




How to Solve One Digit Division Problems Easily
Division is the inverse mathematical action of multiplication. We divide a number into equal parts when we divide it. Division is the process of repeatedly subtracting integers. Let us look at a real-life example to learn more about this. Assume you need to give 30 candies among 3 of your buddies in an equitable manner. To ensure that each child receives an equal quantity of candy, divide 30 by the number of friends, which is 3. This is how division functions.
Division By 1 Digit Number
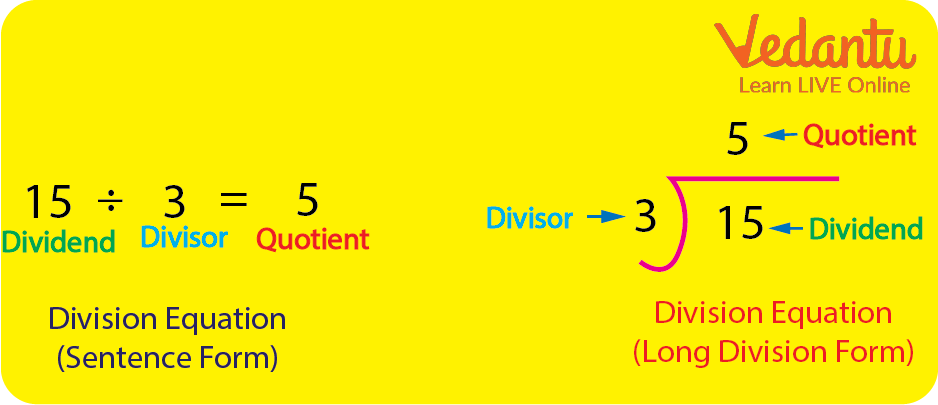
A division equation can be expressed in two ways: sentence form and lengthy division form. Basic arithmetic procedures are employed in the long-division approach. The dividend is the number that is split into equal groups in this case. The divisor is the number of groups by which the dividend is split, and the quotient is the result of the division.
The remainder is a significant portion of a division equation since it is the part that remains after the division operation is completed. The remainder in the preceding case is zero since there is no integer left over.
Example of Division 2-Digit By 1 Digit
One Digit Division Sums
Let us take another example of division 2-digit by 1-digit to understand it better.
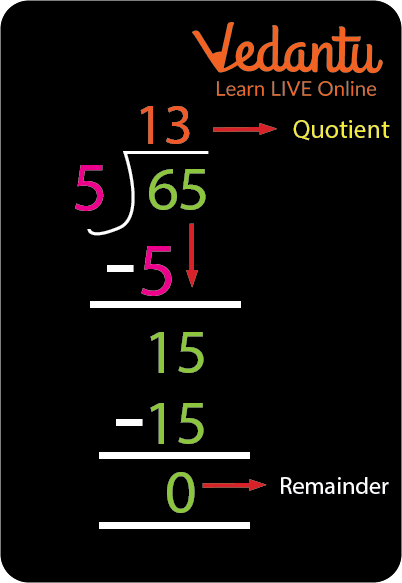
Example 1: Let's divide 65 by 5.
Step One: The first digit 6 is greater than the divisor (5). So we can directly use 5 in this case and subtract 5 from 6. This will give us the remainder as 1 and the quotient as 1.
Step Two: Bring down the next digit and form a new number with the remainder. The new number is 15.
Step Three: 15 is directly divisible by 5 as 5 multiplied by 3 is 15. After their subtraction, we will get the remainder as 0 and the new quotient will be 13.
Example of Division of 2 Digit Number By 1 Digit
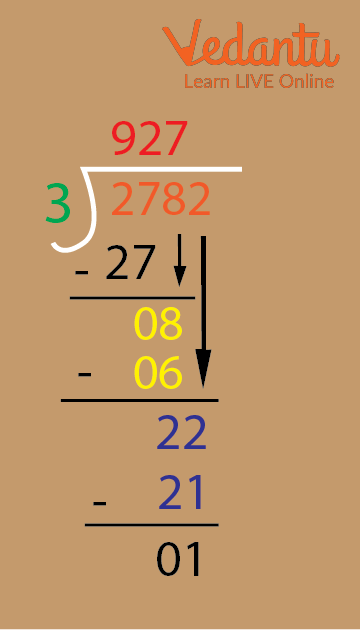
Example 2: Divide 2782 by 3.
Step One: The first digit is less than the divisor which will not be divisible by 3 so we need to take the next digit. 27 is divisible by 3. So we subtract 27 by 27 and get the remainder as 0 and the quotient as 9.
Step Two: Let's take the next digit down. 8 is now subtracted by 6 which leaves us with the remainder of 2 and the new quotient becomes 92.
Step Three: The next digit 2 is now brought down and the new number becomes 22. This can be subtracted from 21 which comes in table 3. We get the remainder as 1. And the quotient is 927.
Division Example
Conclusion
The one-digit division is the easiest type of division. The one-digit divisor can range from 1 to 9. The basis of the division is to find multiple, subtract, bring down the next digit and repeat. A one-digit division is much easier than a two and three-digit division.
Sample Questions
1. If there are 55 pencils to be distributed among 5 people. How many pencils would each one get?
a. 30
b. 40
c. 3
d. 11
Ans: 11
Explanation: Step one: Find the multiple of the first digit and subtract it from that.
Step two: Bring down the next digit and find the multiple of the new number formed.
Step three: The remainder comes out to be 0.
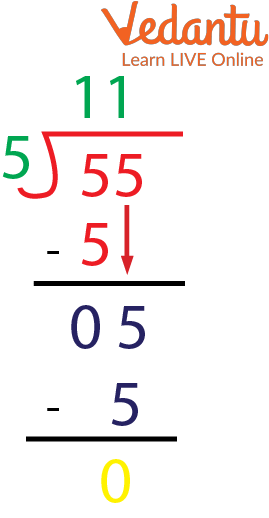
Division of 55 By 5
2. Divide 120 by 4.
a. 30
b. 40
c. 3
d. 10
Ans: 30
Explanation: As 4 when multiplied by 3 gives us 12 so 12 is divisible by 4. This will give us a remainder of 0. As the next digit is also 0 the new number is 0 and 4 when multiplied by 0 will give us 0. Making the quotient 30.
3. We need to distribute 369 candies among 9 students. Each student will receive.
a. 40
b. 41
c. 42
d. 43
Ans: 41
Explanation: total number of candies is 369.
The number of students is 9.
Each student will get 41 candies.
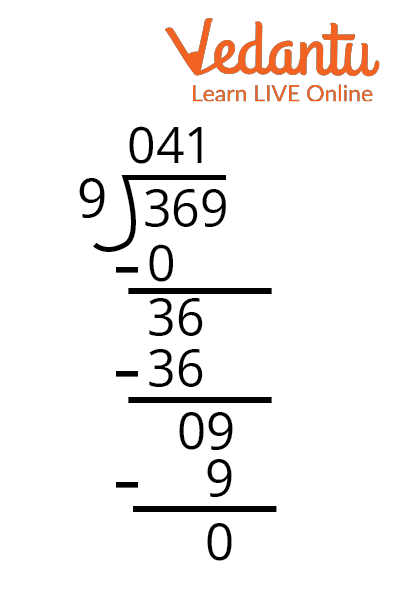
Division of 369 By 9
FAQs on One Digit Division: Step-by-Step Guide
1. What are the basic steps for one-digit division?
Solving a one-digit division problem involves a few simple steps. For example, to solve 45 ÷ 5, you would:
Step 1 (Divide): See how many times the divisor (5) fits into the dividend (45). From multiplication tables, we know 5 x 9 = 45.
Step 2 (Write Quotient): Write the answer, which is called the quotient, on top. In this case, the quotient is 9.
Step 3 (Check Remainder): Since 5 fits perfectly into 45, there is nothing left over. The remainder is 0.
2. What are the important parts of a division problem?
Every division problem has four key parts that you need to know:
Dividend: The number that is being divided (the total amount). For example, in 13 ÷ 4, the dividend is 13.
Divisor: The number you are dividing by. In 13 ÷ 4, the divisor is 4.
Quotient: The result or answer of the division. In 13 ÷ 4, the quotient is 3.
Remainder: The amount that is 'left over' after dividing. In 13 ÷ 4, the remainder is 1.
3. What is the main difference between division and multiplication?
The main difference is that they are opposite operations. Multiplication is about combining equal groups to find a total. For example, 3 groups of 4 apples (3 × 4) give you a total of 12 apples. Division is about splitting a total into equal groups. For example, splitting 12 apples among 3 friends (12 ÷ 3) means each friend gets 4 apples.
4. How can I check if my one-digit division answer is correct?
You can easily check your division answer by using multiplication. This is a great way to ensure you have solved the problem correctly. The rule is: (Divisor × Quotient) + Remainder = Dividend. For example, if you solved 22 ÷ 5 and got a quotient of 4 with a remainder of 2, you can check it like this: (5 × 4) + 2 = 20 + 2 = 22. Since 22 was your original dividend, the answer is correct.
5. What does the remainder really mean in a division problem?
The remainder is the 'leftover' part that cannot be divided equally into the groups. Imagine you have 14 pencils and want to share them equally among 3 friends. Each friend gets 4 pencils (3 × 4 = 12). You will have 2 pencils left over that you cannot share without breaking them. That leftover amount, 2, is the remainder. It represents the part of the dividend that was too small to form another full group.
6. How is one-digit division used in real life? Can you give examples?
One-digit division is used very often in daily situations. It helps us understand how to share things fairly or sort them into groups. Some real-world examples include:
Equal Sharing: If you have a chocolate bar with 15 squares and want to share it among 3 people, you use division (15 ÷ 3) to find out that each person gets 5 squares.
Equal Grouping: If a teacher has 20 students and wants to make teams of 4, she uses division (20 ÷ 4) to find out she can make 5 teams.
Planning: If you need to plant 30 seeds in 5 rows, you divide (30 ÷ 5) to know you must plant 6 seeds in each row.
7. Why is there sometimes a zero in the middle of a quotient?
A zero appears in the quotient when the divisor is larger than a digit in the dividend you are trying to divide. For example, in the problem 612 ÷ 6: First, you divide 6 by 6, which is 1. Next, you bring down the 1 from the dividend. You cannot divide 1 by 6 to get a whole number, so you place a zero in the quotient (1 ÷ 6 = 0 with a remainder). Then, you bring down the next digit, 2, making the new number 12. Finally, you divide 12 by 6, which is 2. The final answer is 102. The zero shows that there were no groups of 6 in the 'tens' place.























