




Vocabulary List: Math Terms Beginning With V Explained
In Mathematics, many important words start with the letter ‘V’. These are important to learn and add to your dictionary. It will not only make a better understanding of the subject, but you can differentiate with their meaning as used in the English language.
Let’s read the article till end to know more about some maths words that start with v which are widely used.
Maths Words that Start with Letter V
1. Variable: A variable is a mathematical alphabet or any symbol that is used to represent any quantity or value. It is widely used in coordinate geometry or anywhere the equations are used.
For example: 2x + 3y = 20; Here, x and y are variables.
2. Vector: Vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. Displacement and Velocity are vector quantities. Any vector quantity is represented by adding a vector sign (→) over a variable.
3. Velocity: As we know, velocity is a vector quantity. It tells the speed of an object along with its direction. Velocity is equal to the displacement of an object with respect to the time taken to cover the distance.
4. Venn Diagram: It is the pictorial representation of mathematical or logical sets. They are generally made of circles and enclosed in a rectangle to represent a universal set.
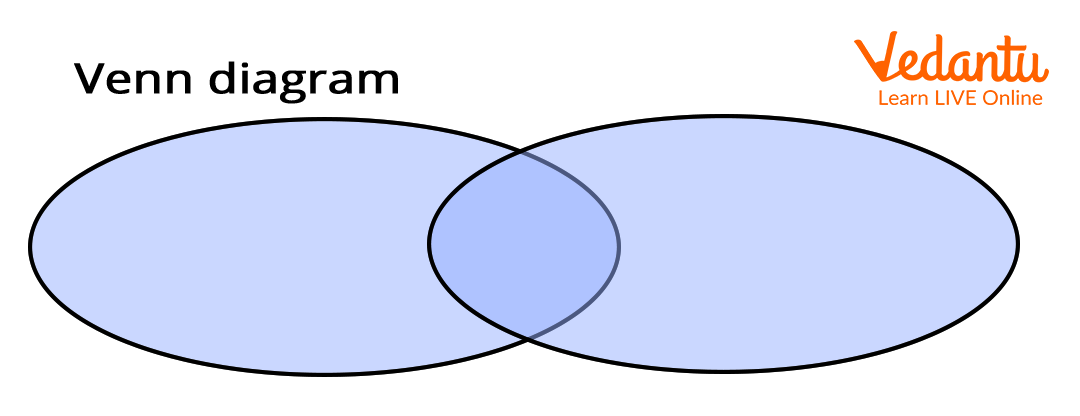
Venn Diagram
5. Vertex: A vertex is a point where two lines or one line and a curve or two curves meet at a point. The plural of vertex is ‘vertices’. A triangle has three vertices, a rectangular figure and a square has four vertices, a pentagon has five vertices, and so on. If we make an angle, then there will be only one vertex that made where two rays met at each other.
6. Vertical Axis: The axis which is perpendicular to the horizontal plane or horizontal axis is called the vertical axis. In general, it is denoted as the Y-axis.
7. Vertical Angles: The angles formed by the two intersecting lines are called vertical angles. Vertical angles, a and b are shown in the below figure:
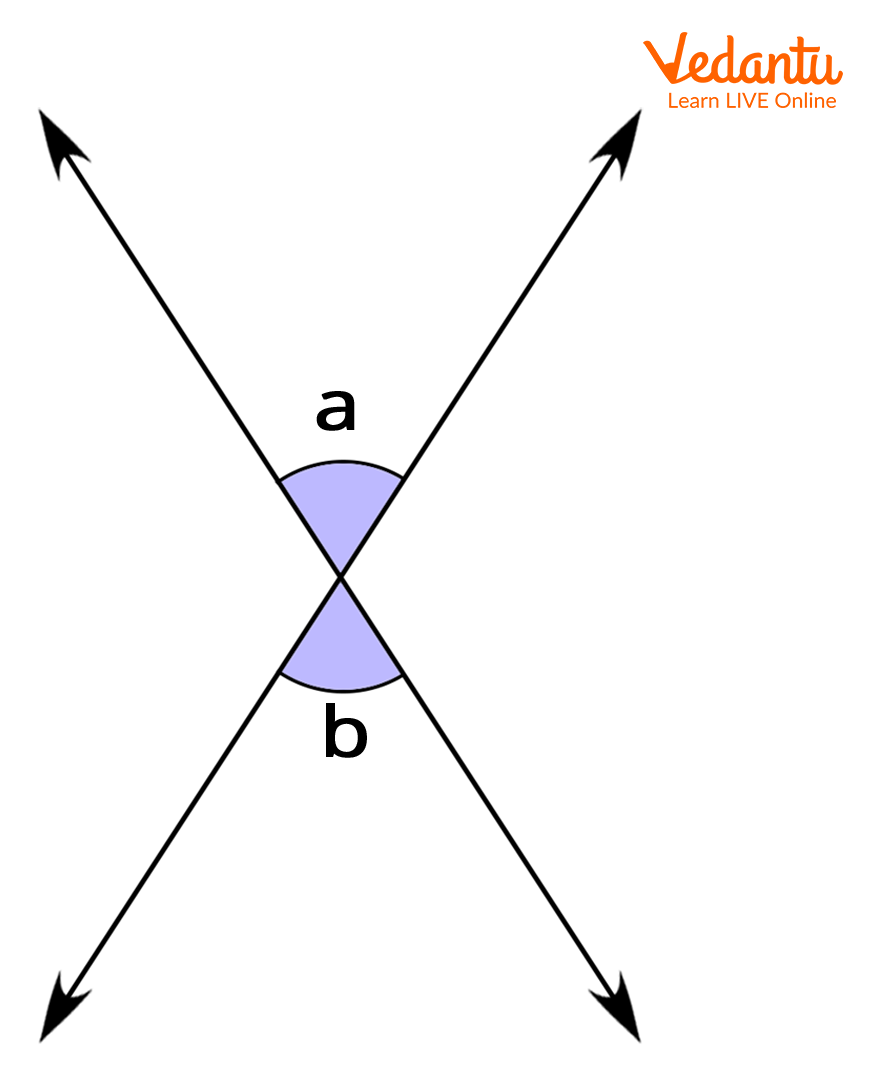
Vertical Angles
8. Volume: The space occupied or enclosed within a 3-dimensional object or solids is called volume. It is usually denoted by the English alphabet ‘V’. There are various methods and certain formulas to evaluate the volume of an object. Some of the formulas to evaluate the volume of fixed shape objects are following:
Volume of Cube = side x side x side
Volume of Cuboid = length x breadth x height
The volume of Sphere = V = $\frac{4}{3}$πr3, where r is the radius of the sphere.
9. Vigesimal: Vigesimal is the number system based on ‘20’.
10. Value: Value is any magnitude, quantity, or number that is used to denote any numerical amount by an algebraic term.
Do You Know?
A circle or sphere has no vertex.
Conclusion
In this article, you learnt about some key mathematical words starting from the alphabet ‘V’. Learning these maths words will enhance your vocabulary and communication skills. Also, you can differentiate their meaning used in Mathematical context or general context.
To learn more keywords started from other alphabets, explore our website. Also, you can learn more topics and methods to solve any type of mathematical problem; for that, you only need to discover the stuff we had for you, my dear child!
FAQs on Essential Math Words That Start With V
1. What is velocity?
Velocity is a vector quantity. It is defined as the rate of change of an object’s position with respect to a frame of reference. It is a function of time. Its SI unit is metre/sec.
2. What is a vertex in Geometry?
In Geometry, a vertex is a point where two lines or rays or arcs with any line coincide with each other. The plural of vertex is vertices. In angle, there is only one vertex. In a triangle, there are three vertices and in a quadrilateral, there are four sides. Therefore, the number of vertices in the closed figure is equal to the number of sides.

















