Study of Compounds Ammonia Solutions for ICSE Board Class 10 Chemistry (Concise - Selina Publishers)
ICSE Syllabus for Class 6 Physics 2025-26 Examination
Ammonia is a compound containing only nitrogen and hydrogen elements in a distinct ratio. It was first discovered by Joseph Priestley. It can be found in nature in free States as well as in the combined states. It is found in the atmosphere, sewage water and animal tissues. It is found in a combined state in the form of ammonium salts. Ammonia is a weak base. Although sometimes it also acts as a weak acid. So it is called an amphoteric compound.
Access ICSE Selina Solutions for Grade 10 Chemistry Chapter 9- Ammonia
Intext Questions
1. (a) State the type of bonding present in ammonia, show by a diagram.
Ans: Ammonia is having three N-H covalent bonds, hence covalent bonding is shown by a diagram below-
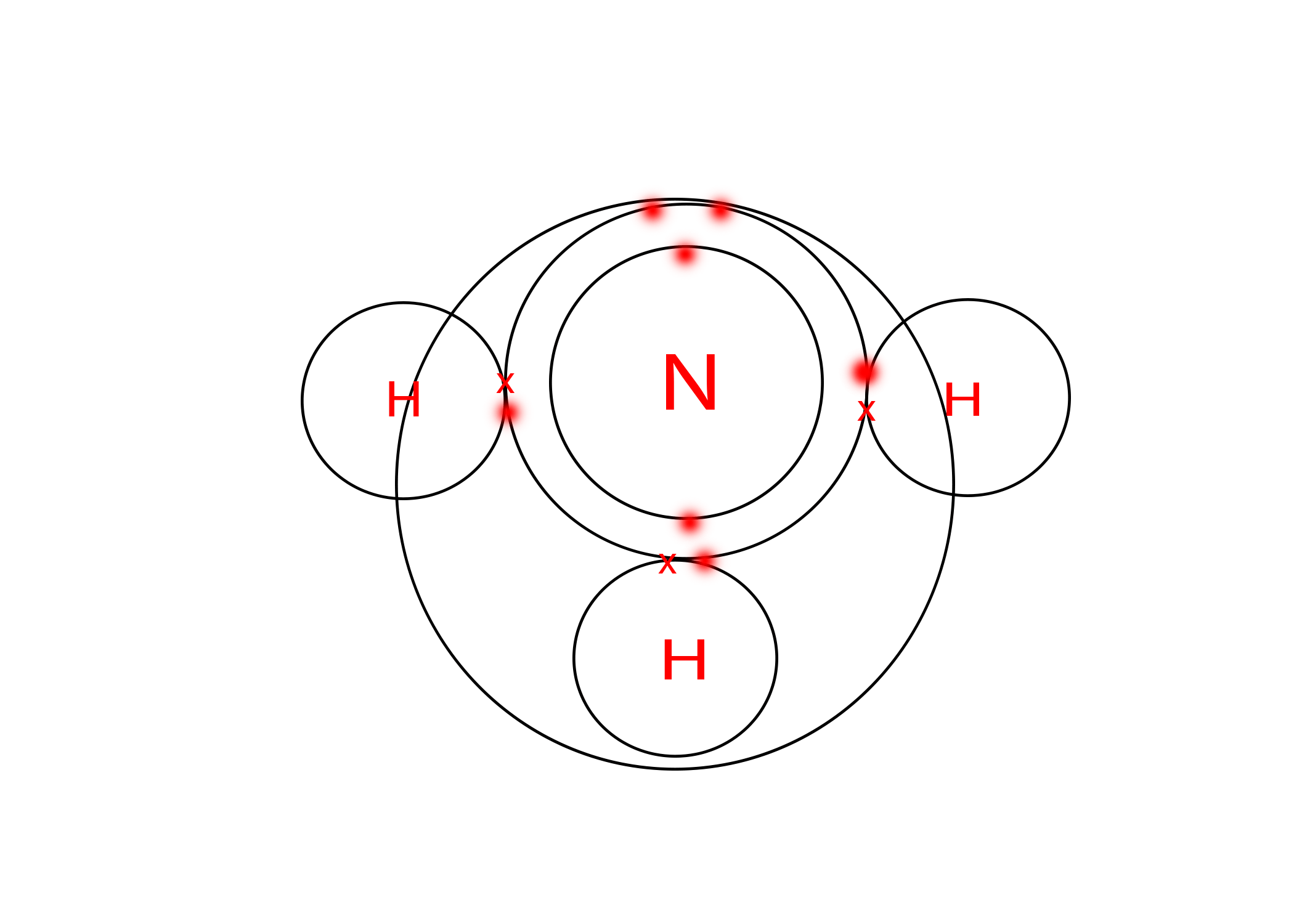
(b) What is the formula of liquid ammonia? Account for the basic nature of this compound.
Ans: Ammonia molecule is made up of nitrogen and hydrogen atoms. It is a colourless and pungent-smelling gas, but it easily liquefies due to the formation of hydrogen bonds between molecules. The basic nature of the compound is attributed to its electron-donating nature. Ammonia is a hydride of nitrogen that exists as a colourless and pungent-smelling gas. Due to the electronegativity difference between the nitrogen and hydrogen atoms, hydrogen bonding is possible between the molecules of ammonia. And that is why it is found in liquid form also.
So, the formula of liquid ammonia is \[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\]. Here, the nitrogen is sp3 hybridized and possesses a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. According to Lewis's theory of acids and bases, any electron-donating species act as a base. So, the liquid ammonia also acts as a base.
It readily dissolves in water and forms ammonium hydroxide that further furnishes hydroxyl ions which makes the medium basic. The reaction involved can be written as follows:
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\to \text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH}\]
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH}\rightleftharpoons \text{N}{{\text{H}}^{\text{+4}}}\text{+O}{{\text{H}}^{\text{-}}}\]
Thus, liquid ammonia has the molecular formula of NH3 and it is basic in nature.
2.(a) Write a balanced chemical equation for the lab preparation of ammonia. (2018)
Ans: The balanced chemical equation for the lab preparation of ammonia is given as-
\[\text{2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl + Ca}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{\text{2}}}\to \text{CaC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ + 2}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ + 2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\]
(b) How is ammonia dried and collected in the laboratory?
Ans: The ammonia gas can be dried by passing through a drying tower containing lumps of quicklime that is CaO. Also, ammonia is highly soluble in water and therefore it cannot be collected over water.
(c) Ammonia cannot be collected over water. Give reason.
Ans: Ammonia cannot be collected over water as it is highly soluble in water.
3.(a) Explain with a diagram the preparation of aqueous ammonia.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation for the lab preparation of ammonia is given as-
\[\text{2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl + Ca}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{\text{2}}}\to \text{CaC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ + 2}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ + 2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\]
The diagram for the preparation of aqueous ammonia is shown below-
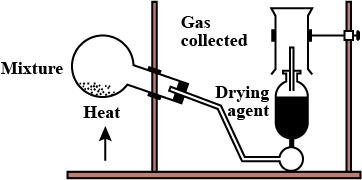
(b) Why drying agents such as\[{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}\]and \[\mathbf{CaC}{{\mathbf{l}}_{\mathbf{2}}}\]are not used to dry \[\mathbf{N}{{\mathbf{H}}_{\mathbf{3}}}\]?
Ans: The ammonia gas can be dried by passing through a drying tower containing lumps of quicklime that is CaO, as ammonia is being basic in nature hence it reacts with \[{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}\]and \[\text{CaC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\], hence these are not used.
4. A substance 'A' was heated with slaked lime and a gas 'B' k with a pungent smell was obtained. Name the substances A and B and give a balanced equation.
Ans: The balanced chemical reaction for the reaction is -
\[\text{2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl+Ca(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\to \text{CaC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+2}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O+2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\]
Substance A is Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl).
Gas B is Ammonia (with pungent smell - NH3).
5. Ammonia is manufactured by Haber’s process-
(a) Under what conditions do the reactants combine to form ammonia? Give a balanced equation for the reaction.
Ans: The formation of ammonia is occurred when the reactants nitrogen and hydrogen combine at low temperature and high pressure in the presence of a catalyst. The balanced chemical reaction is given as-
\[{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\to \text{2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\]
(b) In what ratio by volume, are the above gases used?
Ans: The balanced chemical reaction is given as-
\[{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\to \text{2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\]
According to the above equation, nitrogen and hydrogen combines in 1:3 ratio by volume.
(c) State one possible source of each reactant used in Haber Process.
Ans: Source of Nitrogen that can be used in the Haber’s process is through the fractional distillation of air.
Source of Hydrogen that can be used in the Haber’s process is from the water gas by the Bosch process.
(d) State whether the formation of ammonia is promoted by the use of high pressure or low pressure?
Ans: The formation of ammonia is promoted by the use of high pressure as it favours the forward direction.
(e) Mention two possible ways by which ammonia produced is removed from unchanged gases.
Ans: Two possible ways by which ammonia produced is removed from unchanged gases.
1)By Liquefaction- As ammonia is easily liquefiable.
2) By Absorbing in water- As ammonia is highly soluble in water.
(f) What is the function of (i) finely divided iron, (u) molybdenum in the above process?
Ans: (i) Function of Finely divided iron is to increase the rate of reaction.
(ii) Function of Molybdenum is to act as a promoter to increase the efficiency of the catalyst.
(g) What is the percentage formation of ammonia?
Ans: The percentage formation of ammonia is 15%.
(h) How can this percentage formation be increased?
Ans: This percentage of formation of ammonia can be increased by the unchanged nitrogen and hydrogen are recirculated through the plant to get more ammonia, by this way we can achieve 98% of ammonia.
6. Give reasons-
(a) Ammonia chloride does not occur in minerals.
Ans: Due to the high solubility of Ammonia chloride in water it does not occur in minerals.
(b) Ammonium nitrate is not used in the preparation of ammonia.
Ans: Ammonium nitrate is explosive in nature hence it decomposes and forms nitrous oxide and water vapours. Hence, it is not used in the preparation of ammonia.
(c) Conc. H2SO4 is a good drying agent. yet it is not used to dry NH3.
Ans: Conc. H2SO4 is a good drying agent. yet it is not used to dry NH3 as conc. Sulphuric acid reacts with ammonia because ammonia is basic in nature.
(d) In the lab. preparation of ammonia
(I) calcium hydroxide is used in excess.
(II) Flask is fitted in slanting position.
Ans: (I) In the lab. preparation of ammonia, calcium hydroxide is used in excess as to do the better mixing of ammonium chloride, calcium hydroxide is used in excess.
(II) In the lab. preparation of ammonia flask is fitted in slanting position because the water is formed in the reaction does not trickle back into the heated flask.
7. State the following conditions required in the Haber’s process-
(a) Temperature
Ans: Temperature should be = 400-500 degree Celsius
(b) Pressure
Ans: Pressure should be = 200-800atm
(c) Catalyst
Ans: Catalyst = Finely divided iron (Fe).
8. Choose the correct word or phrase from the brackets, to complete the following sentences and write balanced equations for the same.
(a) Ammonium chloride is a soluble salt prepared by______ (precipitation. neutralization).
Ans: The balanced chemical reaction is shown as ammonium chloride salt is formed by the reaction of acid and base hence it’s a neutralization reaction.
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ + HCl}\to \text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl}\]
Ammonium chloride is a soluble salt prepared by neutralization (precipitation. neutralization).
(b) When ammonium chloride is heated. it undergoes_____ (thermal decomposition/dissociation).
Ans: The balanced chemical reaction is shown as when ammonium chloride is heated it undergoes thermal dissociation.
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl}\to \text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ + HCl }\]
When ammonium chloride is heated. it undergoes thermal dissociation (thermal decomposition/dissociation).
(c) Heating ammonium chloride with sodium hydroxide produces________ (ammonia, nitrogen).
Ans: The balanced chemical reaction is shown as when we heat ammonium chloride with sodium hydroxide it produces ammonia.
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl + NaOH}\to \text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3 }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }}}\text{+ NaCl + }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\]
Heating ammonium chloride with sodium hydroxide produces ammonia (ammonia, nitrogen).
9. An element has 2 electrons in its N shell. It reacts with a non-metal of atomic number 7. The compound formed reacts with warm water and produces a basic gas Identify the elements and write the balanced chemical reactions.
Ans: An element has 2 electrons in its N shell it means 2 (electrons in K shell) + 8 (electrons in L shell) + 8 (electrons in M shell) + 2 (electrons in N shell which is already given in ques.) = 20
It means 20 is the atomic no. of calcium therefore the first element is calcium. Nitrogen has an atomic number '7' and it is also a non-metal, hence another element is nitrogen when these both calcium and nitrogen react, they can form calcium nitride.
\[\text{3Ca}\left( \text{s} \right)\text{+ }{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\left( \text{g} \right)\to \text{C}{{\text{a}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{(s)}\]
when this compound reacts with water it gives calcium hydroxide and ammonia. The balanced chemical reaction is given as-
\[\text{C}{{\text{a}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+6}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\to \text{3Ca}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{\text{2}}}\text{+2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\]
10. The following reactions are carried out-
A: Nitrogen + metal\[\to \] compound X.
B: X + water \[\to \]ammonia + another compound.
C: Ammonia + metal oxide\[\to \]metal + water + \[{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\]
One metal that can be used for reaction A is magnesium.
(a) Write the formula of the compound X formed
(b) Write the correctly balanced equation for reaction B where X is the compound formed.
(c) What property of ammonia is demonstrated by reaction C ?
Ans:
(a) One metal that can be used for reaction A is magnesium. Hence, the balanced chemical reaction is given below-
\[{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+3Mg}\to \text{M}{{\text{g}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\]
Hence the formula of compound X is - Mg3N2
(b) The balanced equation for reaction B where X is the compound formed is given below-
\[\text{M}{{\text{g}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+6}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\to \text{3Mg}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{\text{2}}}\text{+2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\]
(c) Ammonia is a reducing agent and hence it reduces the less reactive metal oxide to the respective metal.
11. Correct the following:
(a) A reddish-brown precipitate is obtained when ammonium hydroxide is added to ferrous sulphate.
Ans: The given statement is incorrect as a dirty green precipitate of ferrous hydroxide is obtained when ammonium hydroxide is added to ferrous sulphate.
(b) Liquid ammonia is a solution of NH3.
Ans: The given statement is incorrect as the Liquid ammonia is liquefied ammonia.
(c) Finely divided platinum is used in Haber’s Process.
Ans: The given statement is incorrect as finely divided Iron is used in Haber’s Process.
(d) Conc. H2SO4, Is a drying agent for NH3,
Ans: The given statement is incorrect as Quicklime is a drying agent for NH3.
(e) Ammonium salts, on heating, decompose to give ammonia.
Ans: The given statement is incorrect as when ammonium salts when heated with caustic alkali then they decompose and give ammonia.
12. Choose the correct from the following-
Ammonia can be obtained by adding water to
A. Ammonium chloride. B. Ammonium nitrite.
C. Magnesium nitride. D. Magnesium nitrate
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given as-
\[\text{M}{{\text{g}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+6}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\to \text{3Mg}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{\text{2}}}\text{+2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\]
Our correct option is (C) Magnesium nitride.
Exercise
1. (a) Is ammonia more dense or less dense than air?
Ans: Ammonia is less dense than air as its vapour density is 8.5 means it is lighter than air.
(b) What property of ammonia is demonstrated by the Fountain Experiment?
Ans: By Fountain Experiment we can concluded the high solubility of ammonia gas in water.
(c) Write the balanced equation for the reaction between ammonia and sulphuric acid.
Ans: The balanced equation for the reaction between ammonia and sulphuric acid is given as-
\[\text{2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\to {{\left( \text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}} \right)}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\]
2. Pick the odd member from the list giving reasons:
(a) Ammonia, sulphur dioxide, hydrogen chloride, carbon dioxide,
Ans: Ammonia is basic in nature from the rest of the given compounds.
(b) Copper oxide, aluminium oxide, sodium oxide, magnesium oxide.
Ans: Copper oxide because CuO is less reactive can be reduced by C, CO or by hydrogen whereas aluminium oxide, sodium oxide, magnesium oxide are reduced by electrolysis.
3. Give reasons for the following-
(a)Liquid ammonia is used as a refrigerant in ice plants.
Ans: Liquid ammonia is used as a refrigerant in ice plants as it takes a lot of energy to vaporize. This heat is taken from the surrounding bodies which are consequently cooled down. Hence, it is used as a refrigerant in ice plant.
(b)Aqueous solution of ammonia is used for removing grease stains from woollen clothes.
Ans: Aqueous solution of ammonia is used for removing grease stains from woollen clothes as it emulsifies or dissolves fats, grease so it is used to remove grease from woollen clothes.
(c) Aqueous solution of ammonia gives a pungent smell.
Ans: Aqueous solution of ammonia gives pungent smell as due to the presence of ammonia which has pungent smell characteristic property.
(d) Aqueous solution of ammonia conducts electricity.
Ans: Aqueous solution of ammonia conducts electricity as when it is dissolved in water it breaks into ions which help in the conductance of electricity.
4. A gas 'P' gives dense white fumes with chlorine. Its aqueous solution gives a blue colour with copper (II) hydroxide. Give the name and formula of the gas P.
Ans: Ammonia gas gives dense white fumes with chlorine. Its aqueous solution gives a blue colour with copper (II) hydroxide. Name of the gas P is ammonia and formula is NH3.
5. Ammonia solution in water gives a blue precipitate when it combines with a solution of copper salt. The blue precipitate further dissolves in excess of ammonia solution to give an azure blue solution. Explain with equation.
Ans: Ammonia solution in water gives a blue precipitate when it combines with a solution of copper salt. The pale blue precipitate of copper hydroxide dissolves in excess of ammonium hydroxide forming tetraamine copper (II) sulphate, an azure blue (deep blue) soluble complex salt. The balanced chemical equations are given as-
\[ CuSO_{4} + 2NH_{4}OH \rightarrow Cu(OH_{2}) + (NH_{4})_{2}) SO_{4}\]
\[ Cu(OH_{2}) + (NH_{4})_{2} SO_{4} + 2NH_{4} OH \rightarrow (Cu(NH_{3})_{4}) SO_{4} + 4H_{2}O \]
6. Give chemical equation(s) to prove that NH3 contains nitrogen and hydrogen?
Ans: The chemical equation which shows that ammonia contains nitrogen and hydrogen is that ammonia dissociates into nitrogen and hydrogen at high temperature or by electric sparks. The balanced chemical equation is given as-
\[\text{2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\rightleftharpoons {{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\]
7. Copy and complete the following equations.
\[\left( \mathbf{a} \right)\mathbf{ AlN+}{{\mathbf{H}}_{\mathbf{2}}}\mathbf{O }\to \]
Ans: The balanced and completed equation are given below-
\[\text{AlN+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O }\to \text{Al(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\]
\[\left( \mathbf{b} \right)\mathbf{ N}{{\mathbf{H}}_{\mathbf{3}}}\mathbf{ + 3C}{{\mathbf{1}}_{\mathbf{2}}}\to \]
Ans: The balanced and completed equation are given below-
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ + 3C}{{\text{1}}_{\text{2}}}\to {{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+6N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl}\]
\[\left( \mathbf{c} \right)\mathbf{ 2N}{{\mathbf{H}}_{\mathbf{3}}}\mathbf{ + 3PbO}\to \]
Ans: The balanced and completed equation are given below-
\[\text{2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ + 3PbO}\to \text{3Pb+3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O+}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\]
\[\left( \mathbf{d} \right)\mathbf{ N}{{\mathbf{H}}_{\mathbf{3}}}\mathbf{ + C}{{\mathbf{O}}_{\mathbf{2}}}\to \]
Ans: The balanced and completed equation are given below-
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ + C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\to \text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{CON}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\]
(i) Which property of ammonia is illustrated by equation (c)?
Ans: Ammonia is acting as the reducing agent as it is losing hydrogens in equation (c).
(ii) What important fertiliser is prepared from equation (d)? State the conditions.
Ans: Important fertiliser is prepared from equation (d) is Urea.
8. (a) What do you observe when ammonium hydroxide added to the aqueous solution of:
(i) \[\mathbf{FeS}{{\mathbf{O}}_{\mathbf{4}}}~~~\] (iii) Lead nitrate.
(ii) Iron (Ill) chloride. (iv) Zinc nitrate
Ans: (i) → Dirty green ppt. of Ferrous hydroxide is formed which is insoluble in excess of NH4OH.
\[\text{FeS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{+2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH}\to {{[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}]}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ + Fe(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\]
(ii) → Reddish brown ppt. of ferric hydroxide is formed which is insoluble in ammonium hydroxide.
\[\text{6N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH+2FeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\to \text{2Fe}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{\text{3}}}\text{+6N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl}\]
(iii) → White ppt. of lead hydroxide is formed which is insoluble in NH4OH.
\[\text{Pb(N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH}\to \text{2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ + Pb(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\]
(iv) → White gelatinous ppt. of Zinc hydroxide is formed which is soluble in NH4OH.
\[\text{Zn(N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH}\to \text{ 2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3 }}}\text{+ Zn(OH}{{)}_{\text{2}}}\]
(b) Write balanced equation for Q.8(a).
Ans: The balanced chemical equations are given as-
(i) \[\text{FeS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{+2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH}\to {{[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}]}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ + Fe(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\]
(ii) \[\text{6N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH+2FeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\to \text{2Fe(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+6N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl}\]
(iii) \[\text{Pb(N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH}\to \text{2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ + Pb(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\]
(iv) \[\text{Zn(N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH}\to \text{ 2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3 }}}\text{+ Zn(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\]
9. Distinguish between the following (using ammonia solution)-
(a) Ammonium chloride and sodium chloride.
Ans: Ammonium chloride on strong heating sublimes to form dense white fumes which condense to white powdery mass on cooler parts of the tube whereas no white fumes on heating sodium chloride.
(b) Ferric salt and ferrous salt.
Ans: When ammonium hydroxide is added drop wise to solution to be tested. Ferrous salt gives dirty green ppt whereas Ferric salt gives reddish brown ppt of their hydroxides.
(c) Sodium sulphate and ammonium sulphate.
Ans: Ammonium sulphate on warming with sodium hydroxide solution Gives ammonia gas. Sodium sulphate does not liberate ammonia gas.
10. Give balanced equation for the following conversions-
(a) Ammonia to nitrogen using an acidic gas.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given below-
\[\text{8N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ + 3C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\to {{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ + 6N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl }\]
(b) Ammonia to brown gas.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given below-
\[\text{4N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ + 5}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\xrightarrow[\text{80}{{\text{0}}^{\centerdot }}\text{C}]{\text{Pt}}\text{ 4NO + 6}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O +Heat }\]
\[\text{2NO+}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\to \text{2N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ }\]
Brown gas
(c) Ammonia to nitrogen trichloride.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given below-
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ +3C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\to \text{3HCl +NC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\]
(d) Ammonia solution to an amphoteric hydroxide.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given below-
\[\text{AlC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ +3N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH}\to \text{3N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl + Al}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{\text{3}}}\]
(e) A nitride of a trivalent metal to ammonia.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given below-
\[\text{AlN +3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\to \text{Al}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{\text{3}}}\text{+ N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\]
(f) lead oxide to lead.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given below-
\[\text{3PbO+2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\to \text{3Pb + 3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O +}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\]
11. Name:
(a) the gas which is prepared by Haber’s process.
Ans: Ammonia is the gas which is prepared by Haber’s process
(b) two gases which give dense white fumes with ammonia.
Ans: Hydrogen chloride and chlorine gas are the two gases which give dense white fumes with ammonia.
(c) one salt of ammonia in each case which is used in:
(i)dry cell.
Ans: Ammonium chloride is salt of ammonia which is used in dry cell.
(ii) explosives.
Ans: Ammonium nitrate is salt of ammonia which is used in explosives.
(iii) medicine.
Ans: Ammonium carbonate is salt of ammonia which is used in medicine.
(d) an acidic gas which reacts with a basic gas liberating a neutral gas.
Ans: Acidic gas: HCl
Basic gas: Ammonia
Neutral gas: NH4Cl
(e) a metallic chloride soluble in ammonium hydroxide.
Ans: Silver chloride is a metallic chloride soluble in ammonium hydroxide
(f) the gas obtained when ammonia burns in an atmosphere of oxygen without any catalyst.
Ans: Nitrogen is the gas obtained when ammonia burns in an atmosphere of oxygen without any catalyst.
(g) a nitride of a divalent metal which reacts with warm water liberating ammonia.
Ans: Magnesium nitride is a nitride of a divalent metal which reacts with warm water liberating ammonia.
(h) an amphoteric oxide reduced by the basic gas.
Ans: Lead oxide is an amphoteric oxide reduced by the basic gas.
(i) a white salt produced by an acidic gas and a basic gas.
Ans: Ammonium chloride is a white salt produced by an acidic gas and a basic gas.
12. When ammonium hydroxide is added to solution B, a pale blue precipitate is formed. This pale blue precipitate dissolves in excess ammonium hydroxide giving an inky blue solution. What is the cation (positive ion) present in solution B? What is the probable colour of solution B.?
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given as-
\[\text{CuS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{+2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH}\to {{\left( \text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}} \right)}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4 }}}\text{+ Cu}{{\left( \text{OH} \right)}_{\text{2}}}\]
The cation present in solution B is Copper (Cu2+) The colour of solution B is Blue. → The pale blue precipitate of copper hydroxide dissolves in excess of ammonium hydroxide forming tetra amine copper (II) sulphate, an azure blue (deep blue) soluble complex salt. The balanced chemical equation is given as-
\[\text{Cu(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+(N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{+2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH}\to [\text{Cu(N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{4}}}]\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ + 4}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\]
13. When an ammonium salt is warmed with sodium hydroxide solution, a gas is evolved. State three ways in which you could identify this gas.
Ans: When an ammonium salt is warmed with sodium hydroxide solution, ammonia gas is evolved.
Three ways in which ammonia gas can be identified is:
1. It has a sharp characteristic odour.
2. When a glass rod dipped in HCl is brought in contact with the gas white colour fumes of ammonium chloride are formed
3.It turns moist red litmus blue, moist turmeric paper brown, and phenolphthalein solution pink.
14. A gas 'A’ reacts with another gas 'B' in the presence of a catalyst to give a colourless gas 'C'. The gas 'C' when comes in contact with air produces a brown gas 'D'. The solution of 'A' in water turns red litmus blue. Explain the observations.
Ans: As the 'A' turns red litmus blue it is a base. Now the gas 'A' combines with 'B' in presence of Catalyst to give colourless gas Nitrogen monoxide. It reacts with oxygen to give brown gas which is Nitrogen dioxide. The gases are given as-
A = \[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\]
B = \[{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]
C = NO
D = \[\text{N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]
The balanced chemical reactions are given as-
\[ 4NH_{3} + 5 O_{2} \xrightarrow[800^0C]{pt}\: 4NO + 6H_{2}O + Heat \]
\[ 2NO + O_{2} \rightarrow 2NO_{2}\]
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\]in water forms ammonium hydroxide, which turns red litmus blue.
15. (i) Name the common refrigerant. How does it deplete ozone layer?
Ans: The main refrigerants used are Freon chlorofluorocarbons (CFC). They deplete ozone layer. The chlorofluorocarbons are decomposed by ultraviolet rays to highly reactive chlorine which is produced in the atomic form. This causes depletion of ozone layer and chlorine monoxide so formed reacts with atomic oxygen and produces more chlorine free radicals Again this free radical destroys ozone, and the process continues thereby giving rise to ozone depletion.
(ii)What is the alternative of chlorofluorocarbon?
Ans: Liquid ammonia can be used as a refrigerant, as an alternative for chlorofluorocarbons.
(iii) State the advantages and disadvantages of using ammonia as refrigerant?
Ans: Advantages of ammonia as refrigerant:
(i) Ammonia is environmentally compatible. It does not deplete ozone layer and does not contribute towards global warming.
(ii) It has superior thermodynamic qualities as result ammonia refrigeration systems use less electricity. Ammonia has a recognizable odour and so leaks are not likely to escape.
Disadvantages of ammonia as a refrigerant are as follows:
(i) It is not compatible with copper, so it cannot be used in any system with copper pipes.
(ii) It is poisonous in high concentration although it is easily detectable due to its peculiar smell and since it is less dense than air it goes up in the atmosphere not affecting the life too much on earth.
16. Name a compound prepared by ammonia and is used as:
(a) Explosive.
Ans: Ammonium nitrate is a compound prepared by ammonia and is used as explosive.
(b) Fertilizers
Ans: Ammonium sulphate is a compound prepared by ammonia and is used as Fertilizers.
(c) Medicine
Ans: Ammonium carbonate is a compound prepared by ammonia and is used as Medicine.
(d) Laboratory reagent.
Ans: Ammonia solution is a compound prepared by ammonia and is used as Laboratory reagent.
17. Write the action of heat on:
(a) Ammonium chloride
State whether each reaction is an example of thermal decomposition or thermal dissociation.
Ans: (a) On heating Ammonium chloride, we will get ammonia and hydrochloric acid.
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl}\to \text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ + HCl}\]
This reaction is an example of thermal dissociation.
(b) Ammonium nitrate
State whether each reaction is an example of thermal decomposition or thermal dissociation.
Ans: (b) On heating Ammonium nitrate, we will get nitrous oxide and water.
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\to {{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O + 2}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\]
This reaction is an example of thermal dissociation.
18. (a) Which feature of ammonia molecule leads to the formation of the ammonium ion when ammonia dissolves in water?
Ans: It is the basic nature of ammonia molecule which leads to the formation of the ammonium ion when ammonia dissolves in water.
(b) Name the other ion formed when ammonia dissolve, in water.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given as-
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ +}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\to \text{N}{{\text{H}}^{\text{4 +}}}\text{ + O}{{\text{H}}^{\text{-}}}\]
Hydroxide ion is formed when ammonia dissolve, in water.
(c) Give one test that can be used to detect the presence of the ion produced in (b).
Ans: The red litmus paper turns blue in the solution that can be used to detect the presence of the ion produced in (b).
19. (a) Of the two gases. ammonia and hydrogen chloride. Which is more dense? Name the method of collection of this gas.
Ans: HCl gas is denser as its vapour density =18.25, and those of ammonia is 8.5 and it is collected by the upward displacement of air.
(b) Give one example of a reaction between the above two gases which produces a solid compound.
Ans: The example of a reaction between the above two gases which produces a solid compound is given as-
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\left( g \right)\text{+HCl(g)}\to \text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl(s)}\]
(c) Write a balanced equation for a reaction in which ammonia is oxidized by:
(i) a metal oxide.
Ans: The balanced chemical reaction is given as-
\[\text{2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+3CuO}\to \text{3Cu+3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O+}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\]
(ii) a gas which is not oxygen.
Ans: The balanced chemical reaction is given as-
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+3C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\to {{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+ 6HCl}\]
20. Study the flow chart given and give balanced equations to represent the reactions A, B and C.
\[\mathbf{M}{{\mathbf{g}}_{\mathbf{3}}}{{\mathbf{N}}_{\mathbf{2}}}\xrightarrow{\mathbf{A}}\mathbf{ N}{{\mathbf{H}}_{\mathbf{3}}}\mathbf{ N}{{\mathbf{H}}_{\mathbf{4}}}\mathbf{Cl}\]
Ans: The balanced chemical equations are given as-
\[ (A) Mg_{3} N_{2} + 6H_{2}O \rightarrow 3Mg(OH_{2}) + 2NH_{3}\]
\[ (B) NH_{3} + HCl \rightarrow NH_{4}Cl \]
\[ (C) NH_{4} Cl + NaOH \overset {Heat} \rightarrow NaCl + H_{2}O +NH_{3} \uparrow \]
(2019)
21. (a) Ammonia reacts with excess chorine to form ....... (nitrogen/nitrogen trichloride/ammonium chloride).
Ans: When the chlorine is taken in excess, it reacts with colourless gas ammonia to give a yellow-coloured explosive liquid nitrogen trichloride.
(NCl3). The balanced chemical equation is given below-
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+3C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\left( \text{excess} \right)\to \text{3HCl+NC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\]
Ammonia reacts with excess chlorine to form ammonium chloride (nitrogen/nitrogen trichloride/ammonium chloride).
(b) Give a balanced equation: Ammonium hydroxide is added to ferrous sulphate solution.
Ans: The balanced chemical reaction is given below-
\[\text{FeS}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{+2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH}\to {{\text{(N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{+Fe(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\downarrow \]
(c) Write observations: Ammonia gas is passed over heated copper (II) oxide.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given as-
\[ 3CuO + 2NH_{3} \overset{Heat} \rightarrow 3Cu + N_{2} + 3H_{2}O\]
Black Reddish Pink
Observation is - The black colour copper oxide will change to reddish pink copper.
(2009)
(a) Name the gas evolved in each case (formula is not acceptable). The gas that burns in oxygen with a green flame.
Ans: The gas evolved is ammonia gas which on burning in oxygen which gives a green flame. The balanced chemical equation is given as-
\[\text{4N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+3}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\to \text{2}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+6}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\]
(b) Write a fully balanced equation for — Magnesium nitride is treated with warm water.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given as-
\[\text{M}{{\text{g}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+6}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\to \text{2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+3Mg(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\]
(c) Identify the substance “Q” based on the information given — The white crystalline solid “Q” is soluble in water. It liberates a pungent smelling gas when heated with sodium hydroxide solution.
Ans: The white crystalline solid is ammonium chloride which is formed by mixing gases ammonia and hydrochloric acid. When ammonium chloride is heated with sodium hydroxide solution ammonia gas is evolved. The balanced chemical equation is given as-
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl+NaOH}\to \text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+NaCl+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\]
(2010)
(a) Complete the blanks (i) to (v) in the passage given, using the following words. (Ammonium, reddish brown, hydroxyl, nitrogen dioxide, ammonia. dirty green, alkaline, acidic).
In the presence of a catalyst nitrogen and hydrogen combine to give (i) _______gas.
Ans: In the presence of a catalyst nitrogen and hydrogen combine to give (i) Ammonia gas.
When the same gas is passed through water it forms a solution. which will be (ii)_________ in nature.
Ans: When the same gas is passed through water it forms a solution. which will be (ii) Alkaline in nature.
and will contain the ions (iii)_______.
Ans: and will contain the ions (iii) Ammonium.
and (iv)________.
Ans: and (iv) Hydroxyl.
A (v)__________ coloured precipitate of iron (III) hydroxide is formed when the above solution is added to iron (II) sulphate solution.
Ans: A (v) Dirty green coloured precipitate of iron (III) hydroxide is formed when the above solution is added to iron (II) sulphate solution.
(b) State your observation when-- in the absence of catalyst, ammonia is burnt in an atmosphere of oxygen.
Ans: when in the absence of catalyst, ammonia is burnt in an atmosphere of oxygen then the combustion of ammonia proceeds to yield nitrogen gas and water. With the use of a catalyst and under correct conditions of temperature, ammonia reacts with oxygen to produce nitric oxide which is oxidized to nitrogen dioxide and is used in the synthesis of nitric acid.
(c) Give the equation for the reaction - ammonium chloride is heated with sodium hydroxide.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given as-
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl+NaOH}\to \text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+NaCl+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\]
(d) ln the manufacture of ammonia-
(i) Name the process.
Ans: The process used in the manufacture of ammonia is Haber’s process.
(ii) State the ratio of the reactants taken.
Ans: Ratio taken for the reactants that is nitrogen and hydrogen, these are taken in a ratio of 1:3.
(iii)State the catalyst used.
Ans: Catalyst used is Finely divided iron (Fe).
(iv) Give the equation for the manufacture of the gas- ammonia.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given as-
\[{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\xrightarrow[\text{Fe}]{\text{400-50}{{\text{0}}^{\centerdot }}\text{C}}\text{2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+Heat}\]
(e) Write a relevant equation to show that ammonia acts as a reducing agent.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given as here ammonia is acting as a reducing agent as it loses hydrogen and forms nitrogen.
\[\text{2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+3C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\to {{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+6HCl}\]
(f) Name two gases which can be used to study the fountain experiment. State the common property demonstrated by the fountain experiment.
Ans: Two gases that are used in the study of fountain experiment is ammonia gas and hydrogen chloride gas. The common property demonstrated by the fountain experiment the concepts like solubility and the gas laws at the entry level. It explains the alkalinity or acidity property of gases when litmus is added to the reaction mixture and shows the colour change by the gas dissolving in water.
(2011)
(a) State what is observed when — Ammonium hydroxide is first added in a small quantity and then in excess to a solution of copper sulphate.
Ans: When ammonium hydroxide solution is added drop by drop to copper sulphate solution a pale blue / bluish white precipitate is formed which is soluble in excess of ammonium hydroxide and deep blue / inky blue solution is formed. The balanced chemical equations are given as-
\[ CuSo_{4} + 2NH_{4}OH \rightarrow Cu(OH_{2}) + (NH_{4})_{2} SO_{4}\]
\[ Cu(OH_{2}) + 4NH_{4}OH \rightarrow Cu(NH_{3})_{4} (OH)_{2} + 4H_{2}O \]
(b) The diagram below shows the setup for the laboratory preparation of a pungent alkaline gas.
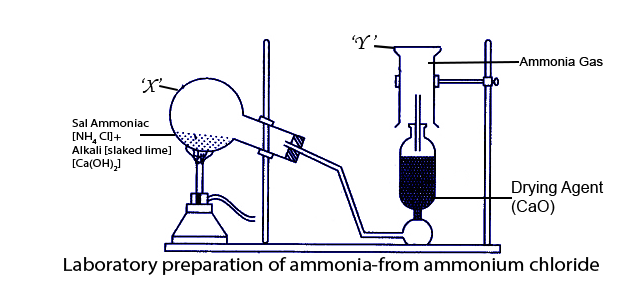
(i) Name the gas collected in the jar.
Ans: The gas collected in the jar is ammonia.
(ii) Give a balanced equation for the above preparation.
Ans: The balanced equation for the above preparation-
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl + Ca(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\to \text{ CaC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+2}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O + 2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\uparrow \]
(iii) State how the above gas is collected.
Ans: The above gas is collected due to the downward displacement of air.
(iv) Name the drying agent used.
Ans: The drying agent used is Quicklime (CaO).
(v) State how you will find out that the jar is full of the pungent gas.
Ans: We will find out that the jar is full of the pungent gas when we bring a rod dipped in HCl near it. Dense white fumes of ammonium chloride will be formed.
(c) Write the balanced chemical equation – Chlorine reacts with excess of ammonia.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given as-
\[\text{8N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\left( \text{excess} \right)\text{+3C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\to {{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\uparrow \text{+ 6N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl + }{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\]
(d) State your Observation-Water is added to the product formed when Al is burnt in a jar of nitrogen gas.
Ans: When Water is added to the product formed when Al is burnt in a jar of nitrogen gas, a Pungent smelling and alkaline gas is evolved.
\[\text{2Al+}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\to \text{2AlN}\]
\[\text{AlN+3OH}\to \text{Al(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+ N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\uparrow \]
Pungent gas
(2012)
(a) Name - The gas produced when excess ammonia reacts with chlorine.
Ans: Nitrogen gas is being produced when excess ammonia reacts with chlorine. The balanced chemical equation is given as-
\[\text{8N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{(excess)+3C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\to {{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\uparrow \text{+ 6N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl + }{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\]
(b) Rewrite the correct statement with the missing words: Magnesium nitride reacts with water to liberate ammonia.
Ans: The correct statement is –
Magnesium nitride reacts with warm water to liberate ammonia along with magnesium hydroxide.
(c) Give balanced equation for the reaction: Ammonia and oxygen in the presence of a catalyst.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given as-
\[\text{4N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+5}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\xrightarrow[\text{Pt}]{\text{80}{{\text{0}}^{\centerdot }}\text{C}}\,\text{4NO+6}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O+heat}\]
(d) The following questions are based on the preparation of ammonia gas in the laboratory:
(i) Explain why ammonium nitrate is not used in the preparation of ammonia.
Ans: Ammonium nitrate is not used in the preparation of ammonia as ammonium nitrate is explosive in nature and dissociates into nitrous oxide and water on heating.
(ii) Name the compound normally used as a drying agent during the process.
Ans: Quick lime is the compound normally used as a drying agent during the process.
(iii) How is ammonia gas collected? Explain why it is not collected over water.
Ans: Ammonia gas is collected by downward displacement of air. Ammonia gas is not collected over water as it is highly soluble in water.
(2013)
State one appropriate observation for:
(a) Excess of chlorine gas is reacted with ammonia gas.
Ans: When Excess of chlorine gas is reacted with ammonia gas then a yellow explosive liquid (Nitrogen trichloride) is formed.
(b) Nitrogen gas can be obtained by heating:
(i) Ammonium nitrate
(ii) Ammonium nitrite
(iii) Magnesium nitride
(iv) Ammonium chlorite
Ans: Nitrogen gas can be obtained by heating ammonium nitrite. The balanced chemical equation is given as-
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\to {{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\uparrow \text{+2}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\]
Option(ii) is the correct answer.
(c) State two relevant observations for: Ammonium hydroxide solution is added to zinc nitrate solution slowly and then in excess.
Ans: Two relevant observations are-
When Ammonium hydroxide solution is added to zinc nitrate solution slowly white precipitates of ammonium nitrate is formed and when ammonium hydroxide is added in excess then the white precipitates are soluble in it.
(d) Give a balanced equation for: Reduction of hot copper (II) oxide to copper using ammonia gas.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given as-
\[\text{3CuO +2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\to \text{3Cu +}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\text{.}\]
(e) Copy and complete the following table relating to important industrial process: (2019)
Name of the process | Temperature | Catalyst | Equation for the catalysed reaction |
Haber’s process |
Ans:
Name of the process | Temperature | Catalyst | Equation for the catalysed reaction |
Haber’s process | 700K | Iron (Fe) | \[{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\xrightarrow[\text{Fe}]{\text{700K}}\text{2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] |
(f) Identify: An alkaline gas which produces white dense white fumes when reacted with HCl gas.
Ans: Ammonia is an alkaline gas which produces dense white fumes when reacted with HCl gas and fumes are of compound ammonium chloride.
(2014)
(a) Fill in the blank from the choices given in bracket-
Ammonia gas is collected by_______________ (upward displacement of air, downward displacement of water, downward displacement of air).
Ans: Ammonia gas is lighter than air hence it is collected by downward displacement of air. Therefore, Ammonia gas is collected by downward displacement of air.
(b)Write balanced equation for: Action of warm water on magnesium nitride.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given as-
\[\text{M}{{\text{g}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+6}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\to \text{3Mg(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\]
(c) Distinguish between the following pairs of compounds using the test given in bracket-
(i) Iron (II) sulphate and Iron (III) sulphate (using ammonium hydroxide).
Ans: Iron (II) sulphate gives dirty green precipitate with ammonium hydroxide solution. These precipitates obtained are insoluble in excess. Whereas Iron (III) sulphate gives reddish brown precipitates with ammonium hydroxide solution. These precipitates obtained are insoluble in excess.
(ii) A lead salt and a zinc metal (using excess ammonium hydroxide).
Ans: Lead salt gives chalky with precipitates of lead hydroxide with ammonium hydroxide. These precipitates are insoluble in excess. Whereas Zinc salt gives gelatinous with precipitates of zinc hydroxide with ammonium hydroxide. These precipitates are soluble in excess.
(d) State your observation: Calcium hydroxide is heated with ammonium chloride crystals.
Ans: When calcium hydroxide heated with ammonium chloride, ammonia gas is liberated. This gas is a pungent smelling gas and is alkaline in nature.
(e) Name the other ion formed when ammonia dissolves in water. Give one test that can he used to detect the presence of the ion produced.
Ans: When ammonia is dissolved in water ammonium hydroxide is formed.
The balanced chemical equation is given as-
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\to \text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{OH}\text{.}\]
It contains 2 types of ions: NH4+ and OH-.
(f) State the conditions required for Catalytic oxidation of ammonia to nitric oxide.
Ans: The required conditions for the catalytic oxidation of ammonia are:
1) Catalyst required is platinum.
2) Temperature required is \[\text{80}{{\text{0}}^{\centerdot }}\text{C}\].
(2015)
(a) Give balanced chemical equations for –
(i) Lab preparation of ammonia using an ammonium salt.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given as-
2NH4Cl + Ca (OH)2 → CaCl2 + 2H2O + 2NH3
(ii) Reaction of ammonia with excess of chlorine.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given as-
NH3 + Cl2 → NCl3 + HCl
(iii) Reaction of ammonia with sulphuric acid.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given as-
2NH3 + H2SO4 → (NH4)2SO4
(b) From the list of gases- ammonia, ethane, hydrogen chloride, hydrogen sulphide, select the gas which is used as a reducing agent in reducing copper oxide to copper.
Ans: Ammonia gas is used to reduce copper oxide to copper. The balanced chemical equation is given as-
2NH3 + 3CuO → 3Cu + 3H2O + N2↑
(2016)
(a)Name the gas evolved when the following mixtures are heated.
(i)Calcium hydroxide and ammonium chloride.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given as-
\[\text{Ca(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl}\to \text{CaC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\]
Ammonia gas is evolved when Calcium hydroxide and ammonium chloride are heated.
(ii) Sodium nitrite and ammonium chloride.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given as-
\[\text{NaN}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl}\to \text{NaCl+}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+2}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\]
Nitrogen gas is evolved when Sodium nitrite and ammonium chloride. are heated.
(b) Write balanced equation-
(i) When excess of ammonia is treated with chlorine.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given as-
Here the ammonia is taken in excess-
\[\text{8N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+3C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\to \text{6N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\text{Cl+}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\]
(ii) An equation to illustrate the reducing nature of ammonia.
Ans: The balanced chemical equation is given as-
In this, Ammonia is losing hydrogen and forming nitrogen, hence reducing in nature.
\[\text{3CuO+2N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\xrightarrow{\text{Heat}}\text{3Cu+}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\]
Preparation of Ammonia
It is prepared by heating ammonium salt with Alkali.
(NH4)2SO4 + Ca(OH)2 ---> CaSO4 + 2 H2O + 2NH3
In the laboratory, it is prepared by heating a mixture of ammonium chloride and slaked lime.
2NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2 → CaCl2 + 2 H2O + 2 NH2
Ammonia can also be prepared by reacting metallic nitride with water.
Mg2N2+ 6 H2O → 3 Mg( OH)2 + 2 NH3
Physical Properties of Ammonia
It is a colourless gas.
Ammonia is bitter.
Ammonia has a pungent smell.
Ammonia is lighter than air.
It is highly soluble in water.
It has irritating effects on the human body.
Chemical Properties of Ammonia
The aqueous solution of ammonia is called ammonium hydroxide.
Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base and so dissociates partially to give hydroxyl ions.
NH3 + H2O → NH4OH
NH4OH → NH4++ OH-
Ammonium hydroxide precipitates hydroxides of metals like Fe, Pb, Mg and Zn from the solution of their salts.
Ammonia is a strong reducing agent. It reduces metallic oxide and Chlorine.
Ammonia does not burn in the presence of air. But it burns with greenish-yellow flame in the presence of an atmosphere of oxygen.
FAQs on Study of Compounds Ammonia Solutions for Class 10 Chemistry
1. What are the different tests to identify the presence of ammonia?
Here are different tests for ammonia. Some of them are lab tests and others are physical tests.
Ammonia turns moist red litmus paper into blue. So it can be tested on litmus paper.
It turns methyl orange-yellow.
Ammonia has a pungent smell. You can identify ammonia with its distinct odour.
Ammonia gives white precipitates with lead nitrate solution. Reacting the given compound with lead nitrate, you can find out if it is ammonia or not.
Ammonia gives white fumes with concentrated hydrochloric acid.
Ammonia causes a burning sensation in our eyes.
2. What are the uses of Ammonia?
The different uses of Ammonia are :
Ammonia is used as a refrigerant in ice plants.
Ammonia is used as a cleansing agent in its liquid form.
It is also used for the manufacture of compounds such as plastics, nylon, rayon, dyes and explosives.
It is used for the manufacture of ammonium salts.
Ammonia is used as an important compound in laboratories.
Ammonia is used as a non-aqueous solvent in the presence of liquid ammonia
Ammonia is also used in the production of fertilizers.
3. What is the Haber process?
The Haber process is one of the most important and efficient processes for the preparation of ammonia. The Haber process is used at a big scale in industries. In the Haber process atmospheric nitrogen reacts with hydrogen to form ammonia. The important raw materials for the Haber process are Air, Hydrogen and Iron. Here, iron is used as a catalyst and so is not used up. It is an exothermic reaction and so heat is released up during the process. This ammonia produced here is used for its different applications.
4. Why is the Haber process important?
The Haber process is an important method of production of Ammonia, which is a necessary component for fertilizers. Fertilizers are an essential component in the production of various crops so it makes them more valuable. Ammonia produced there is used for Agriculture Uses, Explosives, Pharma, Refrigeration and consumer products. The major advantage of the Haber process is that hydrogen is produced at a much lower pressure.
5. Which is the best platform to learn the concepts of class 10th ICSE chemistry?
To learn the concepts of chemistry, you need a platform where you can find each concept well explained. Vedantu can be a great choice for those students. On Vedantu, you will get study material, previous year questions, and the syllabus of different boards and competitive examinations. Vedantu focuses more on strengthening the concepts of the students rather than just simply writing the solution. You can download the syllabus PDFs, material, and important questions in a single place. So that's why Vedantu can be the best choice for you.



































