What Does the Thyroid Gland Do? Key Roles and Symptoms
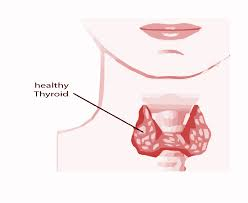
The thyroid gland is an important endocrine organ located at the front of the neck. It is shaped like a butterfly, with two lobes connected by a thin tissue called the isthmus. Despite its relatively small size, the thyroid gland plays a significant role in regulating various metabolic processes throughout the body.
Thyroid Gland Anatomy
To understand the structure of thyroid gland, imagine two elongated lobes (each about 4–6 cm long) resting on either side of the windpipe (trachea). These lobes are connected by the isthmus, creating the characteristic butterfly shape. This overall thyroid gland anatomy allows it to wrap around the trachea effectively.
Parathyroid Gland
Behind the thyroid are four small, round parathyroid glands that help control the body’s calcium and phosphate balance. Although these are separate from the thyroid, any surgery or disorder affecting the thyroid might also impact these tiny but essential glands.
Thyroid Gland Location
The thyroid gland location is between the C5 and T1 vertebrae in the neck, lying just below the Adam’s apple. It sits on top of the trachea, making it easily palpable in some individuals, especially when it becomes enlarged or inflamed.
Thyroid Gland Function
The primary thyroid gland function is to produce and release hormones that regulate the body’s metabolism. In simpler terms, these hormones control how quickly the body uses energy, generates heat, and supports growth. Moreover, thyroid hormones impact nearly every organ system, influencing heart rate, digestion, brain function, and more.
Thyroid Gland Hormones
The thyroid gland hormones include:
T4 (Thyroxine or Tetraiodothyronine): Contains four iodine atoms. Most of the thyroxine released into the bloodstream later converts into the active T3 hormone in organs like the liver and kidneys.
T3 (Triiodothyronine): Contains three iodine atoms and is the more active hormone that affects many physiological processes, including growth, development, and metabolism.
A healthy thyroid gland ensures a balanced level of T3 and T4 hormones in the body. When the balance is disturbed, it can lead to various disorders.
Common Disorders of the Thyroid Gland
Numerous conditions affect the thyroid, ranging from thyroid gland swelling to hormonal imbalances:
Goitre: A noticeable thyroid gland swelling or enlargement. In some cases, a large goitre can obstruct the windpipe or food pipe, causing breathing or swallowing difficulties.
Hyperthyroidism: Occurs when the gland produces too much thyroxine (T4). Common signs include weight loss, a rapid heartbeat, irritability, and trouble sleeping. Early treatment with medications can help restore hormonal balance.
Hypothyroidism: Occurs when the gland produces inadequate hormones. Signs include constant fatigue, weight gain, hair loss, and dry skin. An autoimmune condition called Hashimoto’s disease is often a trigger, where the body’s own antibodies attack the thyroid tissue.
Thyroid Cancer: Malignant lumps or nodules within the thyroid tissue can lead to cancer. Though serious, thyroid cancer has a relatively high survival rate compared to other cancers. Common types include papillary, follicular, medullary, and anaplastic thyroid cancer.
Thyroid Gland Symptoms
The thyroid gland symptoms differ depending on whether the gland is overactive, underactive, or enlarged. Some general symptoms include:
Difficulty concentrating
Changes in menstrual cycle
Rapid or irregular heartbeat
Muscle pain and weakness
Unexplained weight changes (gain or loss)
Feeling excessively hot or cold
High cholesterol (in hypothyroidism)
Because these signs can overlap with other conditions, it’s important to consult a medical professional for accurate diagnosis.
Thyroid Treatment and Management
Treatments vary based on the specific thyroid disorder:
Medications: Hyperthyroidism might be managed using drugs that reduce thyroid hormone production, while hypothyroidism often requires thyroxine replacement therapy with levothyroxine.
Radioactive Iodine: In certain cases of hyperthyroidism or thyroid cancer, radioactive iodine can be used to target abnormal thyroid cells.
Surgery: Surgical removal of part or all of the gland may be needed if there is a large goitre, nodules causing obstruction, or cancer.
Regular check-ups and thyroid function tests (T3, T4, and TSH) can help detect problems early.
Quick Quiz (with Answers)
Where is the thyroid gland located?
A. Near the brain
B. In the anterior neck
C. In the abdomen
D. At the back of the skull
Answer: B
Which hormone is more active, T4 or T3?
A. T4
B. T3
C. Both are equally active
D. Neither is active
Answer: B
Which disease is linked to hypothyroidism due to an autoimmune reaction?
A. Graves’ disease
B. Hashimoto’s disease
C. Goitre
D. Diabetes
Answer: B
What is the name of the small glands behind the thyroid?
A. Renal glands
B. Adrenal glands
C. Parathyroid glands
D. Pituitary glands
Answer: C
Related Topics to Explore


FAQs on Thyroid Gland Overview: Structure, Hormones, Functions & Common Disorders
1. What is the thyroid gland and where is it located in the human body?
The thyroid gland is a major endocrine gland located in the anterior region of the neck, just below the larynx (Adam's apple). It is composed of two lobes situated on either side of the trachea (windpipe), which are connected by a thin flap of connective tissue called the isthmus, giving it a characteristic butterfly shape.
2. What are the main hormones produced by the thyroid gland and what are their functions?
The thyroid gland produces and secretes three primary hormones that are crucial for regulating bodily functions:
- Thyroxine (T4 or Tetraiodothyronine): The primary hormone produced, which regulates metabolism, mood, and body temperature. It is later converted to T3 in the liver and other tissues.
- Triiodothyronine (T3): The more active form of the thyroid hormone. It plays a vital role in controlling the body's metabolic rate, heart and digestive functions, muscle control, and brain development.
- Thyrocalcitonin (TCT): This hormone helps regulate blood calcium levels by suppressing the activity of osteoclasts, the cells that break down bone.
3. What is the importance of iodine for the normal functioning of the thyroid gland?
Iodine is an essential mineral required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. The thyroid gland actively absorbs iodine from the bloodstream and incorporates it into the structures of thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). A deficiency of iodine in the diet can lead to insufficient hormone production (hypothyroidism) and the enlargement of the thyroid gland, a condition known as a simple goitre.
4. What are the key differences between hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism?
Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are two common disorders resulting from abnormal thyroid function. Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland is underactive and produces insufficient hormones, leading to symptoms like weight gain, fatigue, and intolerance to cold. In contrast, hyperthyroidism results from an overactive thyroid producing excess hormones, causing symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, and intolerance to heat.
5. How does the pituitary gland regulate the function of the thyroid gland?
The thyroid gland's function is controlled by a negative feedback mechanism involving the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus releases Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which signals the anterior pituitary gland to secrete Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH). TSH then stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release T3 and T4. When T3 and T4 levels in the blood rise, they inhibit the secretion of TRH and TSH, thus maintaining hormonal balance.
6. Why is the thyroid gland considered a major regulator of the body's Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)?
The thyroid gland is a primary regulator of the Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) because its hormones, T3 and T4, control the speed at which the body's cells convert oxygen and calories into energy. By influencing nearly every organ system, these hormones dictate the rate of cellular respiration and heat production, thereby setting the baseline for the body's energy expenditure at rest.
7. How can an autoimmune condition like Hashimoto's disease lead to hypothyroidism?
Hashimoto's disease is an autoimmune disorder where the body's immune system mistakenly produces antibodies that attack the thyroid gland. This chronic inflammation and attack on the thyroid tissue gradually destroys the hormone-producing cells. As the gland's ability to produce thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) diminishes, it leads to the development of hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid).
8. What is the difference between the thyroid and parathyroid glands in terms of function?
Although located close to each other, the thyroid and parathyroid glands have distinct functions. The thyroid gland primarily regulates the body's overall metabolism through the secretion of T3 and T4 hormones. In contrast, the four small parathyroid glands, located on the posterior surface of the thyroid, are solely responsible for regulating calcium and phosphate levels in the blood by secreting Parathyroid Hormone (PTH), which is essential for bone health and nerve function.










