




How to Multiply 3 Digit Numbers Quickly and Accurately
3-digit multiplication involves multiplying 3-digit numbers with 1-digit, 2-digit, and 3-digit numbers by placing them at their correct place values. This multiplication goes difficult with 2 and 3-digit numbers. However, multiplying 3-digit with 1-digit is quite simple.
Therefore, in this article, we will learn about 3-digit with 1-digit multiplication, 3-digit with 2-digit multiplication, and 3-digit with 3-digit multiplication along with regrouping and without regrouping numbers. We will understand these through detailed steps and solve examples so you can have a good grasp of concepts and solve questions easily.
Further, this article will help you score good marks in this chapter and improve your grades.
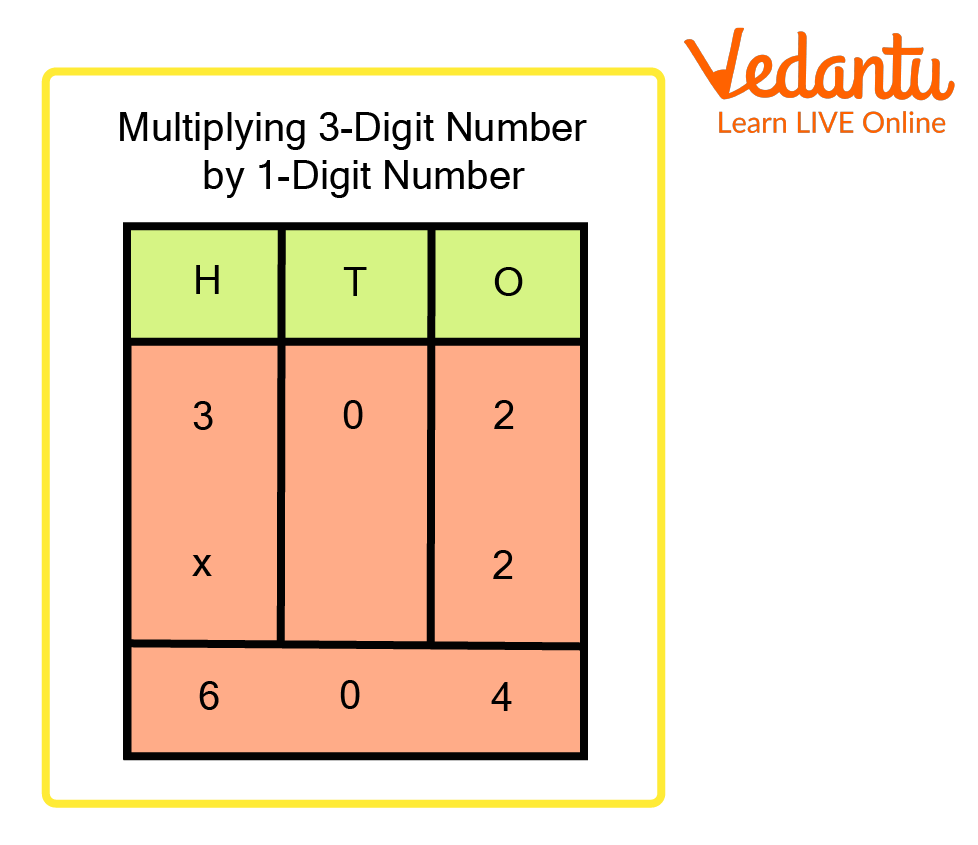
3-Digit Multiplication with 1-Digit
What is 3-Digit Multiplication?
It is a method of multiplying 3-digit numbers with other numbers. During the multiplication, the numbers are arranged in the columns as per their place values. The 3-digit numbers are arranged according to their place values as ones, tens, and hundreds.
While multiplying the two sets of digits, the larger number is kept on the top and the smaller number is placed below it. The number placed on top is called the multiplicand and the number placed below is called the multiplier.

An Example of 3-Digit Multiplication
After arranging the numbers according to their place values, the multiplier is multiplied by all the digits of the multiplicand one by one starting from the left. Firstly, the one digit is multiplied, followed by the tens digit, and then the hundreds digit. Thus, the product obtained is the final result.
Let us understand this with some multiplication examples.
Example 1 – When we multiply 211 by 3, we get 633.

Multiplication of 211 by 3
Let us now understand how to do this multiplication with other numbers.
Multiplication of a 3-Digit By a 1-Digit Number
In this type of multiplication, there are two cases:
3-Digit Multiplication without Regrouping – In this multiplication, the 1-digit number is simply multiplied by the 3-digit number without any carry-overs.
For example –Multiply 314×2

Multiplication of 314 by 2
3-Digit Multiplication with Regrouping – It is multiplication in which the 3-digit number is multiplied by the 1-digit number using the carry-overs.
For example – Multiply 315×2

Multiplication of 315 by 2
Multiplication of a 3-Digit By a 2-Digit Number
In this type of multiplication (3-digit), we multiply the digits by placing the 3-digit on the top and the 2-digit number below it. This multiplication is also performed with regrouping and without regrouping.

An Example of 3-Digit Multiplication with 2-Digit
During the multiplication of a 3-digit number by a 2-digit number, the one digit of the multiplier is multiplied with the multiplicand. Then, zero is placed under the one digit of the number obtained. After this, the tens digit of the multiplier is multiplied with the multiplicand. Then, both these products are added to get the final result.
Let us discuss this through examples.
Example 1 – Multiply 511×21

Multiplication of 511 by 21
Example 2 – Multiply 213×14
It is a 3-digit multiplication with regrouping

Multiplication of 213 by 14
Multiplication of a 3-Digit By a 3-Digit Number
Before doing multiplication, arrange the numbers according to their place values. Firstly, the one digit of the multiplier is multiplied by the multiplicand, followed by the tens digit, and then the hundreds digit.
The products so obtained will get added to obtain the final product. The method of this multiplication is the same as the previous one.
Let us discuss some multiplication sums with answers to understand this.
Example 1 – Multiply 311×123

Multiply 311 by 123
Here two zeroes are placed under ones and tens digit.
Example 2 – Multiply 314×213

Multiply 314 by 213
Summary
3-digit multiplication is multiplication in which each digit of the multiplier is multiplied with the multiplicand. This multiplication is of three types. These are:
3-digitby1-digit multiplication
3-digit by 2-digit multiplication
3-digit by 3-digit multiplication
The above multiplication types have two scenarios, with regrouping and without regrouping. The 3-digit multiplication becomes easy if 3-digit multiplication tricks are followed correctly.
FAQs on 3 Digit Multiplication Explained: Strategies and Examples
1. What exactly is 3-digit multiplication?
3-digit multiplication is the process of finding the product of two numbers where at least one of them contains three digits. For example, multiplying a 3-digit number by another 3-digit number (like 123 × 456) or by a 2-digit number (like 789 × 12). It is an essential arithmetic skill built upon the fundamentals of single and double-digit multiplication, used for solving more complex calculations.
2. How do you solve a 3-digit multiplication problem step-by-step using the standard method?
To solve a 3-digit multiplication problem like 451 × 235, follow these steps:
Step 1: Multiply by the ones digit. Multiply 451 by the ones digit of the second number (5). So, 451 × 5 = 2255. This is your first partial product.
Step 2: Multiply by the tens digit. Multiply 451 by the tens digit (3). So, 451 × 3 = 1353. Add a zero as a placeholder at the end, making it 13530. This is your second partial product.
Step 3: Multiply by the hundreds digit. Multiply 451 by the hundreds digit (2). So, 451 × 2 = 902. Add two zeros as placeholders at the end, making it 90200. This is your third partial product.
Step 4: Add the partial products. Add the results from the previous steps: 2255 + 13530 + 90200 = 105985.
3. Why is it important to learn how to multiply 3-digit numbers?
Learning 3-digit multiplication is crucial as it forms the foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts like algebra, long division, and fractions. It also develops critical problem-solving skills and number sense. In daily life, it is used for practical tasks such as calculating the total cost of multiple expensive items, determining the area of large spaces, or planning budgets for events.
4. What are some of the main strategies used for 3-digit multiplication?
Besides the standard method, students can use several other effective strategies for 3-digit multiplication:
The Area/Box Method: This visual strategy involves breaking down each number into its place values (e.g., 123 becomes 100, 20, and 3) and drawing a grid. You multiply the corresponding parts and then add all the products together.
Partial Products Method: Similar to the box method but without the grid, you multiply each place value of one number by each place value of the other number and then sum up all the resulting 'partial products'.
Vedic Maths Method: This uses a 'vertically and crosswise' formula to get the answer in fewer steps, making it a fast and efficient shortcut.
5. How does the distributive property of multiplication make solving 3-digit problems easier?
The distributive property allows you to break down a large multiplication problem into a series of smaller, simpler ones. For instance, to calculate 524 × 8, you can 'distribute' the 8 across the expanded form of 524. The problem becomes (500 × 8) + (20 × 8) + (4 × 8). This simplifies the calculation to 4000 + 160 + 32, which is easy to add mentally to get the final answer, 4192.
6. Can you provide a real-world example where 3-digit multiplication is necessary?
Certainly. Imagine a concert hall with 28 rows of seats, and each row contains 115 seats. To find the total number of seats in the hall, you need to perform 3-digit multiplication: 115 × 28. This calculation helps the event organisers know the maximum capacity and how many tickets they can sell.
7. What is the most common mistake students make in 3-digit multiplication?
The most frequent error is forgetting to use placeholders (zeros) when multiplying by the tens and hundreds digits. When you multiply by the tens digit, you must add one zero to the partial product. When you multiply by the hundreds digit, you must add two zeros. Missing these placeholders leads to incorrect alignment of numbers and a wrong final answer.
8. How is multiplying a 3-digit number by a 3-digit number different from multiplying it by a 2-digit number?
The core process is similar, but the main difference lies in the number of steps and partial products. When multiplying a 3-digit number by a 2-digit number, you calculate two partial products (one for the ones digit and one for the tens digit). However, when multiplying a 3-digit number by another 3-digit number, you must calculate three partial products (for the ones, tens, and hundreds digits), which are then added together. This makes the 3x3 multiplication longer and requires more careful addition.























