




How Methane Powers Daily Life and the Environment
Methane gas can be produced by distilling coal and natural gas or by the fermentation of organic substances. The biomass of extinct plants is affected by the heat and pressure of the earth, turning its energy-rich carbon molecules into raw materials from which methane can be extracted.
Natural gas primarily consists of methane. Methane combustion results in the release of energy in the form of natural gas. Both residences and businesses can make use of this energy. If left unused and released into the atmosphere, methane can be dangerous since it is more powerful than carbon dioxide in creating greenhouse effect. It is said to contribute 30% to global warming.
Different Uses of Methane
There are 5 uses of methane given below:
A greenhouse gas that impacts ambient temperature is methane. If it is liquefied, it can be used as rocket fuel. Since methane has a lower molecular weight and produces more heat per unit mass than kerosene, it is a better choice for rocket fuel.
Methane is used at home to power appliances like water heaters, stoves, and dryers. Methane dries up quickly. As a result, most methane that gathers in lakes, streams, or soil eventually escapes into the atmosphere. These are a few of the several uses of methane in everyday life.
Methane is utilised to produce electricity since it is a key component of natural gas. By using steam created by boiling water with methane as fuel, energy is produced by powering turbines.
Methane is a clean fuel when compared to other hydrocarbons since it emits less carbon dioxide per unit of heat produced. It is the main ingredient in biogas and CNG and is used as a fuel.
Methane is frequently used as a fertiliser. In addition, methane is utilised to create a variety of chemicals.
Why is Methane Used for Burning in Gas Fires?
Methane can be utilised in houses to power appliances like water heaters, stoves, and dryers. Methane dries up quickly. As a result, most methane that gathers in lakes, streams, or soil eventually escapes into the atmosphere.
On the other hand, methane that is produced underground and flows through soil might last for many years without changing.
It is abundantly present in natural gas reserves all over the world, burns quickly and reasonably cleanly with the byproducts of water and carbon dioxide, and is therefore particularly appealing as a commercial fuel substance due to its low cost.
Methane will mix with air and burn when a spark or naked flame is introduced, which is why the reaction is referred to as explosive.
How is Methane Used To Generate Electricity?
Using conventional technologies, such as chemical conversion or gas-turbine generator sets, methane can be transformed into liquid fuels or electricity. Billion-dollar capital investments as well as a sizable land area are needed for the functioning of these technologies.
Methane is created by microorganisms in the present biogas systems, which are then burned to power a turbine and produce electricity. The highest capacity that can be reached is when less than half of the biogas is turned into electricity.
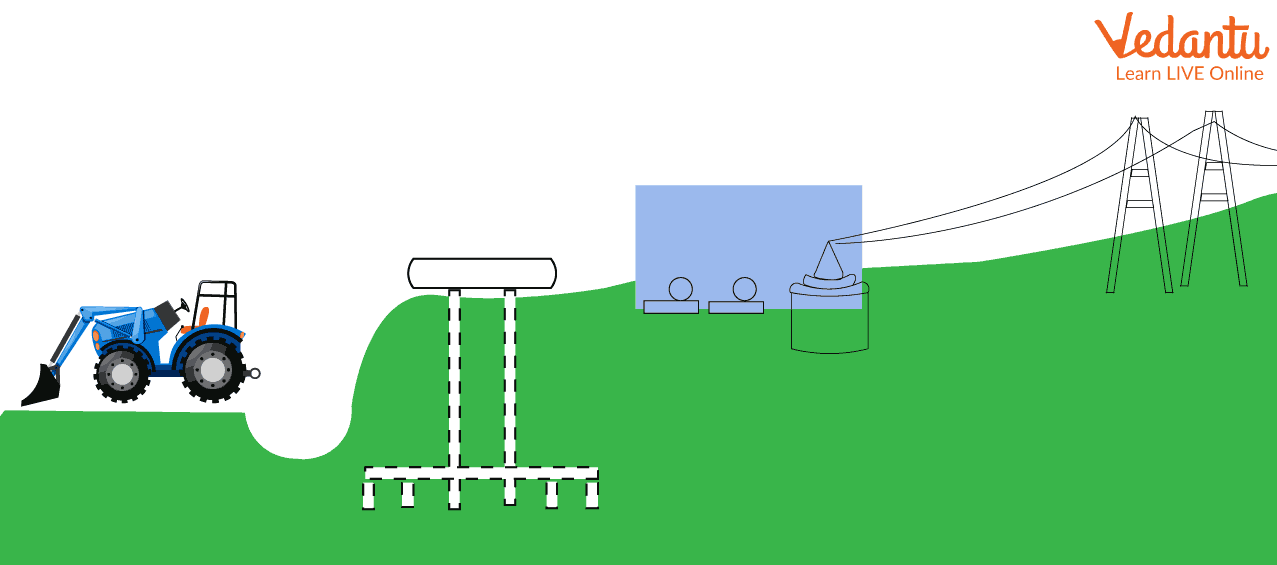
Using Methane to Generate the Electricity
In the above image, cable lines are shown connecting the biogas plant and transmission lines. So, a biogas plant will generate electricity using biogas and the generated electricity will then distribute to the city through the transmission lines making effective use of methane gas.
Conclusion
Methane has significant environmental advantages over other hydrocarbons or fossil fuels, such as coal and gasoline made from refined oil, as it produces more heat and light energy per unit of mass while producing significantly less carbon dioxide and other pollutants that cause polluted air and unhealthy air. Methane is an extremely powerful greenhouse gas because the molecular links in its molecule make it 86 times more efficient at absorbing heat than carbon dioxide.
FAQs on Uses of Methane: Key Applications and Benefits
1. What are the main uses of methane gas?
Methane (CH₄) is a versatile compound with several important uses. Its primary applications include:
- Fuel Source: It is the main component of natural gas, which is widely used for heating homes, cooking food, and heating water in boilers.
- Electricity Generation: Methane is burned in gas turbines or steam generators to produce electricity in power plants.
- Industrial Chemical Feedstock: It serves as a starting material in the chemical industry for producing hydrogen, methanol, acetic acid, and other essential organic chemicals.
- Vehicle Fuel: In its compressed (CNG) or liquefied (LNG) form, methane is used as a cleaner-burning alternative to gasoline and diesel for vehicles.
2. What is the most common use of methane in our daily lives?
The most common use of methane in our daily lives is as natural gas. Many households rely on it for heating, running water heaters, and cooking on gas stoves. It is piped directly to homes and businesses, making it a convenient and efficient energy source for everyday activities.
3. What is the chemical formula and structure of methane?
The chemical formula for methane is CH₄. This indicates that a single molecule of methane consists of one central carbon (C) atom bonded to four hydrogen (H) atoms. Its molecular structure is a tetrahedron, with the carbon atom at the centre and the four hydrogen atoms at the corners, forming bond angles of 109.5 degrees.
4. Where is methane found naturally in the environment?
Methane is produced naturally through the anaerobic decomposition (breakdown without oxygen) of organic material. The largest natural sources include:
- Wetlands: Marshes and swamps are major producers of methane due to microbial activity.
- Oceans and Freshwater Bodies: Microorganisms in aquatic sediments release methane.
- Termites: The digestive processes of termites produce significant amounts of methane.
- Geological Formations: It is trapped in underground deposits as natural gas.
5. How is methane gas produced by human activities?
Human (anthropogenic) activities are a major source of methane emissions. Key sources include the energy sector, through the extraction and transport of coal, oil, and natural gas. Another significant contributor is agriculture, specifically from livestock digestion (enteric fermentation) and rice paddies. Decomposing organic waste in landfills also releases large quantities of methane into the atmosphere.
6. Why is methane considered such a potent greenhouse gas?
Methane is considered a potent greenhouse gas because of its high efficiency in trapping heat. Although it stays in the atmosphere for a shorter time than carbon dioxide (CO₂), its Global Warming Potential (GWP) is much higher. Over a 20-year period, methane is over 80 times more powerful at warming the Earth than CO₂. This makes it a critical factor in short-term climate change.
7. How does the use of methane as a fuel compare to other fossil fuels like coal?
When used as a fuel, methane (natural gas) is considered cleaner than other fossil fuels like coal. Upon combustion, it produces significantly less carbon dioxide, almost no sulphur dioxide, and fewer nitrogen oxides and particulate matter for the same amount of energy generated. However, it is still a fossil fuel that contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, and leaks of unburned methane during extraction and transport are a major environmental concern.
8. What is biogas, and what is the importance of methane in it?
Biogas is a renewable energy source produced from the anaerobic decomposition of organic waste, such as agricultural waste, manure, and sewage. Methane is the most important component of biogas, typically making up 50-75% of its volume. The energy released when biogas is burned comes almost entirely from the combustion of its methane content, making it a valuable fuel for cooking and electricity generation.
9. What are some industrial applications of methane besides being a fuel?
Beyond its use as a fuel, methane is a crucial feedstock in the chemical industry. It is used in a process called steam reforming to produce synthesis gas (a mix of hydrogen and carbon monoxide). This gas is then used to synthesise a wide range of important chemicals, including:
- Hydrogen Gas (H₂): Used for ammonia production (in fertilisers) and in refineries.
- Methanol (CH₃OH): A solvent and a precursor for other chemicals like formaldehyde.
- Acetic Acid: Used in the production of plastics and solvents.
10. Are there any environmental risks associated with using methane, apart from global warming?
Yes, besides its role in global warming, the use of methane has other environmental risks. The extraction process, particularly hydraulic fracturing or 'fracking', can lead to potential groundwater contamination and induce minor seismic activity. Furthermore, methane is highly flammable, and leaks in pipelines or storage facilities can pose a significant risk of fire and explosion.









