




What is a Palindromic Sequence? Definition, Rules & Common Examples for NEET
The concept of palindromic sequences is essential in biology and helps explain real-world biological processes and exam-level questions effectively, especially for NEET aspirants preparing for biotechnology and molecular genetics topics.
Understanding Palindromic Sequences
Palindromic sequences are specific DNA sequences that read the same on both the forward and reverse strands when read in the 5' to 3' direction. This phenomenon is due to the complementary nature of DNA. Such sequences are crucial in molecular genetics, biotechnology, restriction enzyme recognition, and recombinant DNA technology. For NEET, knowing how to spot and memorize palindromic sequences can improve your accuracy in molecular biology MCQs.
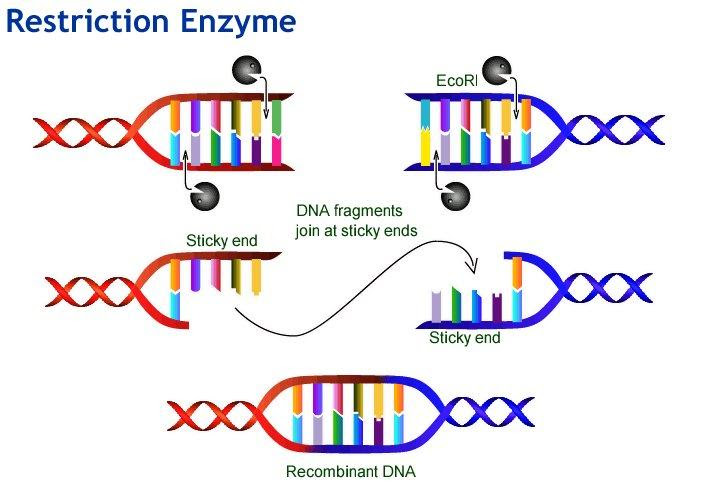
Key Features and Rules of Palindromic Sequences
- Palindromic sequences are typically 4–8 base pairs long.
- They read the same on both strands in a 5' to 3' direction. For example, 5'-GAATTC-3' on one strand pairs with 3'-CTTAAG-5' on the other, which is also 5'-GAATTC-3' in reverse.
- Most restriction enzymes recognize and cut at palindromic DNA sites.
- They are essential for cloning, gene editing, and various lab techniques.
- They should not be confused with English palindromes like "MADAM" or "RACECAR".
Examples of Palindromic Sequences
- EcoRI: 5'-GAATTC-3' / 3'-CTTAAG-5'
- HindIII: 5'-AAGCTT-3' / 3'-TTCGAA-5'
- PstI: 5'-CTGCAG-3' / 3'-GACGTC-5'
- BamHI: 5'-GGATCC-3' / 3'-CCTAGG-5'
- SmaI: 5'-CCCGGG-3' / 3'-GGGCCC-5'
Palindromic Sequences and Restriction Enzymes
Restriction enzymes are molecular scissors that recognize specific palindromic sites and cleave the DNA at or near these sequences. This ability enables scientists to cut and manipulate DNA for applications like gene cloning, DNA fingerprinting, and recombinant DNA technology. For instance, EcoRI cuts between G and A in the sequence GAATTC, producing 'sticky ends' used for ligation of DNA fragments.
Table: 5 Common Palindromic Sequences in NEET
| Restriction Enzyme | Recognition Sequence | Cutting Site |
|---|---|---|
| EcoRI | 5'-GAATTC-3' | G^AATTC |
| HindIII | 5'-AAGCTT-3' | A^AGCTT |
| PstI | 5'-CTGCAG-3' | CTGCA^G |
| BamHI | 5'-GGATCC-3' | G^GATCC |
| SmaI | 5'-CCCGGG-3' | CCC^GGG |
Visualizing Palindromic Sequences
For NEET diagram-based MCQs, practice drawing and recognizing palindromic sequences. Remember, palindromic patterns are symmetric and fit into the double helix structure of DNA, making them easier for enzymes to access and recognize.
Practice Questions
- What is a palindromic sequence? Give two examples.
- Why are palindromic sequences important for restriction enzyme function?
- List any three restriction enzymes and their recognition sites.
- Draw and label a palindromic sequence and its enzyme cut site.
- Explain the difference between a DNA palindrome and an English palindrome.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Confusing palindromic sequences in DNA with normal word palindromes.
- Missing the complementarity of bases (e.g., pairing A with T and G with C).
- Not checking both strands for the same sequence from 5' to 3'.
- Overlooking the role of restriction enzymes and connecting them to palindromic recognition sites.
Real-World Applications
The concept of palindromic sequences is vital in modern biotechnology. They are the key to gene cloning, DNA fingerprinting, genetic engineering, and development of GMOs. In medicine, palindromic sequences are used to diagnose genetic disorders and produce recombinant proteins. Vedantu’s explanations relate these concepts to practical advancements in science and healthcare.
In this article, we explored palindromic sequences, their definition, biological significance, worked examples, and key exam tips. Mastering this topic is crucial for NEET aspirants. To strengthen your knowledge, keep practicing with Vedantu and refer to related topics for deeper understanding.
Explore Related Topics
- Recombinant DNA Technology Process
- Restriction Enzymes
- DNA Structure
- Tools of Recombinant DNA Technology
- Difference Between Restriction Endonuclease and Exonuclease
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Nucleic Acid
- NEET Biology MCQs
- Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA
- DNA Replication
- Transcription (Genetics)
FAQs on Palindromic Sequences in DNA: NEET Revision Notes
1. What is a palindromic sequence in NEET?
A palindromic sequence in DNA is a specific sequence of bases that reads the same on both strands in the 5' to 3' direction. This means the sequence on one strand is the reverse complement of the other strand, which is crucial for recognition by restriction enzymes. Understanding this concept helps students answer questions on molecular genetics and biotechnology in NEET.
2. How to remember palindromic sequences for NEET 2025?
To memorise palindromic sequences effectively for NEET 2025, use these techniques:
• Focus on common restriction enzyme sites like EcoRI (5'-GAATTC-3') and HindIII (5'-AAGCTT-3').
• Visualise the sequences using labelled DNA diagrams.
• Employ mnemonics that highlight the symmetrical nature of palindromes.
• Revise with flashcards or quick reference sheets summarising key patterns.
Applying these strategies improves retention and accuracy in the exam.
3. Give 5 examples of common palindromic DNA sequences?
Here are five classical palindromic DNA sequences commonly asked in NEET:
1. EcoRI: 5'-GAATTC-3'
2. HindIII: 5'-AAGCTT-3'
3. BamHI: 5'-GGATCC-3'
4. SmaI: 5'-CCCGGG-3'
5. PstI: 5'-CTGCAG-3'
Memorising these helps in solving MCQs on restriction sites and recombinant DNA technology.
4. Why are palindromic sequences important in restriction enzyme action?
Palindromic sequences serve as specific recognition sites for restriction endonucleases. These enzymes bind to palindromic sequences and cut DNA at or near these sites, enabling:
• Precise gene cutting for cloning.
• Creation of compatible sticky or blunt ends.
• Application in recombinant DNA technology.
Understanding this action is essential for NEET questions on biotechnology and gene manipulation.
5. What is the palindromic sequence of EcoRI and HindIII?
EcoRI recognises and cuts at the palindrome 5'-GAATTC-3' on one strand and 3'-CTTAAG-5' on the complementary strand.
HindIII recognises 5'-AAGCTT-3' and 3'-TTCGAA-5' respectively.
Both sequences are 6 base pairs long and form perfect palindromes, facilitating enzyme recognition and cleavage.
6. Why do students confuse palindromic DNA with English palindromes?
Students often confuse palindromic DNA sequences with English palindromes because both involve symmetry. However, DNA palindromes are based on complementary base pairing and reading 5' to 3' on both strands, not simple letter reversal. Unlike English palindromes, DNA palindromes require understanding of the reverse complement concept, which is fundamental in molecular biology.
7. How can I avoid missing a palindromic sequence under NEET exam pressure?
To avoid missing palindromic sequences during NEET exams:
• Practice recognising reverse complements swiftly.
• Use diagrammatic representation to visualize strands.
• Familiarise yourself with common restriction sites.
• Memorise key sequence lengths (mostly 4–8 bases).
These techniques reduce error under time constraints.
8. Are all restriction sites palindromic?
Most restriction enzyme recognition sites are palindromic sequences, allowing enzymes to cut DNA symmetrically. However, some enzymes recognise non-palindromic sequences or asymmetric sites. For NEET, the majority of questions focus on palindromic restriction sites, so prioritising these will cover key concepts effectively.
9. Can palindromic errors lead to wrong gene cloning results?
Errors in identifying or cutting at palindromic sequences can cause incorrect gene cloning results by:
• Cutting at wrong sites, leading to unwanted fragments.
• Failure to generate compatible sticky ends.
• Disruption of gene sequences.
Proper understanding and precision in recognising palindromic sites is critical for successful recombinant DNA work in NEET-syllabus biotechnology.
10. What tricks help spot palindromic patterns quickly in MCQs?
To spot palindromic patterns quickly:
• Break sequences into 4-6 base pair segments.
• Check if one strand reads the reverse complement of the other.
• Recall common restriction enzyme sites.
• Use elimination in MCQs by matching sequence length and symmetry.
These tips improve speed and accuracy during NEET exams.























