2x+14 \right)km.....\left( i \right)\]
Distance travelled by car B in 2 hours,
\[{{D}_{B}}=\text{Speed of car B }\times 2\text{ hours}\]
\[{{D}_{B}}=x.2\]
\[{{D}_{B}}=2x\text{ }km.....\left( ii \right)\]
We are also given that after travelling for 2 hours, both cars are at a distance of 34 km, so in the figure, we get CD = 34 km. As we know that the total distance between town A and town B is 300 km, so, from the figure, we get,
\[{{D}_{A}}+{{D}_{B}}+34km=300km\]
By substituting the value of \[{{D}_{A}}\text{ and }{{D}_{B}}\] from equation (i) and (ii) respectively, we get,
\[\left( 2x+14 \right)+\left( 2x \right)+34=300\]
\[4x+48=300\]
\[4x=300-48\]
\[4x=252\]
\[x=\dfrac{252}{4}\]
\[x=63\text{ }km/hr\]
So, we get the speed of car B = x = 63 km/hr and speed of car A = (x + 7) = (63 + 7) = 70 km/hr.
Hence, option (a) is the right answer.
Note: Students must note that in this type of questions, it is very important to draw the diagram to visualize the situation. In this question, students often make this mistake of substituting speed of car B instead of finding the distance travelled by car A or vice versa. So, this must be taken care of that in the formula distance = speed x time, corresponding values of speed, time and distance should be substituted.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we are given that the distance between two towns is 300 km. Car A and car B start simultaneously from these towns and move towards each other. The speed of car A is more than that of car B by 7 km/hr. If the distance between the cars after two hours is 34 km, we have to find the speed of both cars.

\[{{T}_{A}}\text{ and }{{T}_{B}}\] are two towns at a distance of 300 km and car A and car B starts from \[{{T}_{A}}\text{ and }{{T}_{B}}\] simultaneously. Let us consider the speed of car B as x km/hr. As we are given that the speed of car A is more than the speed of car B by 7 km/hr. So, we get the speed of car A as (x + 7) km/hr.
Now, we are given that both cars travel for 2 hours. So, let us consider that car A reaches points C and car B reaches point D after 2 hours as shown below.

We know that Distance = Speed x Time. By using this, we get,
Distance travelled by car A in 2 hours,
\[{{D}_{A}}=\text{Speed of car A }\times 2\text{ hours}\]
\[{{D}_{A}}=\left( 2x+14 \right)km.....\left( i \right)\]
Distance travelled by car B in 2 hours,
\[{{D}_{B}}=\text{Speed of car B }\times 2\text{ hours}\]
\[{{D}_{B}}=x.2\]
\[{{D}_{B}}=2x\text{ }km.....\left( ii \right)\]
We are also given that after travelling for 2 hours, both cars are at a distance of 34 km, so in the figure, we get CD = 34 km. As we know that the total distance between town A and town B is 300 km, so, from the figure, we get,
\[{{D}_{A}}+{{D}_{B}}+34km=300km\]
By substituting the value of \[{{D}_{A}}\text{ and }{{D}_{B}}\] from equation (i) and (ii) respectively, we get,
\[\left( 2x+14 \right)+\left( 2x \right)+34=300\]
\[4x+48=300\]
\[4x=300-48\]
\[4x=252\]
\[x=\dfrac{252}{4}\]
\[x=63\text{ }km/hr\]
So, we get the speed of car B = x = 63 km/hr and speed of car A = (x + 7) = (63 + 7) = 70 km/hr.
Hence, option (a) is the right answer.
Note: Students must note that in this type of questions, it is very important to draw the diagram to visualize the situation. In this question, students often make this mistake of substituting speed of car B instead of finding the distance travelled by car A or vice versa. So, this must be taken care of that in the formula distance = speed x time, corresponding values of speed, time and distance should be substituted.
Recently Updated Pages
Geometry of Complex Numbers Explained

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




