Class 6 Science Mindful Eating Question Answer for Exam Preparation
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Mindful Eatinga Path To A Healthy Body World - 2025-26
1. What are NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 3: Mindful Eating: A Path to a Healthy Body?
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 3 provide detailed, step-by-step answers to all textbook questions. They help students understand key concepts such as mindful eating, balanced diet, and nutrition, following the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus to improve exam performance.
2. How does Chapter 3 define and explain 'mindful eating' according to NCERT Solutions?
Chapter 3 defines mindful eating as being attentive to what and how we eat, making deliberate and healthy food choices. The solutions emphasize the benefits of awareness during meals, which leads to improved digestion, better nutrition, and overall well-being.
3. What are the main components of a balanced diet discussed in NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 3?
The main components listed in the NCERT Solutions are:
- Carbohydrates - provide energy
- Proteins - build and repair tissues
- Fats - store energy
- Vitamins and minerals - maintain body functions
- Dietary fibre - aids in digestion
- Water - necessary for all body processes
4. How do NCERT Solutions for Chapter 3 help differentiate between healthy and unhealthy eating habits?
The solutions offer clear examples and criteria to distinguish healthy eating habits (balanced diet, regular meals, inclusion of fruits and vegetables) from unhealthy eating habits (frequent junk food, irregular timings, excessive sugar or fats), using real-life scenarios for better understanding.
5. According to NCERT Solutions, what are the key benefits of following a balanced diet in Class 6 Science Chapter 3?
- Supports growth and development in children
- Boosts immunity and protects against diseases
- Provides essential nutrients for daily body functions
- Maintains a healthy weight and energy level
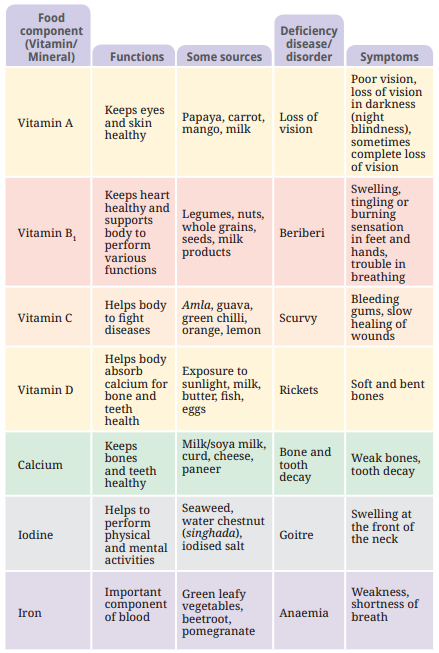
6. How does Chapter 3, as per NCERT Solutions, address the consequences of nutrient deficiencies?
The NCERT Solutions explain that nutrient deficiencies can lead to health problems like night blindness (Vitamin A deficiency), weak bones (calcium/Vitamin D deficiency), and poor immunity. Real-life examples are provided to make this relatable and exam-ready.
7. Why is dietary fibre important according to Class 6 Science Chapter 3 NCERT Solutions?
Dietary fibre is crucial for healthy digestion, preventing constipation, and clearing toxins from the body. The solutions clarify that food sources like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables should be included for optimal digestive health.
8. How do the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 3 recommend students make healthier food choices?
The solutions suggest:
- Choosing fresh, seasonal, and local foods
- Limiting processed and junk foods
- Reading ingredient labels
- Including a variety of food groups in daily meals
9. What role do vitamins and minerals play in our diet, based on NCERT Solutions for Chapter 3?
Vitamins and minerals regulate body processes, prevent infections, and are essential for growth and repair. The NCERT Solutions provide examples like Vitamin A for vision and calcium for strong bones, making it exam-relevant for students.
10. According to NCERT Solutions, how should students plan their meals to include all essential nutrients (FUQ)?
Students are advised to:
- Include elements from all food groups: cereals, pulses, fruits, vegetables, milk, and fats
- Balance portions and meal timings
- Avoid skipping meals to maintain steady energy and nutrition
11. What happens if a student eats only one food group, as explained in NCERT Solutions for Science Chapter 3? (FUQ)
If a student consumes only one food group (for example, only millets or junk food), they will miss out on other essential nutrients, leading to deficiency diseases and poor health, as explained with relevant examples in the solutions.
12. How does the chapter, as covered in NCERT Solutions, recommend handling peer influence regarding junk food? (FUQ)
The solutions emphasize understanding the negative effects of junk food and encourage students to make independent, healthy choices by discussing the long-term benefits of mindfully eating nutritious foods, even in social settings.
13. What insights do NCERT Solutions offer about traditional versus modern eating practices in Chapter 3? (FUQ)
NCERT Solutions compare traditional practices (fresh, local, minimally processed foods) with modern trends (processed, packaged, fusion foods), highlighting the importance of combining the positives of both for a healthy lifestyle.
14. How can students use Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 3 for better exam preparation?
The solutions offer concise, accurate answers following the CBSE guidelines, encourage regular practice of solved questions, and develop conceptual clarity, making revision focused and effective ahead of exams.
15. Are Vedantu's NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 3 aligned with the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus?
Yes, all Vedantu NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 3 strictly follow the latest CBSE 2025–26 guidelines and syllabus, ensuring accuracy and relevance for school assessments.