




Define Respiration
Respiration is a process that occurs within cells to release energy through the breakdown of glucose molecules. Based on the use of oxygen, the process can be conveniently divided into two categories: aerobic and anaerobic respiration. It is a common misconception that humans and other multicellular organisms only use aerobic respiration. This is refuted by the fact that during vigorous exercise, our muscles undergo anaerobic respiration, producing lactic acid as a waste byproduct rather than carbon dioxide.
Types of Respiration
There are two kinds of breathing; they are as follows.
What is Respiration in Plants? There are two types of Respiration in Plants which are as follows:
Aerobic Respiration in Plants
Respiration produces energy in the presence of oxygen. It is a continuous process that occurs within animal and plant cells. The following chemical equation can be used to explain this process:
Glucose+ Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
Anaerobic Respiration in Plants
In the absence of oxygen, respiration generates energy. The anaerobic respiration chemical equation is:
Glucose → Alcohol + Carbon dioxide + Energy (ATP )
Anaerobic Respiration is also known as fermentation.
Steps of Respiration in Organisms
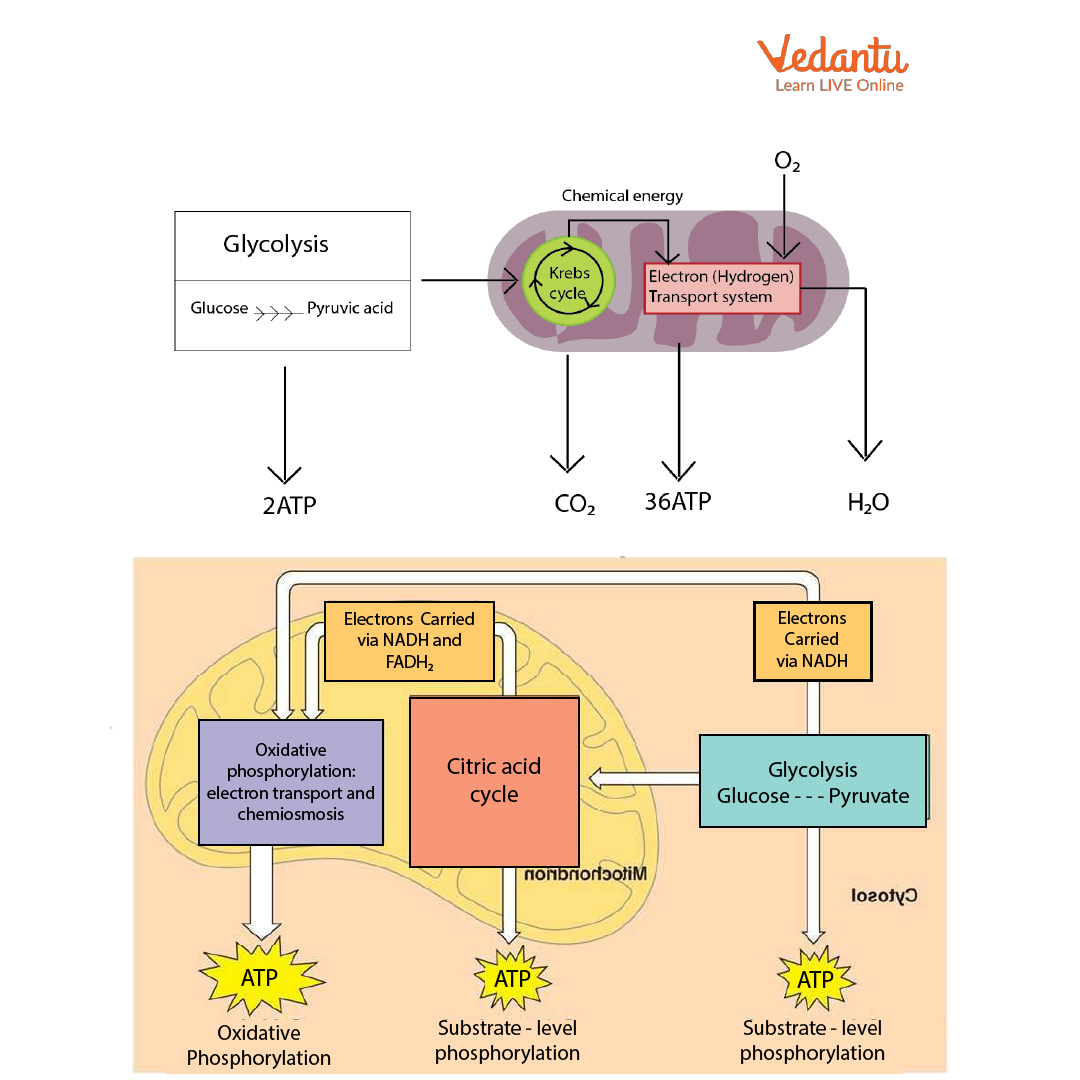
Respiration in Organisms
The first step of respiration in organisms is glycolysis. It converts one glucose molecule into two pyruvate molecules, yielding two molecules of ATP in total. This occurs in the cytosol.
The pyruvate then enters the mitochondria and is oxidised to acetyl CoA, which enters the Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle). The process takes place in the mitochondrial matrix. The third stage occurs on the inner membrane of mitochondria. It's known as oxidative phosphorylation. Chemical energy is converted during this stage and used to synthesise ATP.
What is Respiration and Breathing in Plants:
Plants require oxygen to respire, and the process emits carbon dioxide. Unlike humans and animals, plants lack specialised structures for gas exchange; however, they have stomata (found in leaves) and lenticels (found in stems) that are actively involved in gas exchange. In addition, plant leaves, stems, and roots respire slower than humans and animals.
Breathing is not the same as respiration. Both animals and humans breathe, which is a step in the respiration process. Plants breathe throughout their lives because the plant cell requires energy to survive. Plants, on the other hand, breathe in a unique way known as cellular respiration.
Plants generate glucose molecules in this process of cellular respiration by capturing and converting sunlight energy into glucose. Several live experiments demonstrate plant respiration. All plants respire to provide power to their cells, allowing them to be active or alive.
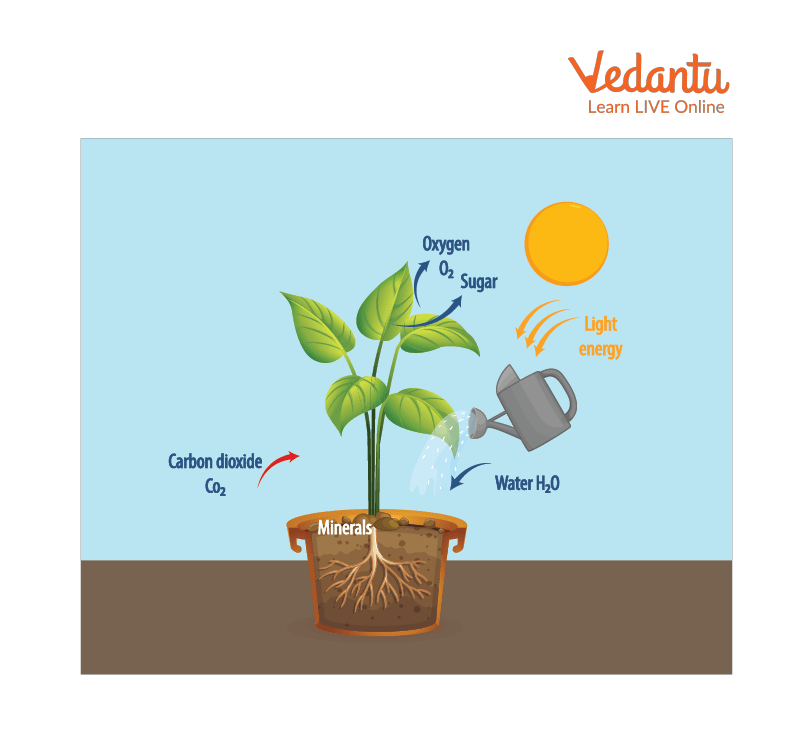
Plant Respiration Process
Solved Examples
1. Which of the following gases is discharged during the respiration process?
(a) Oxygen
(b) Hydrogen
(c) Carbon dioxide
Ans: (c) Carbon dioxide.
2. All organisms are composed of small microscopic units that cannot be seen with the naked eye and are referred to as____.
(a) animals
(b) cells
(c) tissues
Ans: (b) cells
3. Identify the type of breathing that causes muscle cramps.
(a) Aerobic respiration
(b) Anaerobic respiration
Ans: (b) Anaerobic respiration
Summary
The use of oxygen in the process of cellular respiration is the primary distinction between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Anaerobic respiration is similar to aerobic respiration, except that it occurs without oxygen. As a result, this process produces lactic acid and ATP as byproducts.
FAQs on What is Respiration?
1. What is the biological definition of respiration?
In biology, respiration is the fundamental biochemical process that occurs within the cells of all living organisms to produce energy. It involves the breakdown of complex organic molecules, primarily glucose, to release energy in the form of Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP). This energy is then used to power all other metabolic activities.
2. What are the two main types of respiration, and how do they differ?
The two primary types of respiration are aerobic and anaerobic. The key differences are:
Aerobic Respiration: This process occurs in the presence of oxygen. It completely breaks down glucose to produce a large amount of energy (around 38 ATP molecules), carbon dioxide, and water. It takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria.
Anaerobic Respiration: This process occurs in the absence of oxygen. It results in the incomplete breakdown of glucose, yielding a much smaller amount of energy (only 2 ATP molecules) and byproducts like lactic acid (in animals) or ethanol and carbon dioxide (in yeast).
3. Is breathing the same as respiration? Explain the key difference.
No, breathing and respiration are not the same, although they are related. Breathing is a physical or mechanical process of inhaling oxygen and exhaling carbon dioxide. In contrast, cellular respiration is a chemical process that happens inside cells to break down food and release energy. Breathing provides the oxygen needed for aerobic respiration to occur.
4. What is the balanced chemical equation for aerobic respiration?
The fundamental equation that summarizes aerobic cellular respiration is:
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + ATP (Energy)
This equation shows that one molecule of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) reacts with six molecules of oxygen (O₂) to produce six molecules of carbon dioxide (CO₂), six molecules of water (H₂O), and chemical energy in the form of ATP.
5. How does respiration occur in plants?
Plants respire continuously, both day and night, just like animals. They take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide. Gas exchange in plants occurs through various parts:
Stomata: Tiny pores on the surface of leaves.
Lenticels: Pores in the stems of woody plants.
Root hairs: The surface of the roots absorbs oxygen from the air spaces in the soil.
This process should not be confused with photosynthesis, where plants use carbon dioxide and release oxygen.
6. What are the main stages of cellular respiration?
Aerobic cellular respiration is typically divided into three main stages:
Glycolysis: The initial breakdown of glucose into pyruvate, which occurs in the cell's cytoplasm and does not require oxygen.
The Krebs Cycle (or Citric Acid Cycle): Pyruvate is further broken down, releasing carbon dioxide. This happens in the matrix of the mitochondria.
Electron Transport Chain (ETC): The final stage where the majority of ATP is produced using oxygen as the final electron acceptor. This occurs on the inner mitochondrial membrane.
7. How is the energy from respiration stored and used by the body?
The energy released during respiration is not used directly. Instead, it is captured and stored in the chemical bonds of a molecule called Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP). ATP acts as the universal 'energy currency' of the cell. When a cell needs to perform a function, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, or building new molecules, it breaks down ATP to release the stored energy.
8. What happens during anaerobic respiration in human muscles and why does it cause fatigue?
During strenuous physical activity, the oxygen supply to muscle cells can become insufficient for aerobic respiration. To meet the high energy demand, muscle cells switch to anaerobic respiration. In this process, glucose is broken down into lactic acid and a small amount of ATP. The accumulation of this lactic acid in the muscle tissue lowers the pH and is a primary cause of muscle fatigue, cramps, and soreness.
9. Why is respiration considered a catabolic process, while photosynthesis is anabolic?
Respiration is a catabolic process because it involves breaking down a large, complex molecule (glucose) into smaller, simpler ones (carbon dioxide and water) to release energy. In contrast, photosynthesis is an anabolic process because it uses energy (from sunlight) to build a complex molecule (glucose) from simpler ones (carbon dioxide and water). In essence, catabolism releases energy by breaking things down, while anabolism uses energy to build things up.









