




What Is Congestive Heart Failure?
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) is a chronic condition where the heart becomes weak and struggles to pump blood efficiently.
This page aims to provide a comprehensive yet easy-to-understand guide on CHF, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and lifestyle changes, to help those affected manage the condition better.
Understanding Congestive Heart Failure?
CHF is when the heart's ability to pump blood is weakened, leading to fluid buildup in the lungs and other body parts. It can develop due to various underlying heart conditions and requires medical intervention for effective management.
What Is Heart Failure?
Heart failure occurs when the heart cannot pump blood efficiently to meet the body's needs. It does not mean that the heart has stopped working, but rather that it is struggling to supply enough oxygen and nutrients to the tissues. This leads to fatigue, shortness of breath, and swelling in different parts of the body.
The Chambers Of The Heart
The human heart consists of four chambers:
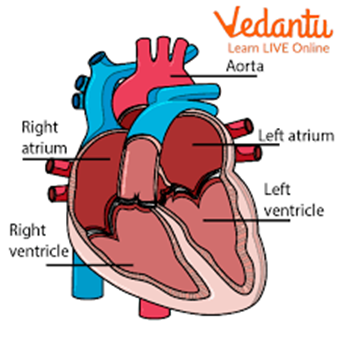
Right Atrium: Receives deoxygenated blood from the body.
Right Ventricle: Pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
Left Atrium: Receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs.
Left Ventricle: Pumps oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body.
In CHF, the ability of the ventricles to pump blood effectively is compromised, leading to congestion and fluid retention.
What Symptoms Does CHF Show?
CHF symptoms develop gradually and worsen over time. Common symptoms include:
Shortness of breath, especially during exertion or lying down
Persistent coughing or wheezing
Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet
Fatigue and weakness
Rapid or irregular heartbeat
Increased need to urinate at night
Sudden weight gain due to fluid retention
Causes Of CHF
Several factors can contribute to CHF, including:
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Narrowing of the arteries reduces blood supply to the heart.
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Increases the workload on the heart.
Heart Valve Disease: Improper functioning of heart valves affects blood flow.
Cardiomyopathy: Damage to the heart muscle weakens pumping ability.
Diabetes: Increases the risk of heart-related complications.
Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats that impair normal circulation.
Treatment Of CHF
Treatment for CHF focuses on managing symptoms, slowing disease progression, and improving quality of life. Options include:
Medications:
Diuretics to reduce fluid retention
ACE inhibitors to relax blood vessels
Beta-blockers to improve heart function
Digitalis to strengthen heart contractions
Lifestyle Changes:
Low-sodium diet to prevent fluid buildup
Regular exercise to strengthen the heart
Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake
Managing stress effectively
Medical Procedures:
Implantable devices like pacemakers or defibrillators
Coronary artery bypass surgery for blocked arteries
Heart transplant in severe cases
Conclusion
CHF is a serious condition that requires early diagnosis and continuous management. By making necessary lifestyle modifications and following medical advice, individuals can improve their heart function and lead healthier lives. Regular check-ups and early intervention play a vital role in managing CHF effectively. Start your preparation with Vedantu’s comprehensive study materials and engaging video lectures, specially designed for NEET and medical entrance exam preparation.
Essential Study Materials for NEET UG Success
FAQs on CHF Full Form : Congestive Heart Failure
What is the full form of CHF?
CHF stands for Congestive Heart Failure, a condition in which the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently, leading to fluid buildup in different parts of the body.
2. What are the causes of CHF?
CHF can be caused by conditions like coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, heart valve disease, diabetes, and cardiomyopathy, among others.
3. What are the symptoms of CHF?
Symptoms include shortness of breath, swelling in the legs and feet, fatigue, persistent coughing, rapid heartbeat, and fluid retention leading to weight gain.
4. What is the treatment of CHF?
CHF treatment includes medications such as diuretics and beta-blockers, lifestyle changes like a healthy diet and regular exercise, and in some cases, medical procedures like pacemaker implantation or heart surgery.
5. Can CHF be seen in children and infants?
Yes, CHF can affect children and infants due to congenital heart defects, viral infections affecting the heart, or metabolic disorders. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for managing the condition in young patients.























