
In this reaction,
$C{H_3}CHO + HCN \to C{H_3}CH(OH)CN \to C{H_3}CH(OH)COOH$
an asymmetric centre is generated. The acid obtained would be:
(A) 50% D + 50% L-isomer
(B) 20% D + 80% L-isomer
(C) D-isomer
(D) L-isomer
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Refer to the nucleophilic addition reaction mechanism to follow the given reaction in the question. In the reagent $HCN$, $C{N^ - }$ is a nucleophile which can attack the electrophilic carbon centre from the two sides that are, front side as well as backside. Thus, there will be a racemic mixture in the product.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us understand the mechanism of the given reaction. In the given reaction, $C{H_3}CHO + HCN \to C{H_3}CH(OH)CN \to C{H_3}CH(OH)COOH$, at the first step, attack of nucleophile cyanide ion ($C{N^ - }$) on acetaldehyde ($C{H_3}CHO$) taking place. The carbon centre of acetaldehyde is an electrophilic centre because double bond electrons shift to oxygen atoms. Now, two possibilities of nucleophile attack on carbon centres are possible. Cyanide ions can attack carbon centres from the backside as well as the front side. Let us say from the front side attack (say, a) product (a) is formed and from the backside, attack (say, b) product (b) is formed. The concentration of both the products will be in an equal percentage.
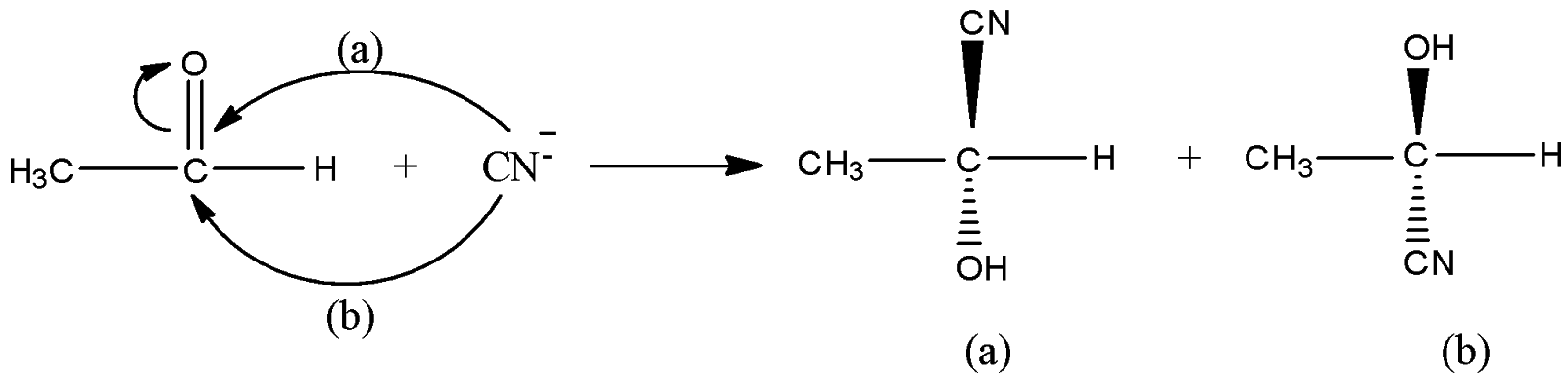
Now, on hydrolysis of the product (a) and product (b), the acid will be obtained as shown in the below reactions. On hydrolysis of (a), D-isomer (50%) obtained because OH is on the right side and on hydrolysis of (b), L-isomer (50%) is obtained. Thus we get a racemic mixture in the product.
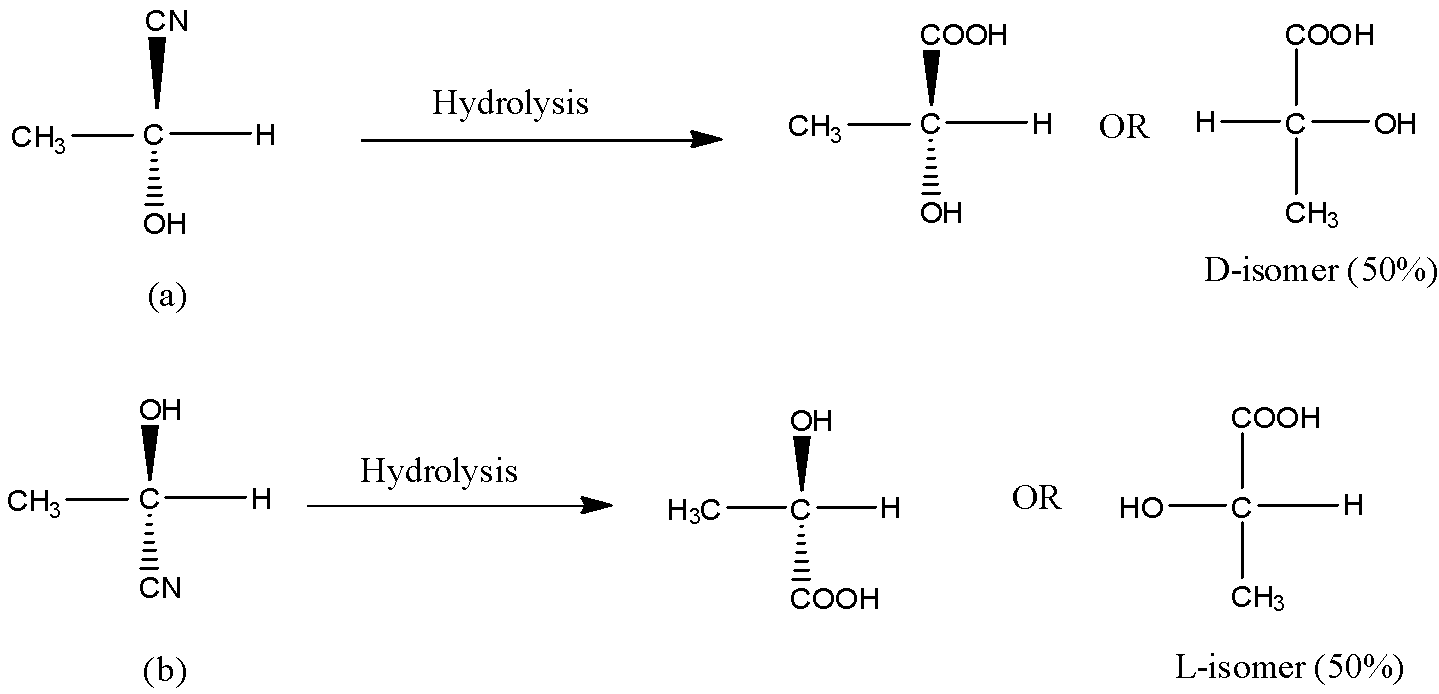
Hence, the acid obtained is 50% D and 50% L-isomer. Thus, option (A) is correct.
Note: Racemic mixture- A racemic mixture is a 50:50 mixture of two enantiomers. Chiral compounds synthesized from achiral starting compounds and reagents are generally racemic. Separation of components of a racemic mixture is done by a process called resolution.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us understand the mechanism of the given reaction. In the given reaction, $C{H_3}CHO + HCN \to C{H_3}CH(OH)CN \to C{H_3}CH(OH)COOH$, at the first step, attack of nucleophile cyanide ion ($C{N^ - }$) on acetaldehyde ($C{H_3}CHO$) taking place. The carbon centre of acetaldehyde is an electrophilic centre because double bond electrons shift to oxygen atoms. Now, two possibilities of nucleophile attack on carbon centres are possible. Cyanide ions can attack carbon centres from the backside as well as the front side. Let us say from the front side attack (say, a) product (a) is formed and from the backside, attack (say, b) product (b) is formed. The concentration of both the products will be in an equal percentage.

Now, on hydrolysis of the product (a) and product (b), the acid will be obtained as shown in the below reactions. On hydrolysis of (a), D-isomer (50%) obtained because OH is on the right side and on hydrolysis of (b), L-isomer (50%) is obtained. Thus we get a racemic mixture in the product.

Hence, the acid obtained is 50% D and 50% L-isomer. Thus, option (A) is correct.
Note: Racemic mixture- A racemic mixture is a 50:50 mixture of two enantiomers. Chiral compounds synthesized from achiral starting compounds and reagents are generally racemic. Separation of components of a racemic mixture is done by a process called resolution.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




