What Are Verbs? Simple Definitions, Examples & Fun Activities
FAQs on Verbs for Kids: Easy Guide to Action Words and Their Uses
1. What is a verb in simple words for kids?
A verb is an action word, also known as a 'doing word'. It tells us what a person, animal, or thing is doing in a sentence. For example, in the sentence 'The bird sings', the word 'sings' is the verb because it shows the action the bird is performing.
2. What are some common action verbs for children to learn?
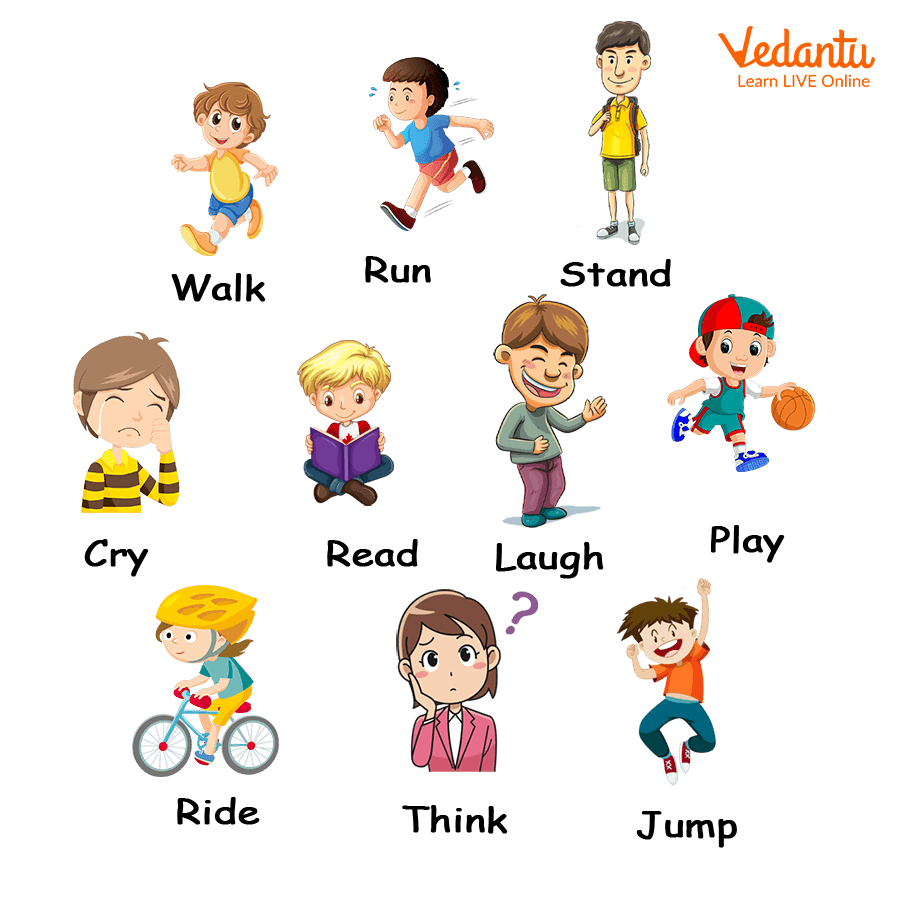
Here are some easy and common action verbs for kids to start with:
- Run
- Jump
- Eat
- Sleep
- Play
- Read
- Write
- Sing
- Dance
- Laugh
3. How can you use action verbs in a sentence?
Using action verbs makes your sentences complete and exciting. You place the verb after the person or thing doing the action. Here are some examples:
- The cat sleeps.
- I play with my toys.
- We eat our lunch.
- The frog jumps high.
4. Why are verbs so important in English grammar?
Verbs are one of the most important parts of a sentence because they show what is happening. Without a verb, a sentence is incomplete and doesn't make sense. It's like having a car without an engine; the verb provides the power and action for the sentence to move forward and convey a complete thought.
5. How can I easily spot the action word in a sentence?
A simple trick to find the verb is to ask yourself, “What is the person or thing doing?” The answer to that question is usually the verb. For instance, in the sentence 'The boy kicks the ball', ask 'What is the boy doing?'. The answer is 'kicks', so kicks is the verb.
6. What is the difference between a verb (action word) and a noun (naming word)?
The main difference is what they describe. A noun is a word for a person, place, or thing (like 'boy', 'school', 'ball'). A verb, on the other hand, is a word for an action (like 'run', 'learn', 'throw'). A noun names something, while a verb shows what that noun is doing.
7. Can you give examples of action words we do at school?
Yes, many actions we do at school are verbs. Some examples include:
- Learn: We learn new things every day.
- Write: I write in my notebook.
- Listen: We listen to the teacher.
- Draw: She can draw a beautiful picture.
- Share: We share our crayons with friends.
8. Do all verbs show actions you can see, like running or jumping?
That's a great question! While many verbs are actions you can see, like running or clapping, some verbs describe actions that happen in our minds or feelings that you can't see. For example, words like think, love, feel, and dream are also verbs because they are things we 'do' internally.