




How to Add Algebraic Expressions: Rules and Examples
The addition of algebraic expressions and the addition of numbers are very similar operations. The classification of terms in an algebraic expression into similar and unlike terms is necessary for the addition of algebraic expressions, then picking up and including similar terms. Similar to this, only the numerical coefficient can be adjusted.
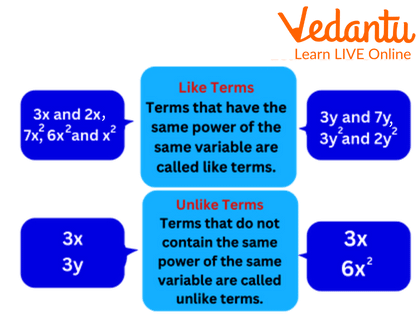
Like terms and Unlike Terms
How to Add Algebraic Expressions:
In order to do addition of algebraic expressions, we must first collect all similar terms. The only like term whose coefficient is the combination of the coefficients of like terms is the sum of the like terms.
Will three pencils and three erasers work? NO will be your answer. Three pencils and three erasers are two different objects; hence we can't add them together. The situation with terms in an algebraic expression is identical. No more than two opposite terms can be combined. It's important to keep in mind that we can only add similar terms to algebraic expressions. Algebraic expressions sums can be obtained by using one of two methods:
Horizontal method of Algebra Addition
Column method for Algebra Addition
Horizontal Method of Algebra Addition
The following list of steps outlines how to add algebraic expressions using the horizontal method:
Step1: Write all the expressions on a horizontal line between an additional sign and brackets.
Step 2: Rewrite the expression after collecting all the similar terms from all the expressions.
Step 3: Add the numerical coefficients of all the similar terms and the common variable.
Step 4: Rewrite the phrase to make it more concise, and ensure that all of the terms in the final solution are opposite terms.
Column Method of Algebra Addition
Step1: Write each expression one below the other in step one. Make sure all terms are in the same column.
\[\begin{array}{l}2{x^2} + 3x - 4y + 7\\{\rm{ }}5x + 4y - 3\end{array}\]
For instance, if a term appears in the first expression but its equivalent does not appear in the second, either write that term below it or leave that column empty.
Step 2: Write the common variable in the same column after adding the numerical coefficients of each column (similar terms).
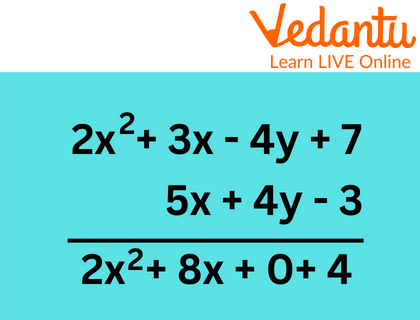
Column Method
Step 3: Rewrite the final response, \[2{x^2} + 8x + 4\]
Conclusion
We need to first assemble all related terms before we can add algebraic expressions. The sum of similar terms is the only like term whose coefficient combines the coefficients of other like terms.
Solved Examples
Example 1: What equation should \[[3{a^2} - 5b + 2c]\] be subtracted from to arrive at \[\left( {{a^2} + 5c} \right)\] as the solution?
Ans: We must sum both formulas \[[3{a^2} - 5b + 2c)\]+\[\left[{{a^2} + 5c} \right]\] \[ = 4{a^2} - 5b + 7c\] to determine from \[[3{a^2} - 5b + 2c]\]what should be subtracted to get \[\left[ {{a^2} + 5c} \right]\].
\[[3{a^2} - 5b + 2c]\] should be subtracted from \[= 4{a^2} - 5b + 7c\]
Example 2: Add \[6x + 4y - 7z,3x - 2y,x + 8y - 9z\]
Ans: Writing like terms one below the other , we will get:
+\[\begin{array}{l}6x + 4y - 7z \\3x - 2y \\x + 8y - 9z\end{array}\]
\[10x + 10y - 16z\]
\[10x + 10y - 16z\]
Example 3: 5. Add the \[\left[ {3x + 2y} \right]\] and \[\left( {x + y} \right]\] by horizontal method.
Ans: Horizontal Method:
\[\left( {3x + 2y} \right] + \left[ {x + y} \right)\]
Arrange the like terms together, and then add.
\[\begin{array}{l} = 3x + 2y + x + y\\ = 4x + 3y\end{array}\]
FAQs on Algebra Addition Explained: Key Concepts & Strategies
1. What is the first and most important rule for adding algebraic expressions?
The most important rule for adding algebraic expressions is to group and combine only 'like terms'. Like terms are terms that have the exact same variables raised to the same power. Before adding, you must identify and arrange these like terms together.
2. What are 'like terms' in algebra and why are they essential for addition?
In algebra, 'like terms' are terms that contain the same variables with the same exponents. For example, 5x² and -2x² are like terms, but 5x² and 5x are not. They are crucial for addition because you can only add or subtract the numerical coefficients of like terms. This concept is similar to how you can add '3 apples and 2 apples' to get '5 apples', but you cannot add '3 apples and 2 oranges'.
3. How do you add algebraic expressions using the column method?
To add algebraic expressions using the column method, as per the CBSE/NCERT curriculum, you should follow these steps:
First, write each expression on a separate row.
Align the expressions so that like terms are placed directly below one another in the same column.
If a term is missing in an expression, you can leave a blank space in that column or write a zero as a placeholder.
Finally, add the numerical coefficients of the terms in each column, and write the result below with the common variable part.
4. Can you provide a simple example of adding two algebraic expressions?
Certainly. Let's add the expressions (3a + 4b) and (5a - 2b).
Step 1: Group the like terms: (3a + 5a) + (4b - 2b).
Step 2: Add the coefficients of the like terms: (3+5)a + (4-2)b.
Step 3: Simplify to get the final answer: 8a + 2b.
5. What is the result of trying to add 'unlike terms' in an algebraic expression?
Unlike terms, which are terms with different variables or the same variables with different powers (e.g., 3x and 4y, or 7a² and 7a), cannot be simplified into a single term. When you add them, the expression remains as a sum of those terms. For example, the addition of 3x and 4y is simply written as the expression 3x + 4y.
6. Why, conceptually, can we only add like terms in algebra?
We can only add like terms because the variable part represents a specific but unknown quantity or object. Think of 'x' as 'books' and 'y' as 'pens'. If you have an expression '2x + 3x', it represents '2 books + 3 books', which can be combined to a total of 5 books (5x). However, an expression like '2x + 3y' represents '2 books + 3 pens'. You cannot combine them into a single item type; you have two distinct groups. Algebra follows this fundamental logic, treating variables as unique categories.
7. How is the addition of algebraic expressions used in real-life problems?
Adding algebraic expressions is a practical tool for modelling real-world scenarios. For example:
Calculating Total Cost: If a family's monthly expense on groceries is (4g + 2m) and on utilities is (3g - m), where 'g' is a cost factor, their total monthly expense is found by adding the two expressions: (4g + 2m) + (3g - m) = 7g + m.
Finding Perimeters: The perimeter of a triangle with sides of length 'a', 'a+2', and 'b' is found by adding the expressions: a + (a+2) + b = 2a + b + 2.
8. What is the primary difference between adding algebraic expressions and adding regular numbers?
The primary difference lies in the concept of like terms. When you add regular numbers like 125 + 53, you are combining quantities of the same type (ones with ones, tens with tens). In algebra, you deal with both numbers (coefficients) and variables. You must respect the variables as distinct categories and can only combine terms that are identical in their variable part. In arithmetic, all numbers are 'like terms' and can be freely combined.
9. What is the main advantage of the column method over the horizontal method for algebra addition?
The main advantage of the column method is its superior organisation, which is especially helpful when adding multiple or complex expressions. By aligning like terms vertically, it provides a clear visual structure that significantly reduces the risk of errors, such as accidentally combining unlike terms or missing a term entirely. The horizontal method, while quicker for very simple problems, can become confusing and prone to mistakes as the number of terms increases.

















