NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Free PDF Download
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life solved by expert Science teachers on Vedantu as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life exercise questions with solutions to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations. The NCERT Solutions are always beneficial in your exam preparation and revision. Download NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths from Vedantu, which are curated by master teachers. Register Online for Class 9 Science tuition on Vedantu to score more marks in your examination.
Access NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Science(Biology) Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life (Examples, Easy Methods and Step by Step Solutions)
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which of the following can be made into crystal?
(a) A Bacterium
(b) An Amoeba
(c) A Virus
(d) A Sperm
Ans: (c) A Virus
Explanation: Virus does not have a cell. They act as an intermediate between living and nonliving organisms. Virus is composed of nuclear material enclosed in a protein coat. They need a host to metabolize. Due to this, it can be made into crystal.
2. A cell will swell up if
(a) The concentration of water molecules in the cell is higher than the concentration of water molecules in surrounding medium
(b) The concentration of water molecules in surrounding medium is higher than water molecules concentration in the cell
(c) The concentration of water molecules is same in the cell and in the surrounding medium
(d) Concentration of water molecules does not matter
Ans: (b) The concentration of water molecules in the surrounding medium is higher than the concentration of water molecules in the cell.
Explanation: If concentration of water molecules in the surrounding medium is higher than water molecules concentration in the cell, it will result in movement of water into the cell. This is a type of hypotonic solution and the process is known as osmosis. This will result in the cell getting swelled up.
3. Chromosomes are made up of
(a) DNA
(b) protein
(c) DNA and protein
(d) RNA
Ans: (c) DNA and protein
Explanation: Chromosomes are made up of tightly coiled DNA around the protein. These proteins are called histones, and they also support the structure.
4. Which of these options are not a function of Ribosomes?
(i) It helps in manufacture of protein molecules
(ii) It helps in manufacture of enzymes
(iii) It helps in manufacture of hormones
(iv) It helps in manufacture of starch molecules
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (iv) and (i)
Ans: (c) (iii) and (iv)
Explanation: Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis. Enzymes are composed of protein. Therefore, Ribosomes help in the manufacture of both protein and enzymes. Hence, options (iii) and (iv) are incorrect.
5. Which of these is not related to endoplasmic reticulum?
(a) It behaves as transport channel for proteins between nucleus and cytoplasm
(b) It transports materials between various regions in cytoplasm
(c) It can be the site of energy generation
(d) It can be the site for some biochemical activities of the cell
Ans: (c) It can be the site of energy generation
Explanation: Energy generation is the function of mitochondria. ER forms a network between nucleus and cytoplasm to transport proteins. It also facilitates transport of material from one cell to another.
6. Following are a few definitions of osmosis Read carefully and select the correct definition
(a)Movement of water molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane
(b)Movement of solvent molecules from its higher concentration to lower concentration
(c)Movement of solvent molecules from higher concentration to lower concentration of solution through a permeable membrane
(d)Movement of solute molecules from lower concentration to higher concentration of solution through a semipermeable membrane
Ans: (a) Movement of water molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane.
Explanation – Osmosis is passive movement of any kind of solvent through a semipermeable membrane from the higher concentration to the lower concentration. If the semipermeable membrane is not present, then the process is known as diffusion.
7. Plasmolysis in a plant cell is defined as
(a) break down (lysis) of plasma membrane in hypotonic medium
(b) shrinkage of cytoplasm in hypertonic medium
(c) shrinkage of nucleoplasm
(d) none of them
Ans: (b) shrinkage of cytoplasm in hypertonic medium.
Explanation: When a cell is kept in hypertonic solution, most of the fluid goes out of the cell, resulting in shrinkage of protoplasm of a plant because of water loss. It happens in extreme conditions as a result of osmosis.
8. Which of the following are covered by a single membrane?
(a) Mitochondria
(b) Vacuole
(c) Lysosome
(d) Plastid
Ans: (b) and (c) Vacuole and lysosome
Explanation: Other organelles in the options are double – membrane structures.
9. Find out the false sentences
(a) Golgi apparatus is involved with the formation of lysosomes
(b)Nucleus, mitochondria, and plastid have DNA; hence they can make their own structural proteins
(c) Mitochondria is said to be the powerhouse of the cell as ATP is generated in them.
(d) Cytoplasm is called as protoplasm
Ans: (a) Golgi apparatus is involved with the formation of lysosomes
Explanation: Golgi apparatus is involved in synthesis and storage of certain biomolecules; it receives proteins from ER and further processes it. It has no role to play in the formation of lysosomes.
10. Find out the correct sentence
(a) Enzymes packed in Lysosomes are made through RER (rough endoplasmic reticulum)
(b) Rough endoplasmic reticulum and smooth endoplasmic reticulum produce lipid and protein respectively
(c) Endoplasmic reticulum is related with the destruction of plasma membrane
(d) Nucleoid is present inside the nucleoplasm of eukaryotic nucleus
Ans: (a) Enzymes packed in Lysosomes are made through RER (rough endoplasmic reticulum)
Explanation: RES has ribosomes on the surface and ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis and thus for enzymes synthesis as well. Hence, option ‘a’ is correct and option ‘b’ is incorrect. ER has no role to play in the destruction of plasma membranes. The undefined nuclear region in prokaryotes is called nucleoid.
11. Which cell organelle plays a crucial role in detoxifying many poisons and drugs in a cell?
(a) Golgi apparatus
(b) Lysosomes
(c) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
(d) Vacuoles
Ans: (c) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Explanation: In the liver cells of vertebrates, SER plays an important role in detoxifying many poisons and drugs like DDT, petroleum products and pollutants. It converts them into water soluble products.
12. The proteins and lipids, essential for building the cell membrane, are manufactured by
(a) Rough endoplasmic reticulum
(b) Golgi apparatus
(c) Plasma membrane
(d) Mitochondria
Ans: (a) rough endoplasmic reticulum
Explanation: There are two types of ER, Rough ER which contains ribosomes on its surface and SER which doesn’t have ribosomes attached to it. Endoplasmic reticulum synthesizes both lipids and proteins. However, RER mainly synthesizes proteins and SER mainly synthesizes lipids.
13. The undefined nuclear region of prokaryotes are also known as
(a) nucleus
(b) nucleolus
(c) nucleic acid
(d) nucleoid
Ans: (d) nucleoid
Explanation: Prokaryotes have disorganized nucleus, and it is called nucleoid. It is present naked in the cytoplasm and contains all the genetic material.
14. The cell organelle involved in forming complex sugars from simple sugars are
(a) Endoplasmic Reticulum
(b) Ribosomes
(c) Plastids
(d) Golgi apparatus
Ans: (d) Golgi apparatus
Explanation: Golgi apparatus is a packaging organelle. It is involved in repackaging of many simple biomolecules and combining them to make complex molecules. These big molecules are then packaged further.
15. Which out of the following is not a function of vacuole?
(a) Storage
(b) Providing turgidity and rigidity to the cell
(c) Waste excretion
(d) Locomotion
Ans: (d) Locomotion
Explanation: Locomotion is carried out by specialized structures which are outside the cell. These structures are known as cilia and flagella and are present in eukaryotes. Vacuoles are present inside the cell and do not help in locomotion.
16. Amoeba acquires its food through a process, termed
(a) Exocytosis
(b) Endocytosis
(c) Plasmolysis
(d) Exocytosis and endocytosis both
Ans: (b) endocytosis
Explanation: The Term endocytosis is composed of two terms, i.e., ‘endo’ means towards the inside and ‘cytosis’ means movement related to the cell. In this process the food is engulfed into the cell. The food is ingested and digested internally. This process is carried out with the help of formation of false feet by the amoeba which helps in engulfing the food and a food vacuole is formed which helps in digestion.
17. Cell wall of which one of these is not made up of cellulose?
(a) Bacteria
(b) Hydrilla
(c) Mango tree
(d) Cactus
Ans: (a) Bacteria
Explanation: Other options show plants in which the cell wall is made of cellulose. But the cell wall of bacteria is made of peptidoglycan. Cell walls in plants help in resisting the loss of water from the plant body.
18. Silver nitrate solution is used to study
(a) endoplasmic reticulum
(b) Golgi apparatus
(c) nucleus
(d) mitochondria
Ans: (b) Golgi apparatus
Explanation: Camillo Golgi carried out a ‘black reaction’ which involved use of silver nitrate. When 2% of silver nitrate is used it is impregnated and distinguishes the morphology. This helped him in staining individual nerve and cell structures.
19. Organelle other than nucleus, containing DNA is
(a) endoplasmic reticulum
(b) Golgi apparatus
(c) mitochondria
(d) lysosome
Ans: (c) mitochondria
Explanation: Apart from DNA, mitochondria contain DNA. The mitochondrial DNA incorporates the nucleic material. It is present in contrast to chromosomal DNA.
20. Kitchen of the cell is
(a) mitochondria
(b) endoplasmic reticulum
(c) chloroplast
(d) Golgi apparatus
Ans: (c) chloroplast
Explanation: Food is produced in plants inside chloroplasts. Chloroplast contains chlorophyll which helps in the process of photosynthesis, the process which helps plants to make their own food. Hence, chloroplast is called the kitchen of the cell.
21. Lipid molecules in the cell are synthesized by
(a) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
(b) Rough endoplasmic reticulum
(c) Golgi apparatus
(d) Plastids
Ans: (a) smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
Explanation: SER synthesizes lipids, phospholipids and steroids and has several metabolic processes.
22. Cell arises from pre-existing cell was stated by
(a) Haeckel
(b) Virchow
(c) Hooke
(d) Schleiden
Ans: (b) Virchow
Explanation: This postulation of Virchow made an addition to the earlier cell theory.
23. Cell theory was given by
(a) Schleiden and Schwann
(b) Virchow
(c) Hooke
(d) Haeckel
Ans: (a) Schleiden and Schwann
Explanation: They were the first to propose the cell theory which stated that all plants and animals are made up of cells and the cell is the basic unit of life.
24. The only cell organelle seen in prokaryotic cell is
(a) Mitochondria
(b) Ribosomes
(c) Plastids
(d) Lysosomes
Ans: (b) ribosomes
Explanation: Other cell organelles are absent in prokaryotic cells and are present in Eukaryotic cells.
25. Organelle without a cell membrane is
(a) Ribosome
(b) Golgi apparatus
(c) Chloroplast
(d) Nucleus
Ans: (a) ribosome
Explanation: Ribosomes act as free structures without any cell membrane. It helps them to pick RNA from the nucleus and to further produce protein. Other cell organelles are membrane – bound.
26. 1 μm is
(a) 10–6 m
(b) 10–9 m
(c) 10–10 m
(d) 10–3 m
Ans: (a) 10 – 6 m
27. Lysosome arises from
(a) Endoplasmic reticulum
(b) Golgi apparatus
(c) Nucleus
(d) Mitochondria
Ans: (b) Golgi apparatus
Explanation – Lysosomes are known as the suicidal bags of the cell as they help in removal of cell debris. They are formed by the vesicle present in the Golgi apparatus.
28. Living cells were discovered by
(a) Robert Hooke
(b) Purkinje
(c) Leeuwenhoek
(d) Robert Brown
Ans: (c) Leeuwenhoek
Explanation: Robert Hooke was the first to observe cells, but he observed dead cells of cork. It was Leeuwenhoek who was the first to observe living cells.
29. Select the odd one out
(a) The movement of water across a semipermeable membrane is affected by the number of substances dissolved in it.
(b) Membranes are made of organic molecules like proteins and lipids
(c) Molecules soluble in organic solvents can easily pass through the membrane.
(d) Plasma membranes contain chitin sugar in plants
Ans: (d) Plasma membranes contain chitin sugar in plants
Explanation: This is a wrong statement, while others are correct. Chitin is present in the cell wall of fungi. Cell membranes of plants do not contain chitin sugar. Sugar or carbohydrates are present in the exterior of the cell membrane.
Short Answer Questions
30. Why are lysosomes known as ‘suicide-bags’ of a cell?
Ans: Lysosomes are known as ‘suicide-bags’ because when cell gets damaged during the disturbance in cellular metabolism, lysosomes may burst and cause lysis of the cell. The digestive enzymes thus released digest their own cell causing the death of the cell.
31. Do you agree that “A cell is a building unit of an organism”. If yes, explain why?
Ans: I agree with the statement that “A cell is a building block of an organism”. This is true because all living beings are made up of cells and the cell is the smallest independent unit of living beings. Cells also perform all the important functions for sustaining life. It also provides structure and nutrients.
32. Why does the skin of your finger shrink when you wash clothes for a long time?
Ans: Soap solution is very concentrated, and it is a type of hypertonic solution, because of which water moves out of our finger cells, as the concentration of water in our cell is more. Our skin acts as a semi permeable membrane. This process is also known as exosmosis, and cells become flaccid.
33. Why is endocytosis found in animals only?
Ans: Endocytosis is a process in which substances outside the cell are internalized by the cell membrane. Cell walls are absent in animals. Due to this, movement of substances inside the cells is easier in animals than in plants. Since, plants contain cell wall they have an extra layer of protection and hence movement of substances is not easy. Due to this, endocytosis is found in animals only.
34. A person takes concentrated solution of salt, after some time, he starts vomiting. What is the phenomenon responsible for such situation? Explain.
Ans: Swallowing a concentration solution of salt results in exosmosis from cells of the alimentary canal. Concentrated salt solution is hypertonic solution, which means the water content is less. Because of which there is an outward movement of water. Due to this, dehydration occurs in the person. As a result, the person starts vomiting.
35. Name any cell organelle which is non-membranous.
Ans: Ribosomes act as free structures without any cell membrane. It helps them to pick RNA from the nucleus and to further produce protein. Other cell organelles are membrane – bound.
36. We eat food composed of all the nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water. After digestion, these are absorbed in the form of glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, glycerol etc. What mechanisms are involved in absorption of digested food and water?
Ans: Diffusion and osmosis respectively. Diffusion is a process in which the molecules move from higher concentration to lower concentration. In the process of Osmosis, the water molecules move from lower solute concentration to higher solute concentration but through a semipermeable membrane. Digested food passes into the blood vessels by the process of diffusion whereas the water is absorbed by the process of osmosis.
37. If you are provided with some vegetables to cook. You generally add salt into the vegetables during cooking process. After adding salt, vegetables release water. What mechanism is responsible for this?
Ans: Exosmosis. Salt water has less water concentration as compared to that of the cell present in the vegetables. Therefore, water moves out of the cell into the salt water which causes vegetables to shrink and finally vegetables are cooked.
38. If cells of onion peel and RBC are separately kept in hypotonic solution, what among the following will take place? Explain the reason for your answer.
(a) Both the cells will swell.
(b) RBC will burst easily while cells of onion peel will resist the bursting to some extent.
(c) a and b both are correct.
(d) RBC and onion peel cells will behave similarly.
Ans: (c) a and b both are correct.
Explanation - When the surrounding medium is hypotonic, water moves into the cells. This will result in swelling of cells. RBCs do not have cell walls and hence they will easily burst. Presence of cell walls in the cells of onion peel will prevent their bursting. Hypotonic solution is a solution which has higher water concentration. Since, the water concentration outside the cell is greater, the water will move inside the cells and will cause cells to swell.
39. Bacteria do not have chloroplast, but some bacteria are photoautotrophic in nature and perform photosynthesis. Which part of bacterial cell performs this?
Ans: Small vesicles which are associated with plasma membranes are present in such bacteria which contain pigments which can trap solar energy to produce food. These reaction centers exist in the form of sacs or tubes and are present in cell membranes.
40. Match the following A and B
Column A | Column B |
(a) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum | (i) Amoeba |
(b) Lysosome | (ii) Nucleus |
(c) Nucleoid | (iii) Bacteria |
(d) Food Vacuoles | (iv) Detoxification |
(e) Chromatin material and nucleolus | (v) Suicidal bag |
Ans:
Column A | Column B |
(a) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum | (iv) Detoxification |
(b) Lysosome | (v) Suicidal bag |
(c) Nucleoid | (iii) Bacteria |
(d) Food Vacuoles | (i) Amoeba |
(e) Chromatin material and nucleolus | (ii) Nucleus |
a—(iv) Liver cell contains SER for detoxification.
b—(v) Lysosome causes cell lysis when the cell is in danger.
c—(iii) Bacteria contain nuclei in cytoplasm.
d—(i) Amoeba has a holozoic mode of nutrient which is carried out by food vacuole.
e—(ii)Eukaryotic cell contains chromatin and nucleolus.
41. Write the name of different plant parts in which chromoplast, chloroplast and leucoplast are present.
Ans: Flower and Fruit— Chromoplast
Leaves of the plant— Chloroplast
Root of the plant— Leucoplast
42. Name the organelles which show the analogy written as under
(a) Transporting channels of the cell __________
Ans: Endoplasmic reticulum, it helps in connecting cell membrane and nuclear membrane.
(b) Powerhouse of the cell __________
Ans: Mitochondria, it helps in energy generation for the cell in the form of ATP. It is known as the powerhouse of the cell.
(c) Packaging and dispatching unit of the cell __________
Ans: Golgi body helps in packaging and transporting of proteins and lipids to the desired destination.
(d) Digestive bag of the cell __________
Ans: Lysosome, it causes cell lysis by the release of enzymes when a cell is in danger. It is known as the “suicidal bag” of the cell.
(e) Storage sacs of the cell __________
Ans: Vacuole, it helps in storage of food.
(f) Kitchen of the cell __________
Ans: Chloroplast, it contains chlorophyll which helps in capturing light and helps in the process of photosynthesis.
(g) Control room of the cell __________
Ans: Nucleus, nucleus controls all the functions of cell growth and functioning.
43. How is a bacterial cell different from an onion peel cell?
Ans:
Bacterial Cell | Onion Peel Cell |
Bacterial cells are made up of peptidoglycan. | Cell wall of onion peel is made up of cellulose |
Nucleus is absent | Nucleus is present |
Bacterial cells are prokaryotic cells. | Onion Peel cells are eukaryotic cells. |
Vacuole is absent. | Vacuole is present. |
44. How do substances like carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) move in and out of the cell?
Ans: The substances such as carbon dioxide and water move in and out of a cell by processes of, diffusion, and osmosis respectively. Diffusion is a process in which there is movement of substances from higher concentration to lower concentration, but no semi permeable membrane is involved. This is how carbon dioxide moves in and out of the cell. Whereas osmosis is movement of substance from higher concentration to lower concentration via a semipermeable membrane, this is how water moves in and out of the cell.
45. How does amoeba obtain its food?
Ans: Amoeba makes pseudopodia which is also known as false feet to surround a food particle present nearby. It then ingests the food particles by engulfing it and then forms food vacuole. This process of obtaining food by Amoeba is called endocytosis.
46. Name the two organelles in a plant cell that contain their own genetic material and ribosomes.
Ans: Mitochondria and plastids. Mitochondria are known as powerhouse of the cell. They produce energy in the form of ATP. Mitochondria and Plastids both have their own DNA which possess genes to produce specific proteins for their functioning. These proteins are otherwise not produced by nuclear DNA.
47. Why are lysosomes also known as “scavengers of the cells”?
Ans: Lysosomes contain enzymes which are used for destroying worn out parts of the cell and causing lysis of the cell. Lysosomes also destroy waste materials. Due to this, lysosomes are also known as ‘scavengers of the cells or also the “Suicidal bag of cell”
48. Which cell organelle controls most of the activities of the cell?
Ans: Nucleus. Nucleus controls major cell activities of growth and metabolism. Without the presence of a nucleus life of a cell is not possible. It also controls the enzymes required for cellular processes.
49. Which kind of plastid is more common in
(a) roots of the plant
Ans: Leucoplast
(b) leaves of the plant
Ans: Chloroplast
(c) flowers and fruits
Ans: Chromoplast
50. Why do plant cells possess large sized vacuole?
Ans: Vacuoles not only store many important substances, but they also contain cell sap that give turgidity to cell. As, plants need to store the food and water they need these vacuoles. Vacuoles occupy 90 percent of plant volume.
51. How are chromatin, chromatid and chromosomes related to each other?
Ans: Chromosomes are made up of chromatids and chromatids are made up of chromatin. Chromatin condenses to form chromosomes; chromatin is made up of mass of DNA and Protein. Chromosomes consist of 2 sister chromatids which are joined together by centromere.
52. What are the consequences of the following conditions?
(a) A cell containing higher water concentration than the surrounding medium
Ans: Exosmosis will occur because cells will lose the water to the outside environment. As, the concentration of water outside is less and inside is more.
(b) A cell having low water concentration than the surrounding medium.
Ans: Endosmosis will occur, as the water will move inside the cell because concentration of water outside the cell is higher and inside the cell is lower.
(c) A cell having equal water concentration to its surrounding medium.
Ans: When concentration of water outside the cell and inside the cell is equal then there is no movement of water inside or outside the cell. Hence, no effect will be there.
Long Answer Questions
53. Draw a plant cell and label the parts which
(a) determines the function and development of the cell
Ans: Nucleus
(b) packages materials coming from the endoplasmic reticulum
Ans: Golgi apparatus
(c) provides resistance to microbes to withstand hypotonic external media without bursting
Ans: Cell wall
(d) is the site for many biochemical reactions necessary to sustain life.
Ans: Cytoplasm
(e) is a fluid contained inside the nucleus
Ans: Nucleoplasm.
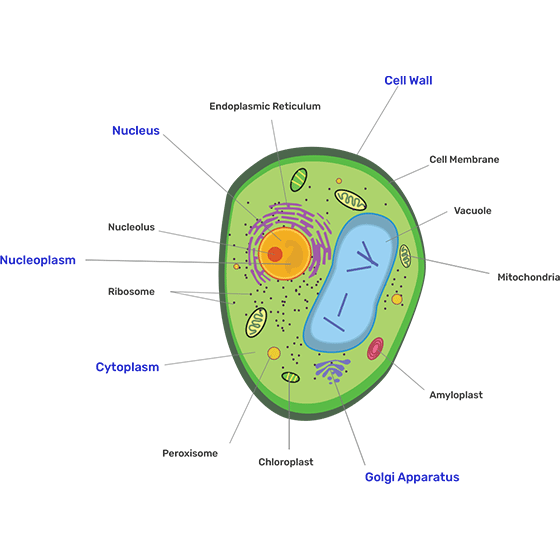
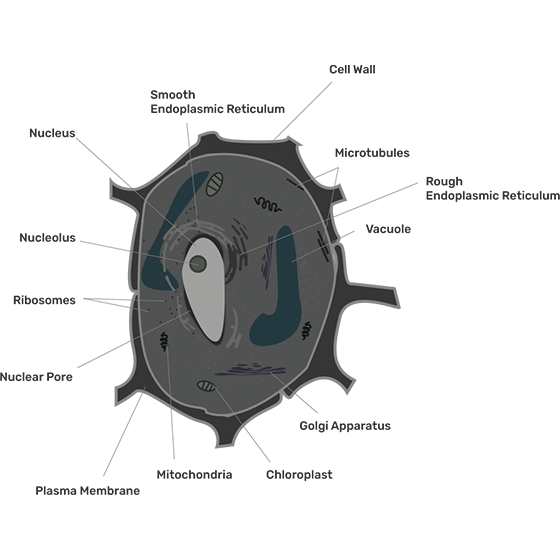
54. Illustrate only a plant cell as seen under electron microscope. How is it different from animal cell?
Ans:
Animal Cell | Plant Cell |
Cell wall is absent | Cell Wall is present |
Plastids are absent in animal cell. | Plastids are present in plant cell. |
Vacuole is absent and if present are very small. | A large vacuole is present. |
Cytoplasm is denser. | Cytoplasm is not very dense. |
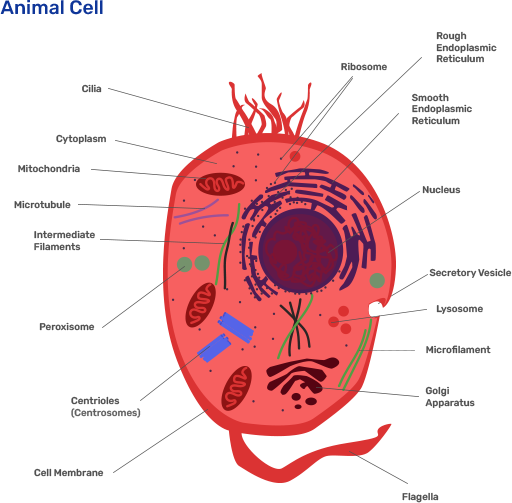
55. Draw a neat, labelled diagram of an animal cell.
Ans:
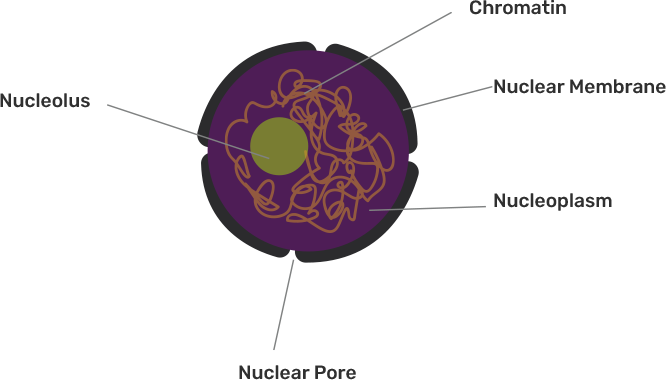
56. Draw a well labelled diagram of a eukaryotic nucleus. How is it different from a nucleoid?
Ans:
Nucleus | Nucleoid |
Nucleus is bounded by nuclear membrane. | Nucleoid do not have any outer membrane. |
It contains nucleolus | Do not contain nucleolus |
Nucleus is present in Eukaryotic cells. | Nucleoid is present in Prokaryotic cells. |
Contains Plastids | Doesn’t contain Plastids |
57. Differentiate between rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum. How is endoplasmic reticulum important for membrane biogenesis?
Ans: The ribosomes, which are present in all active cells, are the sites of protein synthesis. Endoplasmic reticulum helps in transporting these proteins to various places. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum helps in manufacture of fat and lipids which along with proteins help in building the cell membrane.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) | Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) |
SER do not contain any kind of ribosomes on its surface. And hence it is called Smooth endoplasmic reticulum. | RER contains ribosomes on its surface. And hence it is called Rough smooth endoplasmic reticulum. |
SER is responsible for the production of lipids and fat molecules. | Ribosomes present on RER are the main site for protein synthesis. |
58. In brief state what happens when
(a) dry apricots are left for some time in pure water and later transferred to sugar solution?
Ans: First it swells due to endosmosis because pure water has more water concentration and water will move inside. Sugar solution has less water concentration than inside the cell, therefore exosmosis occurs because water will move out of the cell.
(b) a Red Blood Cell is kept in concentrated saline solution.
Ans: It will lose water and shrink. Because saline or salt solution is hypertonic solution and has less water concentration, therefore exosmosis will occur and water will move out of the cell.
(c) the Plasma-membrane of a cell breaks down.
Ans: The cell will die. Plasma membrane provides both protection and shape to the cell, it keeps cellular organelle intact.
(d) rheo leaves are boiled in water first and then a drop of sugar syrup is put on it?
Ans: The cell gets killed on boiling therefore no plasmolysis will occur. Addition of sugar solution halts the process of osmosis.
(e) Golgi apparatus is removed from the cell.
Ans: Golgi apparatus is responsible for many functions, main function includes packaging and transporting of proteins and lipids to the targeted destinations. If Golgi apparatus is removed this transport will not happen.
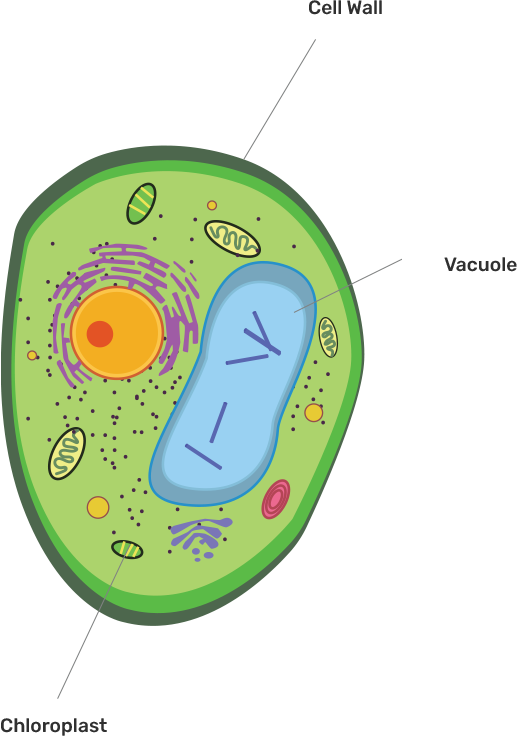
59. Draw a neat diagram of plant cell and label any three parts which differentiate it from animal cell.
Ans:
Tips for creating Revision notes for NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 5- The Fundamental Unit of Life
Go to Vedantu.com’s portal and click on NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life.
Go through each of the topics thoroughly using the revision notes provided on the site
Now, attempt all the exercise questions with their solutions provided in the book
Solve at least 8 questions every day and understand how the approach needs to be changed towards any particular question
Make notes while attempting them and jot down all the important points that will come in handy before tests
Revise everything before assessments or oral exams and build the confidence that you are capable giving of explanations
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life (Book Solutions)
1. Where can I find relevant study material for Cells for NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 5?
You can find the book as well as NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life solved by some expert Science teachers on Vedantu. It has a summarized version of the entire syllabus and has a lot of solved questions to study and practice from. You will get a proper idea of the kind of questions that you might have to solve in your examinations after having gone through this book. A team of Science teachers have together contributed towards the study material that’s in this book.
2. Is NCERT Class 9 Science’s Chapter 5- The Fundamental Unit of Life an important chapter for the exams?
Yes, very much so. The chapter on Cells is quite important. Just as a cell happens to be the building block of any organism, similarly this chapter is like a building block for the other chapters that will ensue. Understanding this chapter will then pave the way for the other chapters and their respective explanations. You can check out a summarized version of the chapter as well as a solved book of questions and answers on Vedantu. The book is a boon for those who wish to understand the chapter in the proper sense.
3. What are the different components of a cell?
All cells have three distinct components- a nucleus, plasma membrane and cytoplasm. These components make activity within a cell possible.
More explanation and pertinent questions along with their solved answers are provided on Vedantu if you go to NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life. The descriptions given are quite useful at the time of studying these chapters from the textbook. They will also help the students in making notes while studying the chapter.
4. Is Vedantu a good site for making notes for Class 9 Science Chapter 5?
Vedantu is one of the most reliable sites for making compiled notes for Class 9 Science Chapter 5. It has free study material which is easily accessible. Being India’s supreme academic platform, it lives up to its standards by containing all relevant study material in its platform. Students can make notes, revise and even appear for online tests by referring to the material on its platform. Regular access to the site will help students struggling to understand vital properly learn about the in a proper explanations manner.
5. What is a prokaryotic cell?
Cells that do not possess a true nucleus are called prokaryotic cells. Such cells are incomplete and mainly found in unicellular organisms. Examples of these are bacteria and blue-green algae.
Vivid explanations for such topics can be found on NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life. The book has all the questions and answers that one is on the lookout for and has been solved in consultation with mavericks in the field of Science.





































