
The volume of frustum of cone \[{\text{1600m}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\], the base and the upper area of the circle is \[{\text{16m}}{{\text{m}}^2}\]and \[{\text{100m}}{{\text{m}}^2}\]. Find the height of the cone.
A. \[{\text{30}}{\text{.76mm}}\]
B. \[{\text{11}}{\text{.25mm}}\]
C. \[{\text{12}}{\text{.25mm}}\]
D. \[{\text{13}}{\text{.25mm}}\]
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: As we know that the area of circle is given as \[{\text{$\pi$ }}{{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}}\]. From this calculate the radius of both base and upper circle. And then apply the formula of volume of frustum which is \[{\text{v = }}\dfrac{{{\text{$\pi$ h}}}}{{\text{3}}}{\text{(}}{{\text{R}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + Rr + }}{{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{)}}\]. And thus from all these we can easily calculate the height of the frustum of cone.
Complete step by step answer:
Diagram:
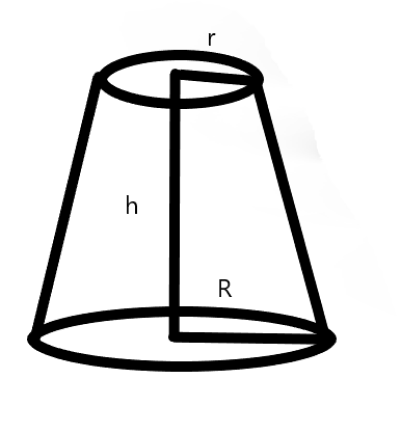
Let R and r be the radius of upper and base circle. As the base and the upper area of the circle is \[{\text{16m}}{{\text{m}}^2}\]and \[{\text{100m}}{{\text{m}}^2}\].
\[
{\text{for ,A = $\pi$ }}{{\text{R}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ = 100}} \\
\Rightarrow {{\text{R}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{100}}}}{{\text{$\pi$ }}} \\
{\text{On taking root we get,}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{R = }}\dfrac{{{\text{10}}}}{{\sqrt {\text{$\pi$ }} }} \\
{\text{for,A = $\pi$ }}{{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ = 16}} \\
\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{16}}}}{{\text{$\pi$ }}} \\
{\text{On taking root we get,}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{r = }}\dfrac{{\text{4}}}{{\sqrt {\text{$\pi$ }} }} \\
\]
Now, put the value of volume given and both the radii in the formula of volume of frustum, we get
\[{\text{v = }}\dfrac{{{\text{$\pi$ h}}}}{{\text{3}}}{\text{(}}{{\text{R}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + Rr + }}{{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{)}}\]
\[
\Rightarrow {\text{v = }}\dfrac{{{\text{$\pi$ h}}}}{{\text{3}}}{\text{(}}\dfrac{{{\text{100}}}}{{\text{$\pi$ }}}{\text{ + (}}\dfrac{{{\text{10}}}}{{\sqrt {\text{$\pi$ }} }}{\text{)(}}\dfrac{{\text{4}}}{{\sqrt {\text{$\pi$ }} }}{\text{) + }}\dfrac{{{\text{16}}}}{{\text{$\pi$ }}}{\text{)}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{1600 = }}\dfrac{{{\text{$\pi$ h}}}}{{\text{3}}}{\text{(}}\dfrac{{{\text{156}}}}{{\text{$\pi$ }}}{\text{)}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{52h = 1600}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{h = }}\dfrac{{{\text{1600}}}}{{{\text{52}}}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{h = 30}}{\text{.76mm}} \\
\]
Hence, option (a) is our correct answer.
Note: In geometry, a frustum is a portion of a solid (normally a cone ) that lies between one or two parallel planes cutting it. A right frustum is a parallel truncation of a right pyramid or right cone.
The formula to calculate the volume of the frustum is basically the volume of the big cone minus the volume of the small cone which is cut off.
The formula of volume of frustum which is \[{\text{v = }}\dfrac{{{\text{$\pi$ h}}}}{{\text{3}}}{\text{(}}{{\text{R}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + Rr + }}{{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{)}}\].
Complete step by step answer:
Diagram:

Let R and r be the radius of upper and base circle. As the base and the upper area of the circle is \[{\text{16m}}{{\text{m}}^2}\]and \[{\text{100m}}{{\text{m}}^2}\].
\[
{\text{for ,A = $\pi$ }}{{\text{R}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ = 100}} \\
\Rightarrow {{\text{R}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{100}}}}{{\text{$\pi$ }}} \\
{\text{On taking root we get,}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{R = }}\dfrac{{{\text{10}}}}{{\sqrt {\text{$\pi$ }} }} \\
{\text{for,A = $\pi$ }}{{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ = 16}} \\
\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{16}}}}{{\text{$\pi$ }}} \\
{\text{On taking root we get,}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{r = }}\dfrac{{\text{4}}}{{\sqrt {\text{$\pi$ }} }} \\
\]
Now, put the value of volume given and both the radii in the formula of volume of frustum, we get
\[{\text{v = }}\dfrac{{{\text{$\pi$ h}}}}{{\text{3}}}{\text{(}}{{\text{R}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + Rr + }}{{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{)}}\]
\[
\Rightarrow {\text{v = }}\dfrac{{{\text{$\pi$ h}}}}{{\text{3}}}{\text{(}}\dfrac{{{\text{100}}}}{{\text{$\pi$ }}}{\text{ + (}}\dfrac{{{\text{10}}}}{{\sqrt {\text{$\pi$ }} }}{\text{)(}}\dfrac{{\text{4}}}{{\sqrt {\text{$\pi$ }} }}{\text{) + }}\dfrac{{{\text{16}}}}{{\text{$\pi$ }}}{\text{)}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{1600 = }}\dfrac{{{\text{$\pi$ h}}}}{{\text{3}}}{\text{(}}\dfrac{{{\text{156}}}}{{\text{$\pi$ }}}{\text{)}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{52h = 1600}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{h = }}\dfrac{{{\text{1600}}}}{{{\text{52}}}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{h = 30}}{\text{.76mm}} \\
\]
Hence, option (a) is our correct answer.
Note: In geometry, a frustum is a portion of a solid (normally a cone ) that lies between one or two parallel planes cutting it. A right frustum is a parallel truncation of a right pyramid or right cone.
The formula to calculate the volume of the frustum is basically the volume of the big cone minus the volume of the small cone which is cut off.
The formula of volume of frustum which is \[{\text{v = }}\dfrac{{{\text{$\pi$ h}}}}{{\text{3}}}{\text{(}}{{\text{R}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + Rr + }}{{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{)}}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





