




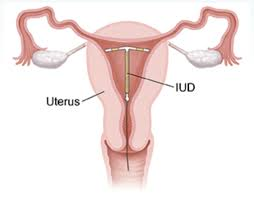
What is an Intrauterine Device?
IUD Full Form stands for Intrauterine Device. It is a small, T-shaped birth control device inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy.
However, it is essential to understand their potential side effects and suitability before choosing this birth control option. Learn and get more insights into ID, its types and benefits.
Understanding Intrauterine Device (IUD): A Reliable Birth Control Method
An Intrauterine Device (IUD) is a small, T-shaped device inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. It is one of the most effective and long-lasting birth control methods, with some types lasting up to 10 years. Depending on the type, an IUD can either release hormones or use copper to prevent pregnancy.
How Does an IUD Work?
IUDs prevent pregnancy by changing the uterine environment, making it difficult for sperm to fertilise an egg. There are two main types of IUDs:
Copper IUDs: Release copper ions, which are toxic to sperm and prevent fertilisation.
Hormonal IUDs: Release progestin, which thickens cervical mucus and thins the uterine lining, preventing sperm from reaching the egg.
What are the Benefits and Risks of IUDs?
Benefits of IUDs
Highly Effective: Over 99% success rate in preventing pregnancy.
Long-Lasting: Protects 3 to 10 years.
Convenient: Once inserted, no daily maintenance is required.
Reversible: Fertility returns immediately after removal.
Non-Hormonal Option: Copper IUDs provide a hormone-free birth control method.
Hormonal Benefits: Some hormonal IUDs help reduce menstrual cramps and lighten periods.
Risks and Side Effects of IUDs
Some women may feel pain during and after insertion.
Hormonal IUDs may cause spotting in the first few months.
Copper IUDs may lead to increased menstrual flow and cramps.
IUDs do not prevent sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
In rare cases, an IUD may move or get expelled from the uterus.
Can an IUD Cause Health Problems?
Most women tolerate IUDs well, but some risks exist, including:
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): Rare but possible if an infection is present during insertion.
Perforation of the Uterus: Very rare but can occur if the IUD punctures the uterus during insertion.
Increased Cramping and Bleeding: More common with copper IUDs, especially in the first few months.
Does an IUD Increase the Risk of Cervical Cancer?
No, IUDs do not cause cervical cancer. Studies suggest that hormonal IUDs may reduce the risk of some cancers, including endometrial cancer. However, women with HPV (Human Papillomavirus) or abnormal Pap smears should consult their doctor before getting an IUD.
Is IUD Insertion Painful?
Some women experience mild to moderate discomfort during insertion.
The pain lasts only a few minutes and can be managed with pain relievers.
Doctors may use local anaesthesia to reduce pain in sensitive patients.
The level of pain varies, but for most women, it is brief and tolerable.
How Long Does an IUD Last?
Copper IUDs: Effective for up to 10 years.
Hormonal IUDs: Last between 3 to 5 years, depending on the brand.
An IUD can be removed anytime if a woman wants to conceive or switch contraceptive methods.
How Effective are IUDs?
IUDs are more than 99% effective, making them one of the most reliable forms of birth control.
They work immediately upon insertion, with copper IUDs also serving as emergency contraception if inserted within 5 days of unprotected sex.
Unlike birth control pills, IUDs do not require daily action, reducing the risk of human error.
Conclusion
IUDs are a safe, effective, and long-term birth control method suitable for many women. They offer high protection, convenience, and reversibility, making them one of the most popular contraceptive choices. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider to determine which type of IUD is best suited for individual needs.Prepare for NEET and medical entrance exams with Vedantu’s comprehensive study materials and interactive video lessons, designed to enhance learning and boost your scores.
Essential Study Materials for NEET UG Success
FAQs on IUD Full Form: Intrauterine Device
1. What is an IUD?
An IUD (Intrauterine Device) is a small, T-shaped contraceptive device inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy.
2. How does an IUD prevent pregnancy?
IUDs prevent pregnancy by either releasing copper ions (toxic to sperm) or progestin (which thickens cervical mucus and prevents implantation).
3. Is an IUD painful to insert?
Some women feel mild to moderate discomfort during insertion, but the pain usually lasts only a few minutes and can be managed with pain relievers.
4. How long do IUDs last?
Copper IUDs can last up to 10 years, while hormonal IUDs last between 3 to 5 years, depending on the brand.
5. Can an IUD fall out on its own?
Rarely, an IUD may get expelled from the uterus, especially within the first few months. Regular self-checks and follow-ups with a doctor help ensure it stays in place.
6. Do IUDs affect periods?
Hormonal IUDs can reduce period flow or even stop periods completely, while copper IUDs may cause heavier periods and cramps in the first few months.
7. Can I get pregnant after removing an IUD
Yes, fertility returns immediately after removal, and many women conceive soon after.
8. Do IUDs protect against STIs?
No, IUDs do not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Using condoms is recommended for STI prevention.
9. Who should avoid getting an IUD?
Women with untreated infections, abnormal uterine shape, or unexplained vaginal bleeding should consult a doctor before considering an IUD.
10. Can I use tampons with an IUD?
Yes, tampons can be safely used with an IUD, but it's important to check that the IUD strings remain in place.























