




Types of Epistasis with NEET-Level Examples and Explanation
The concept of epistasis is essential in biology and helps explain real-world genetic processes and NEET exam-level questions effectively. Understanding epistasis is crucial for solving inheritance pattern questions and distinguishing it from other genetic terms like dominance and codominance.
Understanding Epistasis
Epistasis refers to the genetic interaction where the expression of one gene is masked or altered by the presence of another gene at a different locus. This concept is important in areas like gene interaction, Mendelian ratio alteration, and inheritance patterns in both plants and animals. Epistasis modifies the expected phenotypic ratios based on simple Mendelian genetics, making it a vital chapter in NEET and biology exams.
Types of Epistasis
Epistasis can be classified into different types based on how genes interact:
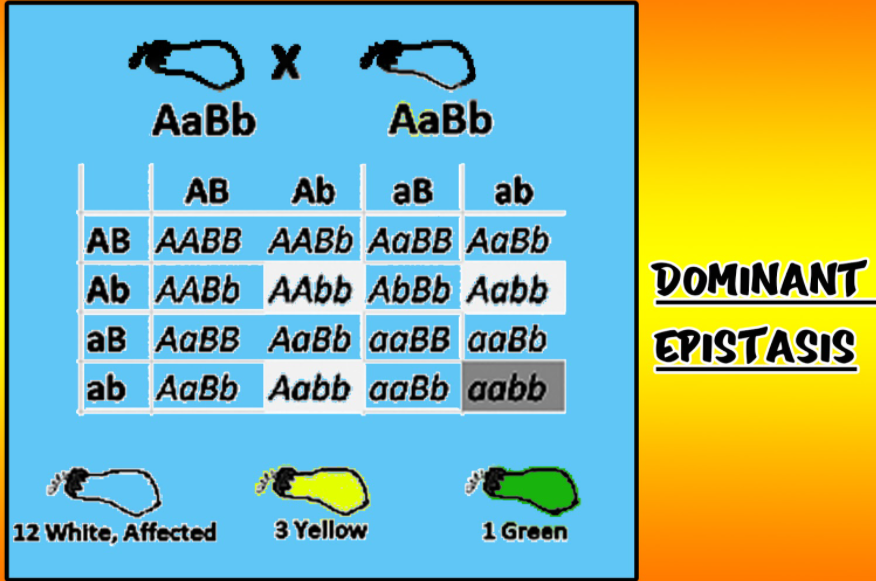
- Dominant Epistasis: A dominant allele masks the expression of alleles at another locus.
- Recessive Epistasis: A recessive pair of alleles masks the expression at a different gene locus.
- Duplicate Epistasis: Either of two genes can produce the phenotype, so one masks the other.
- Suppression Epistasis: A suppressor gene inhibits the expression of another gene.
- Polymeric Gene Interaction: Both dominant alleles contribute to a strengthened or intermediate phenotype.
Here’s a helpful table to understand epistasis better:
Epistasis Types Table
| Type | Description | Typical Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Dominant Epistasis | Dominant allele at one locus masks effects of another gene | 12:3:1 |
| Recessive Epistasis | Homozygous recessive alleles mask effects of another gene | 9:3:4 |
| Duplicate Epistasis | Either gene can mask the effect of the other | 15:1 |
| Suppression Epistasis | A suppressor gene inhibits effect of another gene | 13:3 |
Epistasis Examples
Examples make it easier to remember epistasis for NEET:
- In summer squash, the dominant white gene masks yellow and green, showing dominant epistasis.
- In mice, coat color is affected by recessive epistasis where the albino gene hides other color genes.
- Flower color in sweet peas: Genes C and P both must be present for pigment; any homozygous recessive combination gives a white color – an example of duplicate recessive epistasis.
Difference Between Epistasis and Dominance
| Feature | Epistasis | Dominance |
|---|---|---|
| Gene Interaction | Between different gene loci | Between alleles of same gene |
| Effect | One gene masks another gene’s expression | One allele masks alternative allele |
| Ratio Affected | Alters Mendelian dihybrid ratios (e.g., 9:3:4, 12:3:1) | Standard 3:1 or 9:3:3:1 ratios |
Practice Questions
- What is the basic definition of epistasis in genetics?
- Explain how dominant epistasis affects phenotypic ratios in a dihybrid cross.
- State one example of epistasis in plants or animals.
- Differentiate between epistasis and codominance.
- Draw a diagram showing gene interaction during epistasis.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Confusing epistasis with dominance or codominance—remember, epistasis is always between two different genes.
- Forgetting to check phenotypic ratios when solving dihybrid cross questions.
Real-World Applications
The concept of epistasis is used in plant breeding (improving crop traits), medical genetics (explaining the basis of inherited diseases), and animal breeding (selecting desirable features). Knowing epistasis helps in research, agriculture, and biotechnological innovations. Vedantu helps students connect genetics topics like epistasis to practical life and NEET application questions.
In this article, we explored epistasis, its definition, types, mechanisms, examples, and how it impacts phenotypic ratios. Mastering these points can boost your performance in NEET Genetics questions. For more topics and revision materials, keep practicing with Vedantu and explore related lessons on genetic inheritance.
FAQs on What Is Epistasis? NEET Biology Made Easy
1. What is epistasis in NEET?
In NEET, epistasis refers to a type of gene interaction where one gene (the epistatic gene) masks or modifies the expression of another gene (the hypostatic gene). This interaction often alters the expected Mendelian phenotypic ratios, making it crucial for understanding complex inheritance patterns and solving genetics questions.
2. What is the difference between epistasis and dominance?
The main difference between epistasis and dominance lies in the level of gene interaction: dominance occurs between two alleles of the same gene, where one allele masks the other, whereas epistasis involves interactions between different genes, where one gene masks or modifies the effect of another gene’s alleles.
3. What are the types of epistasis for class 12 and NEET?
The commonly studied types of epistasis in class 12 and NEET include:
- Dominant epistasis: A dominant allele of one gene masks alleles of another gene.
- Recessive epistasis: A recessive allele masks the expression of alleles at another gene.
- Duplicate recessive epistasis: Recessive alleles at either of two loci produce the same phenotype.
- Duplicate dominant epistasis: Dominant alleles at two loci produce similar effects.
- Suppression epistasis (dominant inhibitory): One gene suppresses the effects of another gene.
- Polymeric gene interaction: Combined effect of dominant alleles producing unique phenotypes.
4. Give an example of epistasis in genetics.
A classic example of epistasis is observed in summer squash, where a dominant allele for white color (W) masks the expression of green or yellow color alleles. This is an example of dominant epistasis. Similarly, in Primula plants, production of the pigment malvidin depends on the K gene, but its expression can be suppressed by the dominant D gene, showing dominant inhibitory epistasis.
5. What is an epistatic gene? Who is called a suppressor gene?
Epistatic genes are genes that mask or modify the expression of alleles at another gene locus (hypostatic gene). A suppressor gene is a type of epistatic gene that inhibits or suppresses the expression of another gene’s alleles, often seen in suppression epistasis where the suppressor gene’s product blocks other gene effects.
6. How is epistasis shown in dihybrid crosses for NEET MCQs?
In dihybrid crosses involving epistasis, the typical Mendelian phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1 is altered. For example:
- Dominant epistasis often results in ratios like 12:3:1.
- Recessive epistasis results in a 9:3:4 ratio.
Understanding these ratios helps in solving NEET MCQs by recognizing gene interactions beyond simple dominance.
7. What is epistasis in simple words?
In simple terms, epistasis is when one gene controls or hides the effects of another gene, changing the way traits appear in an organism. This interaction changes the usual inheritance patterns you learn in classic genetics.
8. What is the difference between dominant epistasis and recessive epistasis?
The difference is based on which allele causes the masking:
- In dominant epistasis, a dominant allele of one gene hides the alleles of another gene.
- In recessive epistasis, a recessive allele is responsible for masking the effects of another gene’s alleles.
Each leads to different altered phenotypic ratios in offspring.
9. Why do students confuse epistasis with codominance in NEET?
Students often confuse epistasis with codominance because both involve interactions affecting gene expression. However:
- Epistasis is interaction between different genes where one gene masks another.
- Codominance occurs between two alleles of the same gene, both expressed equally.
Understanding this key conceptual difference helps prevent errors in genetic problem-solving.
10. How can I avoid errors while solving phenotypic ratio MCQs involving epistasis?
To avoid mistakes in epistasis MCQs:
1. Clearly identify which gene is epistatic and which is hypostatic.
2. Memorize standard phenotypic ratios for common epistasis types (e.g., 12:3:1, 9:3:4).
3. Carefully analyze whether masking is due to dominant or recessive alleles.
4. Practice solving multiple dihybrid crosses showing epistasis.
5. Refer to practical examples for conceptual clarity.
11. Are all masking gene effects considered epistasis in NEET questions?
In NEET, not all gene masking effects qualify as epistasis. Epistasis specifically involves one gene masking the effect of another gene at a different locus. Masking within alleles of the same gene (dominance) or other phenomena like gene linkage are not classified as epistasis. Accurate identification is important for correct application in genetics problems.
12. Can epistasis be asked in assertion-reason type NEET questions?
Yes, epistasis is commonly tested in assertion-reason type NEET questions to assess conceptual understanding of gene interactions. Such questions may ask about how epistasis alters phenotypic ratios or distinguish it from dominance and pleiotropy. Practicing these questions helps master the concept efficiently.





















