




What is an Operating System?
An operating system serves as an interface between the program and various computer hardware or software components. The operating system is made to be able to control all of the computer's resources and activities. It is an entirely integrated collection of specialised applications that manage all of the computer's functions. All other programs that are installed on the computer, including applications and other system software, are controlled and monitored by it.

Microsoft Windows OS Logo
Examples of Operating systems are listed below:
Microsoft Windows
Linux
Mac OS.
Classification of the Operating System
Classification of Operating System can be done as follows:
Multiprocessing:
Supports running a program on multiple CPUs within a single computer system.
Multitasking:
This allows you to run more than one program at the same time.
Multi-User:
This allows multiple users to run the program in the same fraction of time.
Multithreading:
Allows every module of a single program to execute simultaneously.
Real-Time:
Response to the input is immediate.
Main Layers in an Operating System
The software that acts as an interface between various computer parts is referred to as layers in an operating system. A clear benefit of layering is evident in an operating system. Each layer may be designed independently and interacted with as needed.
The following five-layer model is often used in an Operating System:
Kernel:
It links a computer's hardware with application software. As a result, it controls how applications in the RAM access memory. Additionally, it decides when each program will execute and allots processing time and memory to each application.
Memory Management:
It is in charge of restarting the computer's physical memory between processes and managing programs that need more memory than is physically accessible.
Input/Output:
This layer manages all physical interactions with other devices, including the keyboard, printer, display, and disc drive. The I/O layer receives a request if a higher layer needs access to a device.
File Management System:
It also goes by the name "file system." It is in charge of planning and overseeing the data storage on long-term storage devices including hard drives, and floppy disc drives.
User Interface:
It is referred to as the area where human and machine interaction takes place. There are two different types of user interfaces: the icon-based Graphical User Interface (GUI), which is used in Windows and Apple Mac OS, and the text-based Command Line Interface (CLI), which is used in MS-Dos and LINUX.
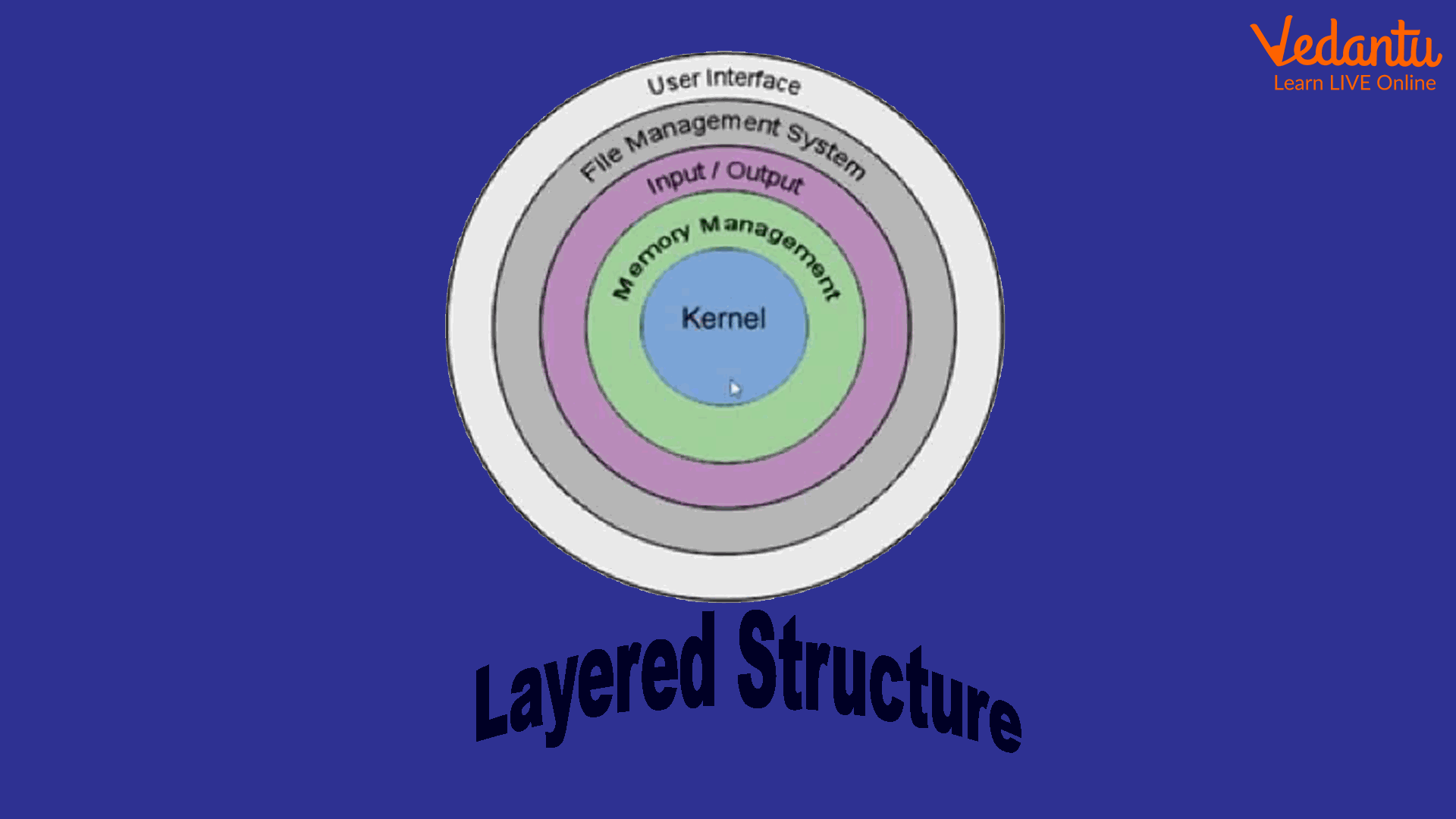
Main Layers in an Operating System
Different Types of Operating Systems
Microsoft Windows
It is a form of an operating system that comes in 32 and 64-bit variants Microsoft Windows. Microsoft was the one that created it. It offers a Graphical User Interface (GUI), the ability to manage virtual memory, multitasking features, and compatibility for a wide range of peripheral devices.

Different Versions of Microsoft Windows
UNIX
The most capable and well-liked operating system for multiple users and tasks is Unix. It is a group of applications that serve as the user's interface with the computer. Dennis Ritchie later contributed to Ken Thompson's original UNIX code. Unix systems are built around a core kernel that manages the system and the other processes.
UNIX Operating System Logo
The following are the major features of UNIX:
A hierarchy of files
Independence from devices
Multi-tasking
Multi-user functionality
Tools and utilities for creating tools
The portability
Integrated Networking
Linux
One of the most widely used variations of Unix OS is the LINUX Operating System. It is an open-source operating system that is freely available online and whose source code is editable by anybody who uses it. Its functionality list resembles Unix in many ways.

LINUX Logo
The major features of Linux operating systems are listed below:
Better security is provided by the LINUX Operating System, which is also seldom harmed by computer viruses.
A LINUX-operated computer won't hang, so anyone may use it for days or even months without having to restart it. The majority of internet servers use the LINUX Operating System for this reason.
The user can use four desktop screens at once on the LINUX-powered PC. A user can change between desktop screens at any moment.
The Linux kernel can be installed on any kind of hardware platform.
Bharat Operating System Solutions (BOSS GNU/Linux)
It is an Indian Linux distribution derived from Debian. BOSS (Bharat Operating System Solutions), a Debian-based Linux distribution called GNU/Linux, was created by CDAC and is tailored to the digital landscape of India. The majority of Indian languages are supported.
Important Points to Remember
The operating system is made to be able to control all of the computer's resources and activities.
Microsoft Windows is the most widely used OS.
Linux and UNIX is an open-source form of operating systems.
Bharat Operating System Solutions (BOSS GNU/Linux) is an Indian Linux distribution.
The most capable and well-liked operating system for multiple users and tasks is Unix.
Summary
An operating system serves as a link between a computer's software and hardware. Typical examples of operating systems are Windows, Linux, Mac OS, and UNIX. An operating system is composed of five layers: the kernel, input/output, memory management, file management system, and user interface. Most current computers utilise Microsoft Windows, a type of operating system that is available in 32- and 64-bit versions. Unix is the operating system that can handle most users and tasks simultaneously. The LINUX OS is one of the most popular Unix OS variants. It is a cost-free open-source operating system. In particular, for the Indian user base, Bharat Operating System Solutions (BOSS GNU/Linux) is an Indian Linux distribution derived from Debian.
Learn by Doing:
1. Which of the following is not an operating system?
Windows OS
UNIX
UNIMIX
LINUX
2. What is the full form of BOSS LINUX?
Bharat Operating System Solutions
Bharat operations system seldom
Bitcoin operations system solutions
3. Which one of the following is the oldest operating system amongst the given options?
Windows 3.1
Windows 95
Vista
Windows 8
Sample Solved Questions
1. What is an operating system?
Ans: A system for controlling a device is referred to as the operating system, which is a self-explanatory word. A piece of software known as an operating system acts as a bridge between computer hardware and end users. The main goal of an operating system is to make computers simple to use.
2. Give an example of an operating system that is free to use.
Ans: LINUX is an open-source operating system that is freely available online.
3. What is BOSS LINUX?
Ans: Bharat Operating System Solutions (BOSS GNU/Linux) is an Indian Linux distribution derived from Debian. It was created by CDAC and is tailored to the digital landscape of India. The majority of Indian languages are supported.
FAQs on Basic Concepts of Operating Systems
1. What is an Operating System and what are its main functions?
An Operating System (OS) is a system software that acts as an essential interface between the computer hardware and the end-user. It manages all the computer's resources and ensures that the system runs efficiently. The primary functions of an OS are:
- Memory Management: Allocating and de-allocating memory space to programs and data.
- Process Management: Managing the execution of various processes, including their scheduling and termination.
- File Management: Organising files in a structured manner on storage devices and controlling access.
- Device Management: Controlling and coordinating the use of hardware devices like printers, keyboards, and disk drives.
- Security: Providing protection to system resources and user data through mechanisms like passwords and access control.
2. What are the major types of Operating Systems used today?
Operating Systems can be classified based on their processing capabilities and design. The major types include:
- Batch Operating System: Executes jobs in batches without direct user interaction.
- Time-Sharing (Multitasking) OS: Allows multiple users to share the computer system simultaneously by allocating a small time slice to each process.
- Distributed Operating System: Manages a group of independent computers and makes them appear to be a single computer.
- Real-Time Operating System (RTOS): Designed for systems where tasks must be completed within strict time constraints, such as in robotics or industrial control.
- Network Operating System: Runs on a server and provides the capability to manage data, users, groups, security, and other networking functions.
3. What is the difference between a Graphical User Interface (GUI) and a Command-Line Interface (CUI)?
The main difference between a GUI and a CUI is how the user interacts with the computer.
- A Graphical User Interface (GUI) uses visual elements like windows, icons, menus, and pointers (WIMP). Users interact with the system by clicking on these elements, making it intuitive and easy to learn. Examples include Windows and macOS.
- A Command-Line Interface (CUI) requires the user to type specific text commands to perform tasks. It is less intuitive but offers more control and is more resource-efficient. Examples include MS-DOS and the Linux Terminal.
4. Can you provide some examples of popular Operating Systems and their typical applications?
Certainly. Different Operating Systems are designed for different devices and applications:
- Microsoft Windows: The most popular OS for desktop and laptop computers, widely used for personal computing, gaming, and business applications.
- macOS: The operating system for Apple's Mac computers, known for its strong GUI, security, and use in creative fields like graphic design and video editing.
- Linux: An open-source OS used extensively in servers, supercomputers, and by developers. Distributions like Ubuntu are also popular for desktop use.
- Android: The world's most popular mobile OS, used in smartphones and tablets from various manufacturers.
- iOS: The mobile OS exclusive to Apple's iPhone and iPad devices, known for its smooth performance and strong app ecosystem.
5. Why is a layered architecture considered an important design concept for an Operating System?
A layered architecture is important because it organises the Operating System into several layers, each with a specific function. This design offers significant advantages:
- Modularity: Each layer is responsible for a distinct task (e.g., hardware management, process scheduling). This makes the system easier to design, develop, and maintain.
- Easier Debugging: If an error occurs, it can be isolated to a specific layer, simplifying the debugging process. The developer only needs to inspect that layer's code.
- Abstraction: Higher-level layers do not need to know the complex details of the hardware or the implementation of lower-level layers. They only need to know how to interact with the layer directly below them.
This structured approach improves the overall stability and manageability of the OS.
6. What is the role of the Kernel in an Operating System?
The Kernel is the core and most fundamental part of an Operating System. It has complete control over everything in the system and acts as the primary bridge between the hardware and software applications. Its main responsibilities include managing the CPU's time (scheduling), system memory, and handling requests from software to access hardware devices. Every other part of the OS relies on the Kernel to provide these basic services.
7. How does an Operating System manage the computer's memory?
Memory management is a critical function of the OS that ensures efficient and fair use of the main memory (RAM). The OS keeps track of every memory location, regardless of whether it is allocated to a process or is free. It decides which process gets memory, when they get it, and how much they get. When a process requests memory, the OS allocates a free block. When the process terminates, the OS deallocates the memory, making it available for other processes. This prevents different programs from interfering with each other's data.
8. What is the conceptual difference between a 'program' and a 'process'?
A program and a process are related but distinct concepts. A program is a passive entity; it is a set of instructions stored on a disk, like an executable file (e.g., chrome.exe). A process, on the other hand, is an active entity. It is a program in the state of execution. When you double-click a program to run it, the Operating System loads it into memory and it becomes a process, complete with its own memory space, CPU time, and resources.























