ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 8 Selina Concise Solutions - Free PDF Download
Updated ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 8 - Study of Compounds – Hydrogen Chloride Selina Solutions are provided by Vedantu in a step by step method. Selina is the most famous publisher of ICSE textbooks. Studying these solutions by Selina Concise Chemistry Class 10 Solutions which are explained and solved by our subject matter experts will help you in preparing for ICSE exams. Concise Chemistry Class 10 ICSE Solutions can be easily downloaded in the given PDF format. These solutions for Class 10 ICSE will help you to score good marks in ICSE Exams 2025-26.
The updated solutions for Selina textbooks are created in accordance with the latest syllabus. These are provided by Vedantu in a chapter-wise manner to help the students get a thorough knowledge of all the fundamentals.
ICSE Selina Solutions for Class 10 Chemistry - Chapter 8 - Study of Compounds A. Hydrogen Chloride
Exercise 8
1. Draw a labelled diagram for the laboratory preparation of hydrogen chloride gas and answer the following.
Ans:
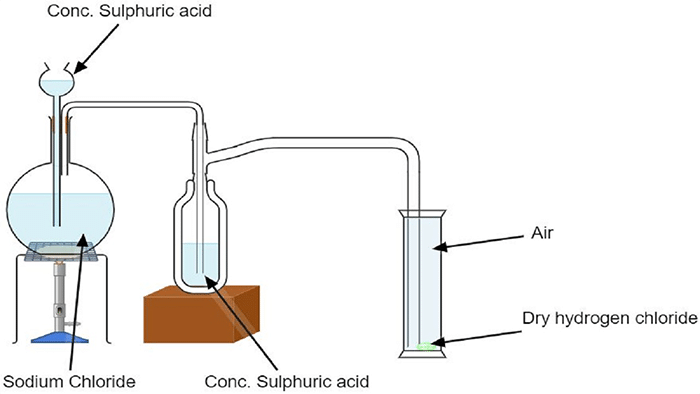
(a) Name the acid used. Why is this particular acid preferred to other acids?
Ans: The acid used for the preparation of hydrogen chloride gas in laboratory is Sulphuric acid.
This acid is preferred over other acids due to the following reasons:-
(1) It is less volatile than HCl gas (so that the produced HCl gas is collected easily).
(2) It has found to have dehydrating properties, so that the HCl gas produced can be effectively dehydrated to remove traces of water from it.
(3) It is found to have comparatively less oxidant power due to which the formation of other by products can be avoided.
(b) Give the balanced equation for the reaction.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation for the reaction can be given as -
\[\text{NaCl+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\xrightarrow{\text{20}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}\text{C}}\text{NaHS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{+HCl}\]
(c) Name the drying agent used in drying hydrogen chloride gas.
Ans: Drying agents are the ones which are used to remove trace amounts of water from an organic solution. Concentrated sulphuric acid has a hygroscopic property and induces dryness in its vicinity. Phosphorus pentoxide and calcium oxide are also good drying agents, but they cannot be used to dry hydrogen chloride gas because they react with it. Hence, concentrated sulphuric acid is the drying agent used for drying hydrogen chloride gas.
(d) Phosphorus pentoxide and calcium oxide are good drying agents, but they cannot be used to dry hydrogen chloride gas. Why?
Ans: Phosphorus pentoxide and calcium oxide are good drying agents, but they cannot be used to dry hydrogen chloride gas since they react with it. The reactions can be shown as-
\[\text{2}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}\text{+3HCl}\to \text{POCl+3HP}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\]
\[\text{CaO+2HCl}\to \text{CaC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\]
(e) Why is direct absorption of HCl gas in water not feasible?
Ans: The direct absorption of HCl gas in water leads to the back suction of water as HCl gas is soluble in water and reaction is found to be highly exothermic in nature.
(f) What arrangement is done to dissolve HCl gas in water.
Ans: The arrangement which is done to dissolve hydrogen chloride gas in water is “Inverted funnel arrangement”. In this arrangement an inverted funnel is used. This arrangement helps in preventing the back-suction of water and also provides large surface area for the maximum absorption of HCl gas.
2. Explain why:
(a) anhydrous HCl is a poor conductor while aqueous HCl is an excellent conductor.
Ans: Anhydrous HCl is found to be the poor conductor this is due to the absence of ions in it while aqueous HCl is found to be the excellent conductor as it gives rise to ions in solution. This can be shown as-
\[HCl+{{H}_{2}}O\to {{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}+C{{H}^{-}}\]
(b) when the stopper of a honk full of hydrogen chloride gas is opened there are fumes in the air.
Ans: When the stopper of a honk full of hydrogen chloride gas is opened this gas comes out of it and gets in contact of water vapours present in air and gives rise to white fumes as a result of the formation of hydrochloric acid.
(c) a solution of hydrogen chloride in water turns blue litmus red and conducts electricity. while a solution of the same gas in toluene
(i) has no effect on litmus, and
(ii) does not conduct electricity.
Ans: A solution of hydrogen chloride in water gives ions, this can be shown as-
\[HCl+{{H}_{2}}O\to {{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}+C{{H}^{-}}\]
And these ions are responsible for conducting electricity and also turns blue litmus red due to the presence of hydronium ions but the solution of same gas in toluene neither (i) turns blue litmus red (ii) nor does conducts electricity. This is due to the absence of hydronium ions in toluene showing that hydrogen chloride is a covalent compound.
(d) thick white fumes are formed when a glass rod dipped in NH4OH is brought near the mouth of a honk full of HCl gas.
Ans: When a glass rod dipped in ammonium hydroxide is brought near the mouth of a honk full of HCl gas, then it leads to the formation of dense white fumes due to the production of ammonium chloride. The reaction can be given as-
\[HCl+N{{H}_{4}}OH\to N{{H}_{4}}Cl+{{H}_{2}}O\]
(e) dry hydrogen chloride gas does not affect a dry strip of blue litmus paper, but it turns red in the presence of a drop of water.
Ans: Dry hydrogen chloride gas does not affect a dry strip of blue litmus paper since it is not acidic due to the absence of H+ ions whereas moist Hydrogen chloride is found to be acidic in nature as in the presence of a water HCl gas dissolves in water and forms hydrochloric acid which is a source of H+ ions which turns blue litmus paper red.
(f) hydrogen chloride gas is not collected over water.
Ans: Hydrogen chloride gas is not collected over water; this is because it is found to be highly soluble in water.
3. The given set up in the figure is for the preparation of an acid
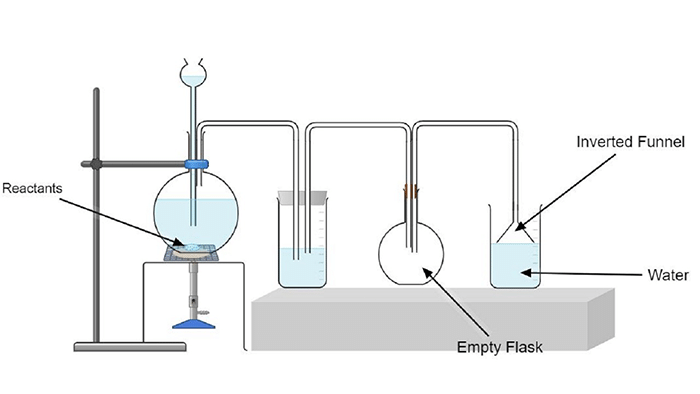
(a) Name the acid prepared by this method.
Ans: The acid prepared by this method is Hydrochloric acid (HCl).
(b) Name the reactants used.
Ans: The reactants which are used in this case is sodium chloride and Sulphuric acid
(c) Why is an empty flask used?
Ans: The empty flask is used since it acts as an Anti-Suction device. Since in case if the back suction takes place then the water gets collected in it and will not reach the generating flask.
(d) What is the drying agent used? Why is this drying agent chosen?
Ans: The drying agent used is Concentrated Sulphuric acid. It is chosen as drying agent because it does not react with HCl unlike phosphorous pentoxide and calcium oxide.
(e) What is the role of inverted funnel in the arrangement?
Ans: The role of the inverted funnel in the arrangement is-
1. It prevents or minimizes back suction of water.
2. It provides a large surface area for absorption of HCl gas.
4. (a) (i) Name the experiment illustrated below.
Ans: (i) The experiment illustrated below is found to be Fountain Experiment.
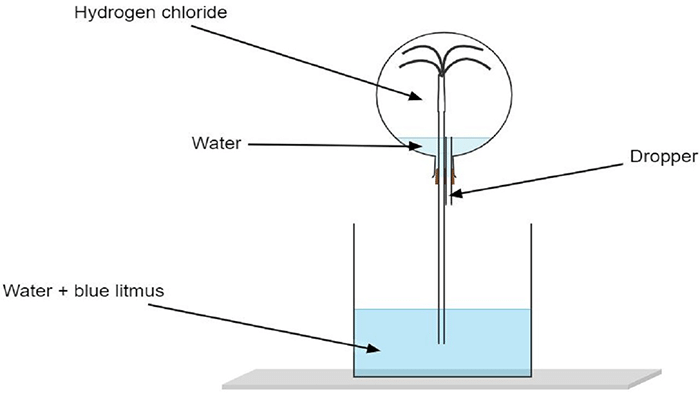
(ii) State the colour of the water that has entered the round-bottomed flask.
Ans: The colour of the water that has entered the round-bottomed flask.is red colour.
(b) What property of hydrogen chloride is demonstrated when it is collected by downward delivery (upward displacement)?
Ans: The property of hydrogen chloride which is demonstrated when it is collected by downward delivery (upward displacement) is that hydrogen chloride is highly soluble in water.
5. (a) Name an element which reacts with hydrogen to form compound which is strongly acidic in water.
Ans: An element which reacts with hydrogen to form compound which is strongly acidic in water is Chlorine. The compound formed which is strongly acidic in water, is HCl. The formation of this compound can be shown as-
\[{{H}_{2}}+C{{l}_{2}}\to 2HCl\]
(b) Explain why dilute hydrochloric acid cannot be concentrated by boiling beyond 22.2%
Ans: A dilute hydrochloric acid cannot be concentrated by boiling beyond 22.2%.
This is because vapours evolved before 110°C are vapours of water but at temperature above 110°C vapours consist mostly of molecules of HCl.
6. How will you prove that Hydrochloric acid contains (I) hydrogen (ii) chlorine. Write equations for the reactions.
Ans: Hydrochloric acid contains (i) hydrogen (ii) chlorine, this can be proved by performing an experiment –
Take a voltammeter used for electrolysis of water, fitted with platinum cathode and graphite anode.
Into the voltammeter pour 4 molar HCl and pass direct current.
Observation made- It is seen that a colourless gas is evolved at cathode and a greenish gas is evolved at anode.
When a burning splinter is brought near a colourless gas, it bursts into flame thereby showing that it is hydrogen gas while a moist starch iodide paper is held in the greenish yellow gas, it turns blue black, and hence showing that the gas is chlorine.
The equation for the reaction can be given as-
\[2HCl\to {{H}_{2}}+C{{l}_{2}}\]
Hence this experiment proves that hydrochloric acid contains both hydrogen and chlorine.
7. Name
(a) a black metallic oxide which reacts with hydrochloric acid to give a coloured solution.
Ans: A black metallic oxide which reacts with hydrochloric acid to give a coloured solution is Manganese dioxide and the reaction can be given as-
\[Mn{{O}_{2}}4HCl\to MnC{{l}_{2}}+2{{H}_{2}}O+C{{l}_{2}}\]
(b) two colourless gases, which when mixed produce a white solid
Ans: The two colourless gases, which when mixed to produce a white solid are
Hydrogen chloride and ammonia, when these are mixed they produce ammonium chloride. This can be shown as-
\[N{{H}_{3}}+HCl\to N{{H}_{4}}Cl\]
(c) two gases which chemically combine to form a liquid.
Ans: The two gases which chemically combine to form a liquid are- Hydrogen and oxygen , they combine to give rise to a liquid called water. This can be shown as–
\[2{{H}_{2}}+{{O}_{2}}\to 2{{H}_{2}}O\]
(d) a chloride which is soluble in excess of ammonium hydroxide.
Ans: A chloride which is soluble in excess of ammonium hydroxide is silver chloride. This can be shown as-
\[2N{{H}_{4}}OH+AgCl\to \left[ Ag{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}} \right]Cl+2{{H}_{2}}O\]
(e) the chemical in which gold can be dissolved.
Ans: The chemical in which gold can be dissolved is Aqua Regia. This can be shown as-
\[Au+HN{{O}_{3}}+3HCl\to AuC{{l}_{3}}+N{{O}_{2}}+2{{H}_{2}}O\]
(f) the experiment which demonstrates that hydrogen chloride is soluble in water.
Ans: The experiment which demonstrates that hydrogen chloride is soluble in water is Fountain experiment. The reaction involved is
\[HCl+{{H}_{2}}O\to {{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}+C{{l}^{-}}\]
(g) the gas produced when chlorine water is exposed to sunlight.
Ans: The gas produced when chlorine water is exposed to sunlight is Oxygen gas. This can be shown as-
\[\text{C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}f\text{ HClO+HCl}\]
The HClO formed further undergoes decomposition-
\[HClO\to HCl+\left[ O \right]\]
\[\left[ O \right]+\left[ O \right]\to {{O}_{2}}\]
8. Solution A reacts with an acid B (which gives yellow gas on reacting with oxidising agents like Pb3O4 to give white precipitate C insoluble in nitric acid but soluble in ammonium hydroxide. Name A, B and C.
Ans:
\[AgN{{O}_{3}}+HCl\to AgCl+HN{{O}_{3}}\]
This reaction shows that solution A is of silver nitrate which reacts with the acid B i.e., Hydrochloric acid to give rise to a white precipitate C of AgCl which is insoluble in nitric acid, and this can be shown as-
\[AgCl+HN{{O}_{3}}\to \text{No reaction}\text{.}\]
But when reacted with Ammonium hydroxide it gets soluble.
\[AgCl+2N{{H}_{4}}OH\to \left[ Ag{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}} \right]Cl\left( aq \right)+{{H}_{2}}O\]
Hence, in this case –
A is Silver nitrate
B is Hydrochloric acid
C is Silver chloride
9. Complete and balance the following reactions, state whether dilute or conc. acid is used-
(a) \[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH+HCl}\to \]
(b) \[\text{NaHS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+HCl}\to \]
(c) \[\text{Pb}{{\left( \text{N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} \right)}_{\text{2}}}\text{+HCl}\to \]
(d) \[\text{P}{{\text{b}}_{3}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{+HCl}\to \]
Ans: The given reactions can be completed and balanced as-
(a)\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH+dil}\text{.HCl}\to \text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\]
(b)\[NaHSO_{3} + \text {dil}.HCl \rightarrow NaCl + H_{2}O +SO_{2} \]
(c)\[\text{Pb}{{\left(\text{N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} \right)}_{\text{2}}}\text{+2dil}\text{.HCl}\to \text{PbC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+2HN}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\]
(d)\[\text{P}{{\text{b}}_{3}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{+8conc}\text{.HCl}\to \text{3PbC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+4}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O+C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\]
10. How will the action of dilute hydrochloric acid enable you to distinguish between the following?
(a) Sodium carbonate and sodium sulphite
Ans: When Sodium carbonate is treated with dil.HCl it results in the formation of sodium chloride, water, and carbon dioxide gas.
\[N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}2HCl\to 2NaCl+{{H}_{2}}O+C{{O}_{2}}\uparrow \]
But when sodium sulphite is treated with dil.HCl it results in the formation of sodium chloride, water, and sulphur dioxide gas.
\[N{{a}_{2}}S{{O}_{3}}+2HCl\to 2NaCl+{{H}_{2}}O+S{{O}_{2}}\uparrow \]
(b) Sodium thiosulphate and sodium sulphite.
Ans: When sodium thiosulphate is treated with dil. HCl it produces sulphur dioxide gas and precipitates out yellow sulphur. This can be shown as-
\[N{{a}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}+2HCl\to 2NaCl+{{H}_{2}}O+S{{O}_{2}}+S\downarrow \]
But Sulphur does not get precipitated when sodium sulphite is treated with dil.HCl.
11. Give three distinct tests apart from using an indicator you would carry out with solution of HCl to illustrate the typical properties of an acid.
Ans: The three distinct tests with solution of HCl to illustrate the typical properties of an acid are:
1) HCl gas gives thick white fumes of ammonium chloride when glass rod dipped in ammonia solution is held near the vapours of the acid. The reaction can be given as-
\[N{{H}_{3}}+HCl\to N{{H}_{4}}Cl\]
2) With silver nitrate HCl gives white precipitate of silver chloride. The precipitate is insoluble in nitric acid but soluble in ammonium hydroxide. The reaction can be given as-
\[AgN{{O}_{3}}+HCl\to AgCl+HN{{O}_{3}}\]
3) A greenish yellow gas is liberated when conc. hydrochloric acid is heated with an oxidizing agent like manganese dioxide. The reaction can be given as-
\[Mn{{O}_{2}}+4HCl\to MnC{{l}_{2}}+2{{H}_{2}}O+C{{l}_{2}}\]
12. MnO2, PbO2 red lead react with conc. HCl and liberates Cl2. What is the common property being shown by these metal oxides?
Ans: MnO2, PbO2 and red lead react with conc. HCl acid and gives rise to Cl2. This shows that hydrochloric acid (HCl) is oxidized to chlorine (Cl2) by oxidizing agents.
13. State which of the two — a solution of HCl in water or in toluene is an electrolyte. Explain.
Ans: It has been observed that HCl dissolves both in water and toluene, when it is added to water it ionizes and forms hydronium and chloride ions as-
\[HCl+{{H}_{2}}O\to {{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}+C{{l}^{-}}\]
but this ionization is not observed in toluene so, a solution of HCl in water can be used as an electrolyte.
14. Convert:
(a) Two soluble metallic nitrates to insoluble metallic chlorides using dil. HCl.
Ans: The conversion of two metallic nitrates to insoluble metallic chlorides using dil. HCl can be carried out as-
\[\left( i \right)Pb{{\left( N{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}+2HCl\to PnC{{l}_{2}}\downarrow +2HN{{O}_{2}}\]
\[\left( ii \right)H{{g}_{2}}{{\left( N{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}+2HCl\to HgC{{l}_{2}}\downarrow +2HN{{O}_{3}}\]
(b) Hydrochloric acid to nascent chlorine
Ans: The conversion of HCl to [Cl] can be carried out as-
\[3HCl+concHN{{O}_{3}}\to NOCl+2{{H}_{2}}O+2\left[ Cl \right]\]
15. A solution of hydrogen chloride in water is prepared. The following substances are added to separate portions of the solution:
S.No. | Substances added | Gas evolved | Odour |
1. | Calcium carbonate | ||
2. | Magnesium ribbon | ||
3. | Manganese(IV) oxide with heating | ||
4. | Sodium sulphide |
Complete the table by writing the gas evolved in case and its odour.
Ans: The reactions taking place can be given as-
\[1.\text{ }2HCl+CaC{{O}_{3}}\to CaC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O+C{{O}_{2}}\uparrow \]
\[2.\text{ }2HCl+Mg\to MgC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}\uparrow \]
\[3.\text{ }Mn{{O}_{2}}+4HCl\to MnC{{l}_{2}}+2{{H}_{2}}O+C{{l}_{2}}\uparrow \]
\[4.\text{ }2HCl+N{{a}_{2}}S\to 2NaCl+HS\uparrow \]
Hence, the given table can be completed as-
S.No. | Substances Added | Gas Evolved | Odour |
1. | Calcium carbonate | Carbon dioxide | Odourless |
2. | Magnesium ribbon | Hydrogen | Odourless |
3. | Manganese(IV) oxide with heating | Chlorine | Strong pungent odour |
4. | Sodium sulphide | Hydrogen sulphide | Rotten egg |
16. State the composition of aqua regia. State which component is the oxidizing agent in aqua regia.
Ans: Aqua regia is a mixture having three parts of conc. Hydrochloric acid and one part of conc. Nitric acid. In aqua regia nitric acid acts as an oxidizing agent as it itself undergoes reduction.
Aqua regia = HCl : HNO3
3 :1
17. Write an equation for the reactions of hydrochloric acid on
a. silver nitrate solution
Ans: The equation for the reaction of HCl on silver nitrate solution
\[AgN{{O}_{3}}+HCl\to AgCl\uparrow +HN{{O}_{3}}\]
b. magnesium foil
Ans: The equation for the reaction of HCl on magnesium foil
\[Mg+2HCl\to MgC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}\uparrow \]
c. caustic soda solution
Ans: The equation for the reaction of HCl on caustic soda solution
\[NaOH+HCl\to NaCl+{{H}_{2}}O\]
d. zinc carbonate
Ans: The equation for the reaction of HCl on zinc carbonate
\[ZnC{{O}_{3}}2HCl\to ZnC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O+C{{O}_{2}}\uparrow \]
e. manganese (IV) oxide
Ans: The equation for the reaction of HCl on manganese (IV) oxide
\[Mn{{O}_{2}}+4HCl\xrightarrow{\Delta }MnC{{l}_{2}}+2{{H}_{2}}O+C{{l}_{2}}\uparrow \]
f. copper oxide
Ans: The equation for the reaction of HCl on copper oxide
\[CuO+2HCl\to CuC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O\]
18. Study the flow chart and give balanced equations with conditions for the conversions A, B, C, D and E
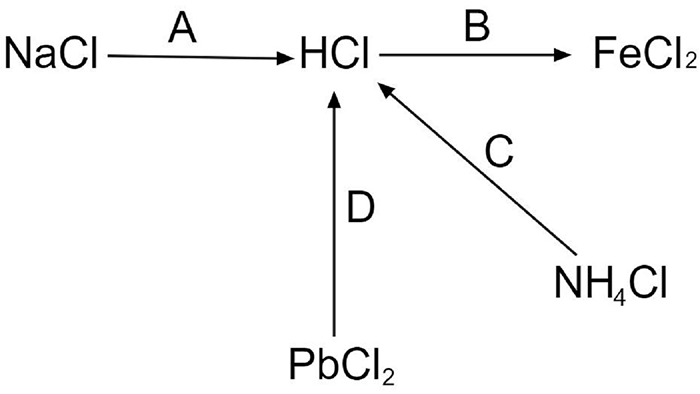
Ans: The balanced chemical reactions can be given as-
\[NaCl+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\xrightarrow{<{{200}^{o}}C}NaHS{{O}_{4}}+HCl\]
\[Fe+2HCl\to FeC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}\]
\[HCl+N{{H}_{3}}\to N{{H}_{4}}Cl\]
\[Pb{{O}_{2}}+4HCl\to PbC{{L}_{2}}+2{{H}_{2}}O+C{{l}_{2}}\]
19. Write the balanced equations for the reaction of dilute hydrochloric acid with each of the following:
(a) Iron
Ans: The balanced equation for the reaction with dil.HCl is given as-
\[Fe+2HCl\to FeC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}\]
(b) Sodium hydrogen carbonate
Ans: The balanced equation for the reaction with dil.HCl is given as-
\[NaHC{{O}_{3}}~+\text{ }HCl~\to NaCl\text{ }+\text{ }{{H}_{2}}O\text{ }+\text{ }C{{O}_{2}}\]
(c) Iron(II) sulphide
Ans: The balanced equation for the reaction with dil.HCl is given as-
\[FeS\text{ }+\text{ }2HCl~\to FeC{{l}_{2}}~+\text{ }{{H}_{2}}S\]
(d) magnesium sulphite
Ans: The balanced equation for the reaction with dil.HCl is given as-
\[MgS{{O}_{3}}+HCl\to MgC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O+S{{O}_{2}}\]
(2018)
20. Write the observation:
Lead nitrate solution is mixed with dilute hydrochloric acid and heated.
Ans: When the lead nitrate is mixed with dilute hydrochloric acid and heated then the following reaction is observed which shows the formation of a white coloured ppt. of lead chloride.
\[Pb\text{ }{{\left( N{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}~+~HCl~\to PbC{{l}_{2}}~+~2HN{{O}_{3}}\]
A small piece of zinc is added to dilute hydrochloric acid.
Ans: If a small piece of zinc is added to dilute hydrochloric acid, bubbles of hydrogen gas is observed.
\[Zn+2HCl\to ZnC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}\]
21. a. The drying agent used to dry HCl gas is:
(a) Conc. H2SO4
(b) ZnO
(c) Al2O3
(d) CaO
Ans: Drying agents are the ones which are used to remove trace amounts of water from an organic solution. The drying agent used is Concentrated Sulphuric acid. It is chosen as drying agent because it does not react with HCl. Hence option a. is correct.
b. When sodium chloride is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid below 200oC one of the product formed is ………………….
(Sodium hydrogen sulphate/sodium sulphate/ chlorine).
Ans: When NaCl is heated with conc. Sulphuric acid, then sodium hydrogen sulphate and HCl gas is formed. This can be shown as-
\[NaCl+conc.{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\xrightarrow[{}]{<{{200}^{o}}C}{{N}_{a}}HS{{O}_{4}}+HCl\]
(2010)
a. Aqua regia is a mixture of
i. Dilute hydrochloric acid and concentrated nitric acid
ii. Concentrated hydrochloric acid and dilute nitric acid
iii. Concentrated hydrochloric acid [1 part] and concentrated nitric acid [3 parts]
iv. Concentrated hydrochloric acid [3 parts] and concentrated nitric acid [1 part]
Ans: Aqua regia is a mixture having three parts of conc. Hydrochloric acid and one part of conc. Nitric acid. In aqua regia nitric acid acts as an oxidizing agent as it itself undergoes reduction.
Aqua regia = HCl : HNO3
3 : 1
Hence option (iv) is found to be the correct one.
b. How would you distinguish between dilute HCl and dilute HNO3 by addition of only one solution?
Ans: When dil. HCl reacts with silver nitrate then the following reaction occurs-
\[AgN{{O}_{3}}+HCl\to AgCl\downarrow +HN{{O}_{2}}\]
This reaction shows the formation of a ppt. of silver chloride.
But when dil. HNO3 is added to silver nitrate then no reaction occurs-
\[AgN{{O}_{3}}+HN{{O}_{3}}\to \]No reaction
c. Name two gases which can be used in the study of the fountain experiment. State the common property demonstrated by the fountain experiment.
Ans:
The two gases which can be used in the study of the fountain experiment are-Hydrogen chloride gas and ammonia whereas the common property demonstrated by the fountain experiment is the solubility of gases.
(2011)
a. Choose the correct answer from the choices given:
Hydrogen chloride gas being highly soluble in water is dried by
i. Anhydrous calcium chloride
ii. Phosphorous pentoxide
iii. Quicklime
iv. Conc. sulphuric acid
Ans: Hydrogen chloride gas being highly soluble in water is dried by conc. sulphuric acid. It is chosen as drying agent because it does not react with HCl. Hence, option (iv) is correct.
b. Write the balanced chemical equation.
i. Sodium thiosulphate is reacted with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Ans:\[N{{a}_{\text{2}}}S{{O}_{\text{3}}}+\text{2}HCl\to \text{2}NaCl+{{H}_{\text{2}}}O+S{{O}_{\text{2}}}\]
ii. Calcium bicarbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Ans:\[CaC{{O}_{\text{3}}}+\text{2}HCl\to CaC{{l}_{\text{2}}}+{{H}_{\text{2}}}O+C{{O}_{\text{2}}}\]
c. In the laboratory preparation of hydrochloric acid, hydrogen chloride gas is dissolved in water.
i. Draw a diagram to show the arrangement used for the absorption of HCl gas in water.
Ans:
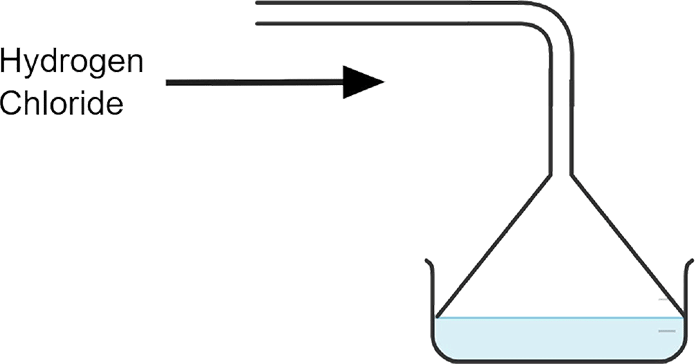
ii. State why such an arrangement is necessary. Give two reasons for the same.
Ans: This arrangement is necessary to prevent back suction of water into the apparatus and it provides a large surface area for dissolution of hydrogen chloride gas.
iii. Write balanced chemical equations for the laboratory preparation of HCl gas when the reaction is
A. Below 200°C.
B. Above 200°C.
Ans: The reactions can be given as-
(A) \[NaCl+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\xrightarrow{<{{200}^{o}}C}NaHS{{O}_{4}}+HCl\]
(B) \[2NaCl+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\xrightarrow{<{{200}^{o}}C}NaS{{O}_{4}}+2HCl\]
(2012)
a. Rewrite the correct statement with the missing word/s:
Aqua regia contains one part by volume of nitric acid and three parts by volume of hydrochloric acid.
Ans: Aqua regia contains one part by volume of concentrated nitric acid and three parts by volume of concentrated hydrochloric acid.
b. Give reason for the following:
Hydrogen chloride gas cannot be dried over quicklime.
Ans: Hydrogen chloride gas cannot be dried over quicklime this is because HCl when comes in contact of quicklime it undergoes a chemical reaction. This can be given as-
\[2HCl\text{ }+~CaO~\to ~CaC{{l}_{2}}~+\text{ }{{H}_{2}}O~\]
c. Give a balanced equation for the reaction: Conc. hydrochloric acid and potassium permanganate solution.
Ans: A balanced chemical equation in this can be given as-
\[2KMn{{O}_{4}}+16HCl\to 2MnC{{l}_{2}}+2KCl+8{{H}_{2}}O+5C{{l}_{2}}\uparrow \]
d. Give balanced equations with conditions, if any, for the following conversions:
i. Sodium chloride → Hydrogen chloride
Ans:\[NaCl+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\xrightarrow{<{{200}^{o}}C}NaHS{{O}_{4}}+HCl\uparrow \]
ii. Hydrogen chloride → Iron (II) chloride
Ans: \[FeS+2HCl\to FeC{{L}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}S\uparrow \]
iii. Hydrogen chloride → Ammonium chloride
Ans: \[HCl+N{{H}_{4}}OH\to N{{H}_{3}}Cl+{{H}_{2}}O\]
iv. Hydrogen chloride → Lead chloride
Ans:\[4HCl+Pb{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow{\Delta}PbC{{l}_{2}}+2{{H}_{2}}O+C{{l}_{2}}\uparrow \]
(2013)
a. Identify the gas evolved when
i. Potassium sulphite is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Ans: When potassium sulphite is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid then it leads to the evolution of Sulphur dioxide gas. This can be shown as-
\[{{K}_{2}}S{{O}_{3}}+2HCl\to 2KCl+{{H}_{2}}O+S{{O}_{2}}\uparrow \]
ii. Concentrated hydrochloric acid is made to react with manganese dioxide.
Ans: When concentrated hydrochloric acid is made to react with manganese dioxide then it leads to the following reaction which can be stated as-
\[Mn{{O}_{2}}+4HCl\xrightarrow{\Delta }MnC{{l}_{2}}+2{{H}_{2}}O+C{{l}_{2}}\uparrow \]
b. State one appropriate observation for
i. Copper sulphide is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Ans: When copper sulphide is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid then
hydrogen sulphide gas has evolved which has the smell of rotten eggs. The reaction can be given as-
\[CuS+dil.HCl\to CuC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}S\uparrow \]
ii. A few drops of dil. HCl are added to AgNO3 solution, followed by addition of NH4OH solution.
Ans: When few drops of dil. HCl are added to AgNO3 solution, followed by addition of NH4OH solution then a white ppt. of silver chloride is formed which is soluble in ammonium hydroxide and the reaction can be shown as-
\[AgN{{O}_{3}}+HCl\to AgCl\downarrow +HN{{O}_{3}}\]
(2014)
a. Fill in the blank from the choices in the brackets:
Quicklime is not used to dry HCl gas because (CaO is alkaline, CaO is acidic, CaO is neutral).
Ans: Quicklime is not used to dry HCl gas because CaO is alkaline.
b. Write the balanced equation for
Action of dilute hydrochloric acid on sodium sulphide.
Ans: When dil.HCl is treated with sodium sulphide then it leads to the following reaction-
\[N{{a}_{2}}S{{O}_{3}}+2HCl\to 2NaCl+{{H}_{2}}O+S{{O}_{2}}\]
c. State your observation:
Dilute HCl is added to sodium carbonate crystals.
Ans: Dilute HCl is added to sodium carbonate crystals this leads to the formation of sodium chloride, water, and carbon dioxide gas. Since here the reaction is taking place between sodium carbonate which is a basic salt and hydrochloric acid which is an acid so, this is a neutralisation reaction. The reaction involved is as follows:
\[NaC{{O}_{3}}+2HCl\to 2NaCl+{{H}_{2}}O+C{{O}_{2}}\]
d. Study the given figure and answer the questions that follow:
i. Identify the gas Y.
Ans: The gas Y in this case is HCl gas.
ii. What property of gas Y does this experiment demonstrate?
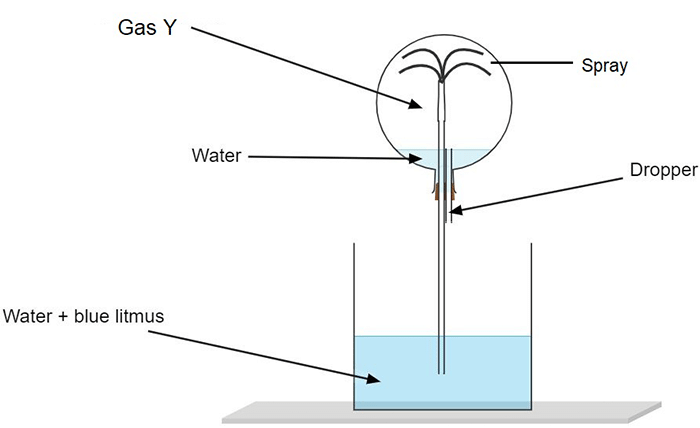
Ans: The fountain experiment demonstrates that the HCl gas dissolves in water due its high solubility in it and is found to be acidic in nature.
iii. Name another gas which has the same property and can be demonstrated through this experiment.
Ans: Another gas having same property and can be demonstrated through this experiment is ammonia gas (NH3).
(2015)
(a) Name the acid which on mixing with silver nitrate solution produces a white precipitate which is soluble in excess of ammonium hydroxide.
Ans: The acid which when mixed with silver nitrate solution produces a white precipitate which is soluble in excess of ammonium hydroxide is found to be HCl. The reaction involved can be given as-
\[AgN{{O}_{3}}+HCl\to AgCl\uparrow +HN{{O}_{3}}\]
(b) Name the gas which produces dense white fumes with ammonia gas.
Ans: The gas which produces dense white fumes with ammonia gas is HCl.
\[N{{H}_{3}}+HCl\to N{{H}_{4}}Cl\]
The white fumes are of ammonium chloride gas which on cooling gives ammonium chloride crystals.
(c) The following questions pertain to the laboratory preparation of hydrogen chloride gas.
(i) Write the equation for its preparation, mentioning the conditions required.
Ans: The equations for its preparation, and the conditions required are-
\[NaCl+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\xrightarrow{<{{200}^{o}}C}NaHS{{O}_{4}}+HCl\]
\[2NaCl+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\xrightarrow{<{{200}^{o}}C}NaS{{O}_{4}}+2HCl\]
(ii) Name the drying agent used in the above preparation and give a reason for the choice.
Ans: Drying agents are the ones which are used to remove trace amounts of water from an organic solution. Concentrated sulphuric acid has a hygroscopic property and induces dryness in its vicinity. Phosphorus pentoxide and calcium oxide are also good drying agents, but they cannot be used to dry hydrogen chloride gas because they react with it. Hence, concentrated sulphuric acid is the drying agent used for drying hydrogen chloride gas.
(iii) State a safety precaution taken during the preparation of hydrochloric acid.
Ans: Safety precautions taken during the preparation of hydrochloric acid
Temperature needs to be maintained at about 200oC.
Delivery tube must be properly dipped in a drying agent i.e., conc. Sulphuric acid. The lower end of a thistle funnel needs to be properly dipped in conc. Sulphuric acid.
(2016)
(a) The aim of the Fountain experiment is to prove that:
(A) HCl turns blue litmus red
(B) HCl is denser than air
(C) HCl is highly soluble in water
(D) HCl fumes in moist air
Ans: The fountain experiment demonstrates that the HCl gas dissolves in water due its high solubility in it. Hence, option (C) is found to be the correct one.
(b) Write a balanced chemical equation:
Action of hydrochloric acid on sodium bicarbonate.
Ans: The action of hydrochloric acid on sodium bicarbonate can be shown as-
\[NaHC{{O}_{3}}+HCl\to NaCl+C{{O}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O\]
(c) State your observations when:
(i) Dilute Hydrochloric acid is added to Lead nitrate solution and the mixture is heated.
Ans: When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to lead nitrate solution and the mixture is heated then the following reaction occurs as-
\[Pb{{\left( N{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}+2HCl\to PbC{{l}_{2}}\uparrow +2HN{{O}_{3}}\]
In this case a white precipitate of lead chloride appears which gets dissolved on heating.
(ii) Dilute Hydrochloric acid is added to Sodium thiosulphate
Ans: Dil. HCl when treated with thiosulphate it produces sulphur dioxide and yellow sulphur gets precipitated. The reaction can be given as-
\[N{{a}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}+2HCl\to 2NaCl+S{{O}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O+S\]
(d)Identify the gas evolved and give the chemical test in each of the following cases:
(i) Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron (II) sulphide.
Ans: When dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron (II) sulphide and sulphur-dioxide gas gets evolved. This is a colourless gas with the smell of burning sulphur and also it turns acidified potassium dichromate orange to green. The reaction involved can be shown as-
\[FeS+2HCl\to FeC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}S\uparrow \]
(ii) Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium sulphite.
Ans: When dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium sulphite then hydrogen sulphide gas gets evolved. This is a colourless gas with rotten eggs like smell. It is observed that it even turns lead acetate paper black. The reaction can be given as-
\[N{{a}_{2}}S{{O}_{3}}+2HCl\to 2NaCl+{{H}_{2}}O+S{{O}_{2}}\uparrow \]



































