




Key Differences Between 2D and 3D Shapes with Visual Examples
Everything we observe in the world has a shape. In the objects we see around us, we can find different basic shapes such as the two-dimensional square, rectangle, and oval, as well as the three-dimensional rectangular prism, cylinder, and sphere. Credit cards, notes and coins, finger rings, photo frames, dart boards, houses, windows, magician's wands, high buildings, flower pots, toys, and balloons are all examples of geometric shapes.
The number of sides or corners of a shape changes from one to another. A side, or vertex, is a straight line that forms part of a shape, and a corner, or vertex, is the point where two sides meet. You're already familiar with the most common shapes, and may not be able to explain the differences between a square and a cube, or a circle and a sphere. In this article you'll start analysing and comparing 2D and 3D shapes, explaining their similarities, differences, and properties.
What are 2D shapes?
2D stands for two-dimensional in 2D shapes. Shapes with two dimensions, such as width and height, are known as 2D shapes. A rectangle or a circle are examples of 2D shapes because they don’t have depth. Basically 2D objects are flat and can't be physically held. We usually refer to dimensions as measurements in a specific direction. Length, width or breadth, depth, and height are examples of dimensions.
Examples of 2D Shapes:
Circle
There is just one bent side of a circle.
A semi-circle has two sides, one curved and one straight.
The full arc of the semi-circle measures 180 degrees.
Triangle
An equilateral triangle is a triangle with each angle measuring 60°.
Any triangle with one right angle is a right-angled triangle.
An irregular triangle is a scalene triangle. All of the sides and angles are unique.
Two sides and two angles of an isosceles triangle are the same.
Quadrilaterals
A square is a regular quadrilateral with 90o angles on all sides.
The diagonals of a kite intersect at right angles and have two sets of equal length sides.
A rectangle is made up of two sets of parallel straight lines, each with a 90° angle.
A rhombus has equal sides and opposite equal angles, as well as two sets of parallel lines.
One pair of parallel lines makes up a trapezium.
Two pairs of parallel lines with opposite equal angles make up a parallelogram.
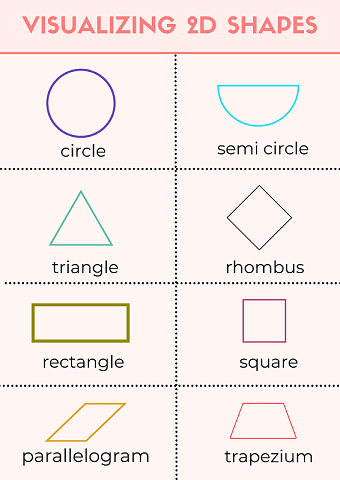
Image Shows the Illustration of 2D Shapes
3D Shapes
3D means it has three dimensions. So , it isn't flat like a 2D shape. The dimensions of 3D shapes include length, breadth, and depth. Examples of 3D shapes include spheres, cuboids, cubes, square-based pyramids, cylinders, and cones.
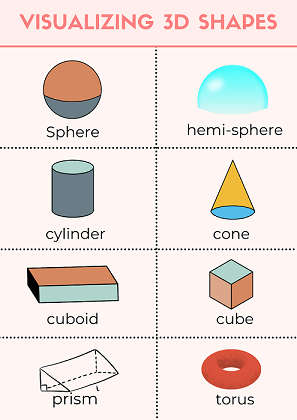
Image Shows the Illustration of 3D Shapes
Properties of 3D shapes
A 3D shape will have faces, edges and vertices.
A face on a 3D form is also known as a 'side.' It can be either flat or curved. As a result, a cube has six faces while a sphere has only one.
An edge is the point where two faces or sides of a face meet. You'll find 12 edges on a cube if you count the edges. However, a sphere, such as a ball, has no edges.
A corner is another name for a vertex. This is the point at where the edges meet.
Depending on the shape of the base, the properties of a pyramid can change. A square-based pyramid, for example, has five faces, while a triangle-based pyramid has four.
Differences Between 2D and 3D shapes
You might be confused by the differences between 2D and 3D shapes. There are some ways to measure an object in space. 3D objects can be measured in length, width, and height. 3D shapes, unlike 2D shapes, do not have a flat surface. Means they have depth. Two-dimensional shapes have two dimensions, while three-dimensional shapes have three dimensions. The most important thing for you to understand is that the primary difference between 2D and 3D shapes is their dimension.
Conclusion
2D and 3D shapes are maths topics that fall under geometry. They're covered in other portions of the curriculum as well. In year 3 shapes, you will study, analyse, and compare the qualities of 2D shapes, as well as create patterns using them and solve problems with them. Know how to spot 2D shapes in things like buildings, road signs, and other common objects. This article also gives you an introduction about 3D shapes which will help you in the higher classes.
FAQs on 2D and 3D Geometric Shapes: Complete Guide for Students
1. What are 2D geometric shapes?
A 2D geometric shape is a flat figure that has only two dimensions: length and width. Examples include a square, circle, triangle, and rectangle.
- These shapes do not have depth
- They are completely flat
2. What is the main difference between 2D and 3D shapes?
The main difference is that 2D shapes have length and width only, while 3D shapes have length, width, and height or depth. 3D geometric shapes occupy space and have volume; 2D shapes are flat and have only area.
3. Can you give examples of common 3D geometric shapes?
Common 3D geometric shapes include the cube, sphere, cylinder, pyramid, and cone.
- These shapes have three measurements
- They occupy space
- They have a measurable volume and surface area
4. How do you calculate the area of a 2D shape?
To find the area of a 2D geometric shape, use a specific formula depending on the shape. For example, the area of a rectangle is $Area = length \times width$, while the area of a circle is $Area = \pi r^2$.
5. How do you calculate the volume of a 3D shape?
The volume of a 3D geometric shape is found using a formula suited for that shape. For a cube, it is $Volume = side^3$. For a cylinder, it is $Volume = \pi r^2 h$, where r is radius and h is height.
6. What is the difference between perimeter and surface area?
The perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a 2D geometric shape. Surface area is the total area covering the outside of a 3D geometric shape, measuring how much space its surfaces cover.
7. Why are 2D and 3D shapes important in real life?
Understanding 2D and 3D geometric shapes helps in daily life and various fields, including art, engineering, construction, and architecture.
- Shapes help design buildings
- Solve math problems
- Understand spatial relationships
8. How many faces, edges, and vertices do 3D shapes have?
A 3D geometric shape has:
- Faces: flat or curved surfaces
- Edges: where two faces meet
- Vertices: where edges meet
9. What is the formula for the area of a triangle?
The area of a triangle, a basic 2D geometric shape, can be found using the formula $Area = (base \times height) / 2$. Here, 'base' refers to any one side, and 'height' is the perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite corner.
10. How do 2D shapes relate to 3D shapes?
A 2D shape forms the faces of many 3D geometric shapes. For example, a cube is made of six square faces, while a cylinder has two circular faces. Knowing 2D shapes helps us understand and build 3D structures.
11. What is the surface area formula for a rectangular prism?
For a rectangular prism, the surface area formula is $Surface\,Area = 2(lw + lh + wh)$, where l, w, and h are the length, width, and height. This sum comes from adding the areas of all six rectangular faces.
12. What is the main property of a circle as a 2D geometric shape?
The most important property of a circle is that all points are the same distance from a central point, called the radius. The formula for a circle’s area is $Area = \pi r^2$, a key aspect of 2D geometric shapes.

















